Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on Chemical Composition of Biochar Obtained From Pyrolysis of Rice Straw
- 1. Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India
ABSTACT
Stubble burning of rice straw is one of the major causes of air pollution during winter months in Northern India, leading to the formation of smog and spike in the Air Quality Index (AQI). Stubble burning can be reduced by using the rice straw either directly or indirectly. The high silica content in rice straw limits its direct utilization for various applications such as cattle fodder, pulp/paper production, bio-ethanol production and many more. Therefore, indirect utilization of rice straw, such as pyrolysis of rice straw, can be explored and the pyrolysis products can be used for various applications. The biochar obtained from rice straw can be used in diverse fields such as environmental remediation, catalysis, electrochemistry etc. However, the utilization of biochar depends upon its physio-chemical properties, such as chemical composition, functional groups, surface area, etc. Therefore, in the present study, efforts have been made to estimate the chemical composition of biochar obtained from pyrolysis of rice straw at different temperatures. The carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur content in rice straw and biochar was determined by CHNS analysis. The carbon content in rice straw was found to be 35% which increased to 48% in biochar obtained at 800?. Further, apart from carbon and oxygen, the rice straw contains large amount of silica. Therefore, the silica content in rice straw and its biochar was determined by chemical precipitation method. It was found that rice straw contains 14% silica which intensified to 35% in the biochar obtained at 800?.
KEYWORDS
• Rice straw
• Stubble burning
• Pyrolysis
• Biochar
• Chemical composition
• Silica content
CITATION
Bhatia D, Saroha AK (2022) Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on Chemical Composition of Biochar Obtained From Pyrolysis of Rice Straw. Chem Eng Process Tech 7(1): 1062.
ABBREVIATIONS
RS: Rice Straw; WRS: Rice straw washed with distilled water; WBX00: Biochar obtained from pyrolysis of washed rice straw at X00 temperature (?).
INTRODUCTION
Sustainable agricultural methods play a significant role in the economic development of a country, and this is particularly true for India, where agriculture contributes significantly to Gross Value Added (GVA) of the country’s economy. A major challenge to the sustainability of agricultural methods is the large amount of crop residue generated during crop harvesting. Approximately 620 million tons per annum of crop residue is generated in India, out of which 371 million tons is contributed by cereal crops [1]. A significant fraction of cereal crop residue is contributed by wheat and rice production, amounting to 27 - 36% and 51 - 57% respectively [2].
The farmers in Punjab, India usually follow rice - wheat cropping pattern i.e. sowing rice and wheat in subsequent seasons. The delay in sowing of rice crop, due to delay in the monsoon season in the past few years has highlighted a need for quick rice harvesting system for subsequent sowing of wheat. In order to facilitate quick harvesting, harvesters are generally used for harvesting rice, leaving long rice straws in the fields, which need to be disposed prior to the sowing of wheat crop.
The rice straw (RS), unlike wheat straw, is generally not used as cattle fodder due to its high silica and low crude protein content. The high silica content in RS straw reduces its digestion by the cattle [3,4]. Further, the high silica content reduces the use of RS as raw material for bio-oil and pulp/paper production [5,6].
Considering the limitations in direct utilization of RS, indirect utilization of RS, such as pyrolysis of RS, can be explored. The pyrolysis products, i.e., biochar, bio-oil and non-condensable gases can be used for various applications. The biochar obtained from RS can be used in diverse fields such as environmental remediation [7], catalysis [8], electrochemistry [9] etc. However, the utilization of biochar depends upon its physio-chemical properties, such as chemical composition, functional groups, surface area, etc. Therefore, in the present study, efforts have been made to estimate the chemical composition of biochar obtained from pyrolysis of RS at different temperatures.
MATERIALS
RS was obtained from an agricultural field in Ghaziabad, India. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific India Pvt. Ltd. All the chemicals used in the present study were of analytical grade.
METHODS
Pyrolysis of rice straw
Initially, RS was washed with distilled water to remove dust and dirt. The washed RS was then air dried and chopped into small pieces of 5±1 cm and denoted as WRS. The pyrolysis of WRS was carried out in inert (oxygen free) environment at desired pyrolysis temperature (300?, 500?, 700?, 800?) for a residence time of 30 min. Thereafter, the setup was allowed to cool to the ambient temperature and the obtained biochar was stored in air-tight containers. The biochar pyrolyzed at different pyrolysis temperatures were labelled as WB300, WB500, WB700 and WB800 {WB represent biochar synthesized from washed rice straw, whereas the numerical value 300, 500, 700 and 800 represent the pyrolysis temperatures (in o C)}.
