The Joint Department of Mental Health of Siena (Italy): A Project for the Integration of Health Services, Specialized Education in Psychiatry and Scientific Research
- 1. Joint Department of Mental Health, Company Health-ULS7-Siena, Italy
ABSTRACT
We describe the construction of a Joint Department of Mental Health in the Province of Siena (Italy), among a population of 272,000 residents. Three institutions took part in the project: the University and the Hospital of Siena, the USL (the Local Health District) 7. In this paper we report the articulation of services for adults and present the first results of the work relating to the low rate of hospital admissions and the high number of patients who underwent the treatment. This model represents an update with respect to the 1978 Italian Health Care Reform, with the involvement of the University in the overall project of Community Mental Health service.
KEYWORDS
• Joint department
• Community mental health services
• No restraint inpatient units
• Low rate admission
CITATION
Lucii C (2013) The Joint Department of Mental Health of Siena (Italy): A Project for the Integration of Health Services, Specialized Education in Psychiatry and Scientific Research. Ann Psychiatry Ment Health 1(1): 1002.
INTRODUCTION
Along with the 1978 Psychiatry Reform an articulation of Mental Health services for each catchment area was made in Italy. Each Mental Health Care Unit has to deal with the prevention, care and rehabilitation of mental diseases of a community. The articulation of such services on the National territory was very “patchy”, in some counties these services were effective whilst in others definitely less [1]. The model is divided in four levels of assistance: The Mental Health Care Center, the Daily Care Center for Rehabilitation, residential facilities and Psychiatric Hospital Units for Diagnosis and Treatment. The Mental Health Care Center is the place where the entire service network is designed. Psychiatric hospital units must be located within the General Hospital with a maximum of 15 beds, for voluntary and compulsory admissions. These levels have been defined in the National Mental Health Project of 1994; in the following years, a project for a community Mental Health Care Service was redefined [2].
This operating model is completely free, universal and tries to respond to all the needs of mental health.
The Mental Health Care Center is open 6 days a week; patients can be admitted to the Center either by direct volunteer access or under suggestion of their General Practitioner. Each patient undergoes an Individual Treatment Plan, which can be: a) monoprofessional (psychiatry or psychology) b) multiprofessional and 3) Therapeutic-rehabilitative for “complex patients”. The 4 levels of assistance co-operate for the realization of the Individual Treatment Plans, according to the patients’ needs. In case of “complex patients” a microequipe is created and an operator is identified, usually a nurse with the function of “case manager” referees. “Complex patients” belong to the following diagnostic categories: schizophrenia spectrum disorder, bipolar disorders and severe personality disorders. In this case we can realize an intensive case management to prevent admission and to follow the patient at home [3-5].
In the Province of Siena, the University, the Local Hospital and the USL 7 set up a programme in 2010 by creating a joint department of Mental Health Care in order to get the University involved in the direct management of mental health problems. In Italy there had previously been a similar experience in Verona [1,6]. More projects are about to start in the rest of Italy, such as in Turin.
This work aims at describing the articulation of the services for adult population and presenting some preliminary results.
The Province of Siena counts 272,638 inhabitants whose 232,100 are > 17 years, in 36 towns (whose the largest is Siena with 54,000 residents), in an area of 3820 km2 (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Province of Siena-Tuscany-Italy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Each Health Care professional inserts the activity data in a software called Caribel programmazione s.r.l. provided by the local Health Care Authority. In this software operators, logging in with username and password, record all the activities of hospitalization, clinic and home visit, all rehabilitation activities and all therapeutic-rehabilitation projects, carried out in any structure of department. All Quantitative data presented here have been taken from that software.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The department in the Province of Siena has:
- 3 Mental Health Care Center (Siena-catchment area 120,000 inhabitants; Colle di Val d’Elsa-catchment area 65,000 inhabitants; Chianciano- catchment area 87,000 inhabitants)
- 3 Daily Care Centers for Rehabilitation
- 6 residential facilities whose:
- 2 therapeutic-rehabilitative type (with no stop assistance) and 4 socio-rehabilitative type (with half-day assistance)
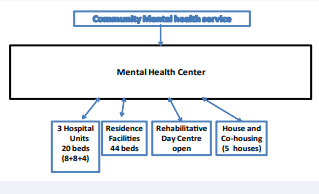
- 3 Inpatient units; whose 2 inpatient units are located at the University Hospital of Siena, with 8 beds belonging to the University Clinic and 8 beds to the Psychiatric Diagnosis and Treatment Department within the USL 7. Both units work in synergy which each other. Each patient is assigned a psychiatrist and a nurse referee during admission. If the patient has already a psychiatric referee at the local Mental Health Care service he can be guaranteed the continuity of care with his own psychiatrist who can visit him when deemed necessary.
