Relationship between Body Mass Index (BMI) and Body Fat Percentage in a Group of Saudi Arabian Adults
- 1. Clinical laboratories science department, INAYA medical college,Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage (% BF) among 100 healthy adults (ages, 19–30 y) from a group of Saudi Arabian adults, during 2016. In this study examined adults were divided into four groups after calculating BMI, and after the correlation between BMI and %BF. The obtained results show that there are significantly more (p < 0.05) males (ages, 19-30) with a healthy weight than females. The correlation between BMI and %BF was very strong, positive, among examined females (r = 0.9) and males (r = 1). In a group with normal % BF and increased BMI there were significantly more (p < 0.01) males than females, and the opposite situation were in a group with normal BMI and % BF, where it was significantly more (p < 0.05) females than males. Obtained results show that the majority of adults in the Saudi Arabia have normal body weight, with a tendency of increase, especially among females who are more prone to unbalanced nutrition.
Keywords
• Body mass index
• Body fat percentage
• Obesity
Citation
Nasr Eldeen SK, Al-Buni R, Al Yami A, Alali H (2017) Relationship between Body Mass Index (BMI) and Body Fat Percentage in a Group of Saudi Arabian Adults. Ann Public Health Res 4(2): 1059.
INTRODUCTION
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation in the body that may impair health which is an agency of the United Nations, established in 1948, concerned with improving the health of the world’s people and preventing or controlling communicable diseases on a worldwide basis through various technical projects and programs. Excessive body fat is associated with increased metabolic risk, and its’ measurement is important in implementing curative and preventive health measures. The most commonly used surrogate measure for prediction of body fat percentage (BF %) is body mass index (BMI) [1]. World Health Organization [2] also recommends BMI as the most useful population level measure of overweight and obesity, and is used as the same for both sexes and in all ages of adults.
Calculating Body Mass Index (BMI), it can be determined which person is overweight or obese. BMI range varies with the age and sex of the adults (Table 1).
Table 1: The International Classification of adult underweight, overweight and obesity according to BMI.
| Classification | BMI(kg/m2) | |
| Principal cut-off points |
Additional cut-off points |
|
| Underweight | <18.50 | <18.50 |
| Severe thinness | <16.00 | <16.00 |
| Moderate thinness | 16.00 - 16.99 | 16.00 - 16.99 |
| Mild thinness | 17.00 - 18.49 | 17.00 - 18.49 |
| Normal range | 18.50 - 24.99 | 18.50 - 22.99 |
| 23.00 - 24.99 | ||
| Overweight | ≥25.00 | ≥25.00 |
| Pre-obese | 25.00 - 29.99 | 25.00 - 27.49 |
| 27.50 - 29.99 | ||
| Obese | ≥30.00 | ≥30.00 |
| Obese class I | 30.00 - 34.99 | 30.00 - 32.49 |
| 32.50 - 34.99 | ||
| Obese class II | 35.00 - 39.99 | 35.00 - 37.49 |
| 37.50 - 39.99 | ||
| Obese class III | ≥40.00 | ≥40.00 |
WHO (2016) defined overweight adults as a BMI at or above 25 kg/m2 , obesity adults as a BMI at or above 30 kg/m2 and underweight adults as a BMI less than18.50 kg/m2
BMI range varies with the age of the adults. The only body measurement that directly calculates the relative composition of the body and present a measure of fitness level, regardless of height and weight, is body fat percentage (% BF). Widespread application of body mass index (BMI) affords a measure which enables comparison with the overweight of individuals of different heights and weights.
So we studied sub-population of Saudi Arabian adults from INAYA medical college, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia to determine the relationship between BMI and BF %, age-BMI and age-BF %. We wish to present our results which would add more evidence to the ongoing discussion; as they were derived from an ethnic group which was not studied before.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study population
During 2016, 100 healthy adults (ages, 19-30 years) were examined. The participants were randomly recruited (who volunteered) from those attending clinical laboratories science open day conducted by clinical laboratories science department, INAYA medical college, Riyadh city, Saudi Arabia. A questionnaire was used to determine demographic data (gender, age).
Anthropometry
Measurement of the body mass was performed using a decimal scale in kilograms, after the removal of shoes and excess clothing. Height was measured without shoes, using a mounted metal centimeter ruler. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated as ratio between weight in kilograms and height in meters squared (weight in kg/heightm2 ). BMI were calculated, and world health organization (WHO) standards were used to classify adults as underweight (BMI <18.50 kg/m2 , healthy weight (BMI= 18.50 - 24.99kg/m2 ), overweight (BMI ≥ 25), obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 ) (Table 1).