The yield of biochar, bio-oil and non-condensable gases were determined using the following correlations:
Chemical composition of rice straw and biochar obtained at various pyrolysis temperatures
The carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur content of WRS, WB300, WB500, WB700 and WB800 was determined using CHNS analysis, whereas the oxygen and inorganic content of rice straw was determined by subtracting the content of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur out of 100. The major inorganic component in rice straw i.e., silica was determined using chemical precipitation method. In this method, 1 g of rice straw/biochar was heated in a muffle furnace at 800? for 1 h. The resultant solid residue was dissolved in 50 mL of 1 M NaOH solution, and the solution was boiled for 15 min at ~100?. Thereafter, the solution was filtered, and the pH of the filtrate was measured. Thereafter, 1 M HCl solution was added dropwise to the filtrate to precipitate silica (precipitation of silica occurs around neutral solution pH). A holding time of 1 h was provided for the precipitation of silica gel after which the precipitated gel was filtered from the solution, washed with distilled water, dried, and weighed. This process was repeated until no precipitate was obtained. The weight of silica in the rice straw/biochar sample was calculated by adding the weight of silica obtained in subsequent extractions. All the extraction experiments were conducted thrice and the error in experimental results was found to be less than 1%.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Yield of pyrolysis products
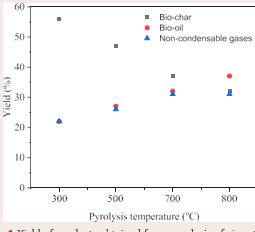
The yield of pyrolysis products obtained from pyrolysis of rice straw at various temperatures is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Yield of products obtained from pyrolysis of rice straw at different temperatures.
It can be noticed from Figure 1 that the yield of biochar decreased whereas yield of bio-oil and non-condensable gases increased with an increase in the pyrolysis temperature. This might be due to the breaking and volatilization of complex compounds facilitated by enhanced heat transfer at higher pyrolysis temperatures. It has been reported in the literature that hemicellulose decomposition starts at temperatures higher than 200? and cellulose decomposition occurs in temperature range of 315 - 400?. However, lignin decomposition is complex and takes place in primary and secondary stages. The primary decomposition occurs in temperature range of 200 - 350?, whereas secondary degradation starts at temperature more than 400? [10]. Thus, the biochar obtained from pyrolysis at 300? will have higher lignin content compared to biochar obtained at higher pyrolysis temperatures (500?, 700? and 800?).
Chemical composition of rice straw and biochar
The CHNS analysis of WRS, WB300, WB500, WB700 and WB800 is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: CHNS analysis of rice straw and biochar.
|
Elements |
Composition (%) |
||||
|
|
WRS |
WB300 |
WB500 |
WB700 |
WB800 |
|
C |
35.670 |
41.530 |
47.020 |
47.100 |
48.03 |
|
H |
5.794 |
3.667 |
2.213 |
1.261 |
1.140 |
|
N |
1.193 |
1.714 |
1.628 |
1.395 |
1.116 |
|
S |
0.116 |
0.391 |
0.291 |
0.191 |
0.141 |
|
O+Ash |
57.227 |
52.698 |
48.845 |
50.053 |
49.573 |
WRS: Washed rice straw; WBX00: Biochar obtained from pyrolysis of washed rice straw at X00 temperature.
It can be noticed from Table 1 that carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur content in WRS is 35.67%, 5.794%, 1.193% and 0.116% respectively. The remaining amount (57.227%) is attributed to oxygen and ash content (major component in ash is silica). Further, it can be noticed from Table 1 that with an increase in pyrolysis temperature from 300? to 500? the carbon content in biochar increased from 41.530% to 47.020% respectively. However, with further increase in pyrolysis temperature from 500? to 800? the carbon content remained almost constant. Moreover, the hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur content of biochar decreased with an increase in pyrolysis temperature.