The other Inpatient Unit consisting of 4 beds is located in The General Medicine Ward of General Hospital of Montepulciano (SI). In sum we have 20 beds for 232.100 residents. In 2012 mean hospital stay was 11.7 days.
All Inpatient units of the department are admitted without the use of restraint. Within the inpatient units a series of programmes aimed at improving the internal relational climate and to prevent restraint are held: psycho educational group sessions conducted by nurses [7,8], newspapers reading activities, walking groups in the hospital, projection and commentary of movies. In 2010 e 2011 no adverse events were recorded; during 2012 only the suicide of one of the admitted patients was recorded.
The medical service in the Inpatient units and the medical counseling at the hospital are guaranteed by all interdepartmental physicians. The doctors of the postgraduate school of Psychiatry participate in the activities at the USL’s territorial offices. This is a method developed in the Anglo-Saxon world and Northern Europe, but in Italy it only affects the Joint Department of Mental Health Care in Verona.
Residential facilities and Daily Care Centers can be accessed only by a project drawn up by therapeutic microequipe and validated by the team of the facilities. The Department has encouraged the development of the co-housing among small groups (maximum 4 people) of patients sharing flats; currently we have 5 apartments with 18 people who are in advanced state of rehabilitation and who receive appropriate medical care at home on a daily basis.
The Province of Siena is divided into 3 districts and for each mental health care centre there is a psychiatrist in charge of the team that manages the therapeutic project and the rational use of resources.
The budget is managed by the Director of the Department that negotiates it with the directors of the three companies mentioned before and then assigns it to the Director of the Adult Mental Health Unit.
Each professional area, including psychiatrists, psychologists, nurses, educators, rehabilitation technicians and social workers, has its own professional Director within the department, which oversees the training and legal aspects. The key word is Individual Treatment Plan, which is always subscribed by the patient. In the common use all members of the staff use the scale Honos [9] to evaluate the projects.
The Department also carries out activities in the “psychiatric outpatient clinic” in the Hospital of Siena and in 12 district surgeries in the Province, together with other specialists. These activities are carried out by Doctors and nurses that refer to the Mental Health Center of the District Area (Figure 2).
Figure 2 The model.
All activities occur within the National Health Services, with the payment of a fee of 18 Euros for citizens. There are a lot of exemptions to the payment of the fee for citizens over 65 years and for reasons of income or illness. However, at the moment there are many problems keeping up the NHS with funds from the general taxation and insurance funds are being born, although very few for the mental health.
As shown in (Table 1) health care workers employed in the public service are now 153 for a cost of around 6 million Euros per year.
Table 1: Mental health professionals (adult area).
| Mental health professionals of Inter-department. (adult area) | Number 153 |
| psychiatrist | 28 |
| psychologist | 4 |
| Nurse and service personnel | 98 |
| Professional educators | 11 |
| Social worker | 12 |
| Others( rehabilitation technicians) | 5 |
The adult area in 2012 has treated 4,403 people which correspond to 1.9 % of the adult resident population.
In 2012 601 psychiatric inpatient admissions were made, in all the departments of Tuscany, considering adult resident population. The 92% were made in our units, minimizing hospitalization outside the Province.
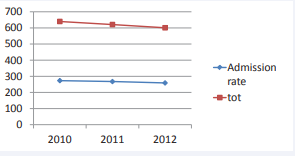
There is also a trend towards the reduction of psychiatric admissions, (starting from 640 in 2010), after the establishment of the Joint Department and this is a signal of a good treatment on the territory. The overall hospitalization rate was reduced from 273.23/100,000 adult inhabitants in 2010 to 258/100,000 in 2012 (Figure 3).
Figure 3 Total admissions and admission rate (2010-2012), in all Psychiatric Units of Tuscany.
The compulsory admission in 2012 were 41 on a total of 601, 6.8% of the total. Moreover we have to consider that compulsory treatment does not improve social functioning and the relation of care between patients and the mental health services [10,11]
Another aspect that may contribute to the low hospitalization rate and that is one of the peculiarities of the Italian Model, is the Collaborative Care with General Practitioners [12-14], starting from programmes conducted in the District of Alta Valdelsa [15- 17] in 2012 a provincial protocol of Collaborative Care between Department and the General Practitioners was signed for the first time. The General Practitioner contributes to the preparation of an Individual Treatment Plan.