Deurenberg et al. [3], derived formulae for estimate the body fat (% BF) from the BMI. For these calculations, age and sex must be included for determination the relationship between densitometrically determined body fat percentage (%BF) and BMI. Internal and external cross-validation of the prediction formulas showed that they gave valid estimates of body fat, between sex at all ages. However, the prediction formulas slightly overestimated the BF %. The prediction error is comparable to the prediction error obtained with other methods of estimating BF %, such as skin fold thickness measurements and bioelectrical impedance. The most commonly used formula for relationship between BMI and BF% in children is present by Deurenberg et al. [3].
Child body fat %
(1.51BMI)-(0.70
Age)- (3.6
sex )+1.4
Adult body fat %
(1.20 BMI) +(0.23
Age) -(10.8
sex)- 5.4
where sex is 1 for males, and 0 for females.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis of the results was conducted using software GrapfPad Prism 5.00 (Version 5.00 for Windows, Graph Pad Software, San Diego California USA, www.graphpad. com). All parameters were represented by descriptive statistical parameters (mean, standard deviation).One-factor analysis of variance-ANOVA and post Tukey test were used for testing differences among BMI of examined females and males of the same age with healthy weight. For examination the ratio of BMI to BF we used Pearson correlation coefficients was used to compare frequencies among females and males in different categories of adolescent, divided into four groups (normal BMI and BF, increased BMI and normal BF, normal BMI and increased BF, and increased BMI and BF).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Nutrition has exerted a role in human evolution [4,5]. Tables (2) and (3) showed characteristics of the adults, by sex and age. Laurson et al. [6],
Table 2: Body Mass Index classification according to age among females (n = 50).
| BMI Rangekg/m2 | ||||||||
| underweight<18.50 | Healthy (18.50 - 24.99) | Overweight ≥25.00 | Obese ≥30.00 | |||||
| Age | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % |
| 19 (n = 5) | 1 | 20 | 4 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 (n = 6) | 2 | 33.3 | 3 | 50 | 1 | 16.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 21 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 1 | 16.6 | 1 | 16.6 |
| 22 (n = 7) | 1 | 14.2 | 2 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 |
| 23 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 33.3 | 2 | 66.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 33.3 | 2 | 66.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 (n = 4) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 66.6 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 27 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 66.6 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 66.6 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 29 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 66.6 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 75 | 1 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
claimed that the BMI thresholds were more strongly associated with metabolic syndrome in males than in females. In our results females become obese earlier than males with 21 years (16.6%), while males get fat with 22 years (20%). females are quick to develop, complete with the growth and metabolism of them is different from males. At the age of 21, 23 and 27 all the males have normal weights, while in females have normal weights at age 25 only. Females in ages from 22 to 30 years have a problem with overweight [7]. Poor nutrition and lack of appropriate physical activity are major cause of obesity. The obtained results showed that the majority of examined adults are in the group of healthy weight. But, also we can concluded that there is significantly more (p < 0.01; p < 0.05) males (ages, 21-29) with a healthy weight than females (Table 3).
Table 3: Body Mass Index classification according to age among males (n = 50).
| BMI Rangekg/m2 | ||||||||
| underweight<18.50 | Healthy (18.50 - 24.99) | Overweight ≥25.00 | Obese ≥30.00 | |||||
| Age | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % |
| 19 (n = 3) | 1 | 33.3 | 1 | 33.3 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 20(n = 3) | 2 | 66.6 | 1 | 33.3 | 1 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 21(n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 22(n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 |
| 23 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | 4 | 66.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 (n = 7) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 71.4 | 2 | 28.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 (n = 4) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| 27 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 29 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 (n = 4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 2 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
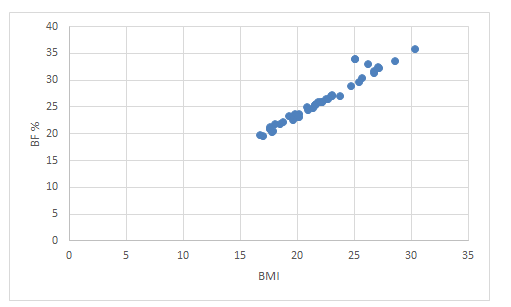
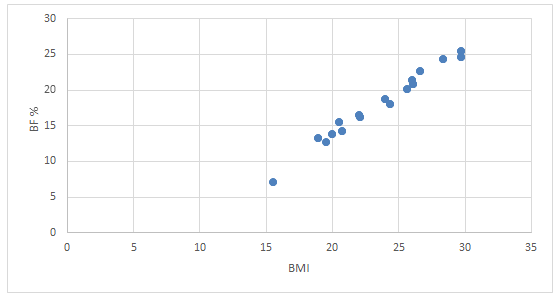
A significant positive correlation was observed between BMI-BF%, in males (r =1, p < 0.05; SE = 0.3) and in females (r = 0.9, p < 0.05; SE = 0.5) of all ages (Figure 1 & 2) and this results agreed with Chatmhuranga et al. [8].