The silica content in rice straw and biochar is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Silica content in rice straw and biochar.
|
Elements |
Composition (%) |
||||
|
|
WRS |
WB300 |
WB500 |
WB700 |
WB800 |
|
SiO2 |
14.22 |
18.60 |
23.15 |
30.78 |
35.11 |
|
Si |
6.64 |
8.68 |
10.80 |
14.36 |
16.38 |
WRS: Washed rice straw; WBX00: Biochar obtained from pyrolysis of washed rice straw at X00 temperature.
It can be noticed from Table 2 that the silica content in rice straw is ~ 14% which intensified in the biochar with increase in pyrolysis temperature. This is due to the removal of volatile compounds from biochar at higher pyrolysis temperature resulting in an increase in silica concentration. Further, pyrolysis performed at higher temperature (> 400?) can lead to decomposition of the lignin component present in the cell wall and the silica attached to it can be readily extracted.
The mechanism of silica extraction from rice straw and biochar involves reaction of silica with NaOH to produce soluble sodium silicate. This reaction takes place at high temperature (close to the boiling point of 1 M NaOH solution (~100?). Subsequently, the sodium silicate present in the filtrate reacts with HCl to precipitate silica and salt (salt dissolves in water and the precipitated silica can be separated by filtration).
The reactions involved in the extraction of silica are shown below:
(3)
(4)
The precipitation of SiO2 in form of gel takes place due to presence of hydrolyzed water molecules. The SiO2 gel can be dried to obtain SiO2 powder.
CONCLUSION
The rice straw was pyrolyzed at different pyrolysis temperatures and the yield of pyrolysis products was determined. It was found that yield of biochar decreased whereas yield of bio-oil and non-condensable gases increased with an increase in pyrolysis temperature. Further, the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the chemical composition of biochar was studied and it was found that the carbon content in biochar initially increased with an increase in pyrolysis temperature from 300? to 500? and then became almost constant with further increase in pyrolysis temperature from 500? to 800?. However, the hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur content decreased with an increase in pyrolysis temperature from 300? to 800?. Moreover, as silica is the major inorganic component present in rice straw. The effect of pyrolysis temperature on the silica content in the biochar was determined and it was found that the silica present in biochar intensified with an increase in pyrolysis temperature from 300? to 800?.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Indian Institute of Technology Delhi for providing the financial assistance to carry out this research.
REFERENCES
- Singh R, Yadav DB, Ravisankar N, Yadav A, Singh H. Crop residue management in rice–wheat cropping system for resource conservation and environmental protection in north-western India. Environ Dev Sustain. 2020; 22: 3871–3896.
- Lohan SK, Jat HS, Yadav AK, Sidhu HS, Jat ML, Choudhary M, et al. Burning issues of paddy residue management in north-west states of India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018; 81: 693–706.
- Agbagla-Dohnani A, Nozière P, Gaillard-Martinie B, Puard M, DoreauM. Effect of silica content on rice straw ruminal degradation. J Agric Sci. 2003; 140: 183–192.
- Smith GS, Nelson AB, Boggino EJA. Digestibility of forages in vitro as affected by content of silica. J Anim Sci.1971; 33: 466–471.
- Khaleghian H, Molaverdi M, Karimi K. Silica removal from rice straw to improve its hydrolysis and ethanol production. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2017; 56: 9793–9798.
- Kaur D, Bhardwaj NK, Lohchab RK. Prospects of rice straw as a raw material for paper making. Waste Manag. 2017; 60: 127–139.
- Wang J, Wang S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J Clean Prod. 2019; 227: 1002–1022.
- Liu C, Chen L, Ding D, Cai T. From rice straw to magnetically recoverable nitrogen doped biochar : Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of metolachlor. Appl Catal B Environ. 2019; 254: 312–320.
- Rahman MZ, Edvinsson T, Kwong P. Biochar for electrochemical applications. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem. 2020; 23: 25–30.
- Dhyani V, Bhaskar T. Pyrolysis of Biomass. In: Pandey A, Larroche C, Dussap CG, Gnansounou E, Khanal SK, Ricke S, editors. Biofuels: Alternative feedstocks and converion processes for production of liquid and gaseous biofuels. 2nd edn. London: Elsevier Academic Press. 2019; 217–244.