Hepatic Hydatid Induced Obstructive Jaundice
- 1. Department of Surgery, Zliten Central Hospital, Libya
ABSTRACT
Libya is one of the countries where hydatid disease is endemic. The teams of doctors reviewed retrospectively a total of four hundred patients (400) with hepatic hydatid cysts and were operated at Zliten University Hospital over the period of 24 years. The team of doctors looked for the clinical presentations of hepatic hydatid cysts. Most patients experienced abdominal pain or abdominal mass and few patients came to surgery department with rare presentation like obstructive jaundice. The obstruction of common bile duct was caused by the big cyst compressing on the bile duct or by the daughter cysts or hydatid membrane went into the bile duct. Forty nine patients whose main presentation involved abdominal pain and jaundice had been subjected for ultrasound scan and CT scan. All had open surgery, with two patients died due to multiorgan failure, four patients developed recurrence of the hydatid, seven patients had bile leak which stopped spontaneously and three patients developed wound infection. All patients were cured from the jaundice by surgery.
KEYWORDS
E. granulosus, Hydatid disease, Common bile duct, Obstructive jaundice
CITATION
Yahya AI, Shwereif HE, Thoboot AS, Ekheil MA, Algader KA, et al. (2016) Hepatic Hydatid Induced Obstructive Jaundice. Ann Clin Pathol 4(1): 1059.
INTRODUCTION
Hydatid disease is endemic in certain parts of the world like the Mediatreanin countries, the Middle East countries, Australia and South America. Liver is the most common organ affected by the hydatid. The disease is caused by the ecchinococcous granulosis and multilocularis. The adult tapeworm measures 3 to 6 mm in length and the size of eggs is about 35 µm in diameter. The larval tapeworm of E. granulosus causes unilocular hydatid disease in humans, the accidental host, while animals like dogs are the definitive host. Human gets the parasite by eating contaminated food with dog faeces or by direct contact with the dogs (16). The parasite reaches the liver through the blood from the bowel. Once the larvae reach liver, these larvae will either get destroyed by the macrophage or developed to form a cyst which may stay in the liver for many years without having symptoms and may organize by fibrosis of the wall and form calcification and ends with organized hydatid cyst. The chief clinical manifestations include pressure symptoms, anaphylactic symptoms and abdominal mass. The hepatic hydatid can be treated by medical drug, pair procedure or surgery. Patients may present with abdominal mass. One of the rare presentations is obstructive jaundice. This study presents the number of patients who were treated for obstructive jaundice caused by hydatid liver.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
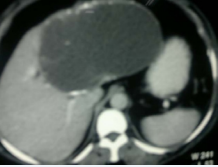
With permission from ethics and research committee of the Zliten University Hospital, files of patients who were operated for hepatic hydatid disease for over a period of twenty four years were retrieved and studied. Forty nine patients came to the surgery department with abdominal pain and jaundice. On clinical examination, all patients had tenderness at the right upper quadrant and yellow sclera. All patients had routine blood investigations including complete blood count and liver functions tests. None of the patients had serological tests for hydatid. Ultrasound of the abdomen showed liver cyst [7]. All patients had CT scan (Figure 1) and MRI.
Figure 1 CT of the liver with huge cyst at the left lobe of the liver.
Few patients had preoperative ERCP [1,17,18]. All patients had open surgery.
All patients had preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis and steroid to avoid anaphylactic reactions. Laparotomy was done under general anesthesia through right subcostal incision. Precautions were taken to avoid the spillage of the parasite in the abdominal cavity. Exploration of the hepatic cysts was done. Twenty two patients had single cyst at the left and right lobe near the hilum, compressing on the bile duct. Twenty seven patients had hydatid cyst away from hilum, with eight patients at left lobe and nineteen at right lobe. All patients had intraoperative ultrasound. Ultrasound was performed to locate the presence of any cysts which might not be seen by the preoperative imaging. Intraoperative ultrasound was also used to find out the relation of the cyst to the big vessels; all the cysts were undergone aspiration of the contents of the cysts. Those cysts near the hilum their contents were clear whitish fluid while those cysts away from the hilum had contents with green yellow indicating communication with the bile ducts. Betadine was the scolicidal agent used. All cysts were opened to remove the endocyst. That cyst at the hilum has no communication with bile ducts, and the ectocysts were excised. Those cysts located away from the hilum and their contents were bile upon removal of the endocyst, checking of cystoductal communication was done [5-10], and exploration of the bile duct through the communication by use of Fagarty catheter was performed. In our twenty seven patients daughter cyst and or parasitic membrane was removed and washed with plenty of saline with squeezing the common bile duct to destroy any daughter cyst which may not come out by the catheter. Only one patient had intraoperative cholangiogram through the communication. The communication was closed by PDS stitch, resection of all critineous wall of the cyst and the remaining cavity was closed from the inside outward (the process called capitonage).