The Departments has a particular focus on outcomes of interventions [18]; two protocols were prepared, one for the assessment of outcomes in admissions and one for the evaluation on the outcomes of therapeutic rehabilitation projects in the Daily Rehabilitation Centers.
Since 2011 all the Doctors of Department, and also nurses and other mental health workers, have been participating in research projects.
Some Doctors have already taken part in research projects within a national network of public services, enabled by the University of Verona, with the first publication [19]. Other studies are in progress.
In Table 2 we list all the facilities that operate in network with each other on the indications of Individual Treatment Plans.
Table 2: Department’s facilities.
|
Access and beds |
location |
|
|
Center MH |
Open h 8-20 |
Siena |
|
Center MH |
Open h 8-20 |
Colle di Val d’Elsa |
|
Center MH |
Open h 8-20 |
Chianciano |
|
Daily Centre |
Admitted with Individual Treatment Plan |
Siena |
|
Daily Centre |
Admitted with Individual Treatment Plan |
Colle di val d’Elsa |
|
Daily center |
Admitted with Individual Treatment Plan |
Chianciano |
|
Therapeutic rehabilitation residence |
12 beds |
Monteroni (SI) |
|
Therapeutic rehabilitation residence |
10 beds |
Abbadia S.S. |
|
Socio-rehabilitative residence |
10 beds |
Siena |
|
Socio-rehabilitative residence |
5 beds |
Abbadia S.S. |
|
2 Socio-rehabilitative residence |
6 beds + 3 beds |
Colle di Val d’Elsa |
|
Cohousing 5 houses |
18 beds |
5 towns of Province |
|
Hospital Psychiatric Unit (8+8) |
16 beds |
Hospital Siena |
|
Hospital Psychiatric Unit |
4 beds |
Hospital Montepulciano |
Table 3 shows the major psychiatric diagnoses of the 4,403 patients treated in 2012, adult area.
Table 3: Diagnoses of treated patients in 2012-Adult Area.
|
Principle diagnosis on 4403 patients |
% |
|
Affective psychotic disorders |
27,8 |
|
Neurotic disorders and disadaptative |
27,2 |
|
Depressive non psychotic disorders |
12,8 |
|
Schizophrenic disorders and others psychosis |
10,5 |
|
Personality disorders |
9,2 |
|
Organic mental disorders (dementia) |
7,3 |
|
Abuse disorders |
3,3 |
|
Alcohol-related disorders |
1,7 |
The diagnoses, pursuant to the directive of the Regional Authorities of Tuscany, are encoded according to ICD IX CM 24th edition.
CONCLUSIONS
In Italy in the upcoming years a massive reduction in the National Health Funds is expected. In 5 years there has been a fall in GDP of 10% in Italy. This model attempts to optimize public resources for the mental health care of a determinate geographical area, in this case the Province of Siena-Tuscany-Italy.
After 3 years of work in Table 4 we summarize strengths and weaknesses of this experience.
Table 4: Strengths and weaknesses.
|
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|
Management of the whole Department Funds |
Difficulty in administrative management |
|
“on-field training” of specialists |
Management of differences in training |
|
Comparison between professional with different backgrounds |
Difficulty in replicating this model in bigger urban areas |
|
Scientific evidences readily available |
|
|
Scientific research from real life |
|
Strengths are:
-The Direction of the whole department that we remember also includes the childhood-adolescence area, with unified management of the fund.
-All professionals are engaged in the Care pathways, teaching in training and scientific research; “on-field training” of specialists, doctors and nurses, is vital in the education. This is very rare in Italy, unfortunately.
-The professional relationship between Doctors who have different backgrounds: University and territorial assistance undergo a mutual improvement.
-All the most recent scientific evidences are readily available for the benefit of patients.
-Scientific research can draw directly from patients and situations from real life, with a significant number of patients enrolled in the studies.
We can consider weaknesses:
- Difficulty in the administrative management of the entire department;
- Difficulty to share Individual Therapeutic Plans by physicians from different professional education and training;
- Difficulty of replicating this model in bigger urban realities.
The data that we have today cannot provide for information about whether this model has a real positive impact on the mental health of the population. We can say that we maintain a low rate of hospitalization, a good level of integration between all the structures and that we cannot use restraint in our inpatients units.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I thank Prof. Andrea Fagiolini, Director of the Joint Department of Mental Health of Siena, with whom I have the honour to work and who called me to share this project that is very important for my professional career.
I also thank Dr. Gabriele Lucii, MD, and Dr. Giuseppe Trotta, Translator, for the contribution to the realization of this work.