Figure 1: Correlation between body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (% BF) for 50females19 to 30 years old.
Figure 2: Correlation between body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (% BF) for 50males19 to 30 years old.
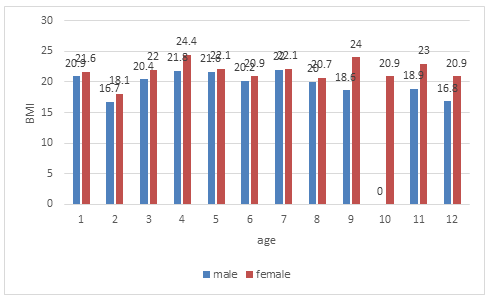
More than a half of respondents had a normal BMI and % BF (Figure 3).
Figure 3: The BMI of examined females and males with healthy weight. groups (1= 19y, 2= 20 y, 3= 21y, 4= 22y,5= 23 y, 6= 24y, 7= 25 y,8=26y,9= 27 y, 10= 28y, 11= 29 y,12=30y)p < 0.05.
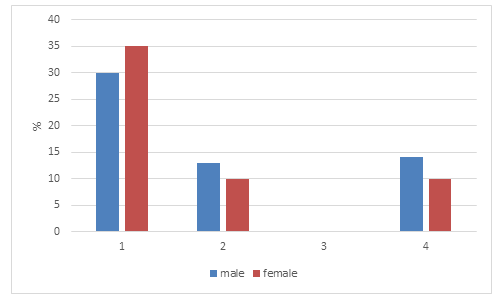
In a groups with normal % BF and increased BMI and increased BMI and %BF there were significantly more (p < 0.01) males than females, and the opposite situation were in a group with normal BMI and % BF, where it was significantly more (p < 0.05) females than males and this results agreed with Jelena et al. [9].There is no one in a group with normal BMI and high % BF (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Participation of adults in different investigated groups (1= normal BMI and BF, 2= increased BMI and normal BF, 3= normal BMI and increased BF, and 4= increased BMI and BF) p < 0.01.
Obtained results emphasize the limitations of BMI as a marker of adiposity among non-overweight adults. Because of the variability in the levels of fat mass, weight–height index needs to be carefully discussed. The high levels of BMI-for-age are associated with substantial increases in fat mass, so the index is most useful as a measure of obesity [9]
CONCLUSIONS
Based on obtained data, in this study, it can be concluded that the majority of adults in the Saudi Arabia have normal body weight, with a tendency of increase, especially among females. There is strong relationship between BMI and % BF among examined females and males and because of the variability in body fat, BMI needs to be carefully discussed. Prevention programs might attempt to improve the situation of Saudi Arabian adults by promoting more regular physical activities with a reduction in sedentary activities and improving healthy dietary behaviours.
REFERENCES
- Jackson AS, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rankinen T, Leon AS, Rao DC, et al. The effect of sex, age and race on estimating percentage body fat from body mass index: The Heritage Family Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002; 26: 789-796.
- World Health Organization: Obesity and overweight: fact sheet N0 311; 2012.
- Deurenberg P, Weststrate JA, Seidell JC. Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: age- and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br J Nutr. 1991; 65: 105-114.
- Baltic M, Nedic D, DjuricJelena, Dimitrijevic Mirjana, Karabasil N, et al. Food and everlasting concern about health. Veterinary J Repub Serbian. 2010; 1: 5-9.
- Boskovic M, Baltic ZM, Ivanovic J, Djuric J, Dokmanovic M, et al. The impact of pork meat and lard on human health. Tehnologija mesa. 2015; 56: 8-15.
- Laurson KR, Welk GJ, Eisenmann JC. Diagnostic performance of BMI percentiles to identify adolescents with metabolic syndrome. Pediatrics. 2014; 133: 330-338.
- Gruji? V, Dragni? N, Radi? I, Harhaji S, Susnjevi? S. Overweight and obesity among adults in Serbia: results from the National Health Survey. Eat Weight Disord. 2010; 15: 34-42.
- Ranasinghe C, Gamage P, Katulanda P, Andraweera N, Thilakarathne S, Tharanga P. Relationship between Body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage, estimated by bioelectrical impedance, in a group of Sri Lankan adults: a cross sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2013; 13: 797.
- Jelena J, Baltic ZM, Glisic M, Ivanovic J, Boskovic M, Popovic M, et al. Relationship between Body Mass Index and Body Fat percentage among Adults from Serbian Republic. J Childhood Obes. 2016; 1: 2-10.