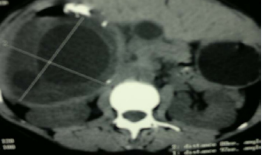
Figure 2 CT scan of the liver with three cysts in the liver one with calcification in the wall.
RESULTS
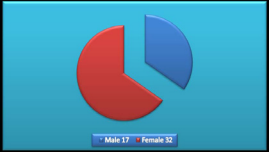
Forty nine patients with hepatic hydatid cysts induced obstructive jaundice were treated at the Zliten University Hospital: 32 were female and 17 were male (Figure 3)
Figure 3 Male to Female distribution.
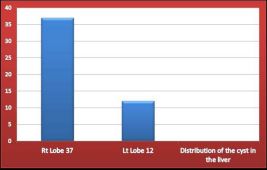
with their ages ranging between 25 to 50 years. 37 patients had their cysts at right lobe and 12 patients with their cysts at left lobe (Figure 4).
Figure 4 Distribution of the Cysts in the Liver.
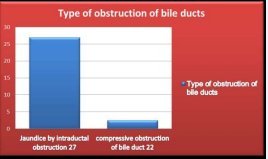
22 patients had their cysts near the hilum causing obstruction of the common bile duct by compression (Figure 5), 27 patients had their cysts at both lobes, the obstruction was caused by daughter cyst and hydatid membrane in the bile ducts (Figure 5)
Figure 5 Distribution of patients with two types of bile duct obstruction, 27 patients had the obstruction of bile duct from inside by daughter cyst. 22 of patients had the obstruction of hydatid cyst by compression on the duct from outside.
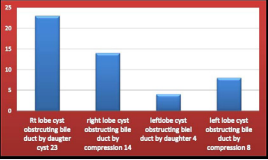
(Figure 6) illustrates liver distribution and type of bile duct obstruction of our forty nine patients.
Figure 6 Distribution of total number of patients indicating location of the cyst and the type of bile duct obstruction. 23 patients had the cyst in the right lobe caused obstruction of bile duct by daughter cyst inside the duct. 14 patients had the cyst in the right lobe caused obstruction of the bile duct by compression on bile duct. 4 patients had the cyst in the left lobe and caused obstruction of bile duct by daughter cyst inside the duct.8 patients had the cyst in left lobe caused obstruction of bile duct by compression on bile duct.
All patients had excision of hydatid cyst and closure of the residual cavity by capitonnage method. One patient had left hepatectomy for left lobe hydatid cyst. Two patients died due to multiorgan failure; both of them female, and both had their haydtidcyts at the right lobe of the liver. These patients had obstruction of bile duct by daughter cysts in the bile duct.
DISCUSSION
Liver is the most common organ infected by echinococcous, being the first organ to receive the blood infected with the parasite from the intestine and the first to filter the blood from any pathogen. Once the parasite, which in oncosphere form, reaches the liver, it will either be killed by the macrophage in the liver or will grow and form a cyst. The cyst form will produce plenty of protoscoleces and daughter cysts. Small cysts of the parasite may grow over years to cause symptoms.
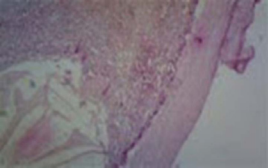
The hydatid cyst is composed of three layers (12,13,15). The inner layer called germinal layer from which broad capsule will grow to produce scoleces, which in turn will produce daughter cysts. The next layer is the laminated layer. It is a vascular and with a thickness of 1mm. The third layer or the outer layer is formed from the organ (i.eliver tissue). It is fibro vascular and supplies the inner layers. Calcification may develop in the third layer (figure 7).
Figure 7 Histology of hydatid cyst showing the three layers of the cyst.
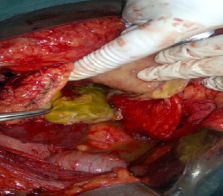
Daughter cysts will float in the fluid produced by the germinal layer. The fluid is antigen to the body. If it comes out, it will cause anaphylactic reaction or anaphylactic shock. The reaction occurs when the antigen enters the circulation through the blood vessels or absorption of the fluid occurs when it comes in contact with big surface area like the peritoneal or pleural cavities. Hypersenstivity will not happen if the fluid is in the cyst because the contents are encased by the wall of the cyst or when the fluid enters the bile duct because of the two reasons: (1) the bile duct is not rich of blood vessel from inside and its surface area is small, and (2) the hydatid fluid is diluted with the bile, thus the bile flow will push the hydatid fluid into the bowel. The cyst in the liver will grow over time and may invade the vessel wall and disseminate to other organs. The cyst will grow in size and will invade the bile duct, daughter cyst and or hydatid membrane will go in the bile duct and obstruct it this happened to the twenty seven patients who had fistula with the bile duct (Figure 8).
Figure 8 Hydatid cyst with yellow fluid content indicating communication with bile duct.
The team of doctors found out that some patients who had big fistula also had small fistulas (2,4-6,8). Big communication was explored with Fogarty catheter (11) and the ducts were cleared of the daughter cyts that caused the obstruction. The doctors also found out that exploration through the communication is better than opening the common bile duct. Those patients discharged earlier than those patients who had common bile duct opened spent less time of the operation and less time of hospital stay, and had no need for preoperative ERCP (1,17,18). Those patient who came with obstructive jaundice due to external compression on bile duct (3,9,11,19,20), no communication between the cyst and bile radicle was found. These patients were cured after excision of the cyst; thus exploration of the bile duct was not needed. Patients with hepatic hydatid induced obstruction jaundice needed surgical treatment to avoid complications of obstructive jaundice like cholangitis and sepsis which will kill the patients. From this study the team of doctors found that hepatic hydatid induced obstructive jaundice can be managed by open surgery and no need for preoperative ERCP because the patient will not be cured only with ERCP. Still surgery is needed. To avoid ERCP complications and the delay for curative surgery, the team of doctors advised that ERCP be done preoperatively for patients who are not fit for surgery with high bilirubin. In such patients relief of bile duct obstruction be done with ERCP and stenting the duct and later the surgery can be utilized. Some surgeons still open the common bile duct (CBD) to remove the daughter cysts and hydatid membrane to relief the obstruction. In those patients the team of doctors avoided exploration of the common bile through the duct and attained good results. Exploration of the common bile duct for stones was also done through cystic duct in some centers, especially during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The team got the idea of CBD exploration when the duct contains hydatid daughter cyst came from the same idea of exploration for stones in CBD trans the cystic duct of the gall bladder (21,22).
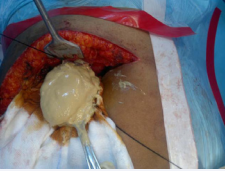
Figure 9 Content of organized hydatid cyst.
Figure 10 Daughter cysts with hydatid fluid mixed with bile.
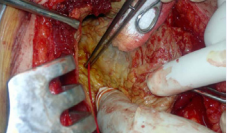
Figure 11 Fagartycathter in cysotbiliary communication for removal of daughter cyst from the bile duct (Common bile duct exploration through the communication between the bile duct and the cyst).
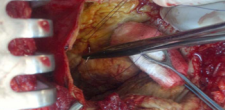
Figure 12 Closure of the Communication.
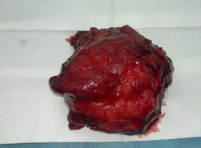
Figure 13 Complete cyst removed from left lobe of the liver.
Figure 14 Open cyst with three layers of the cyst.
Figure 15 Liver after left hepatectomy for left lobe hydatid cyst
CONCLUSION
This study revealedthe following results:
1. Obstructive jaundice by hydatid cyst liver is a rare occurrence, with its incidence at 12.8%
2. Surgery for obstructive jaundice by hydatid cyst carries excellent results.
3. Incidence of cholangitis due to bile duct obstruction by hepatic hydatid cyst is low.
4. Exploration of the bile duct through the communication between the bile duct and the cyst is safe and cures the jaundice.