Dual Allelopathic Effects of Yarrow
- 1. Department of Plant Sciences, University of Tabriz, Iran
Abstract
Allelopathy is a natural phenomenon and an important interaction among plant species. In this investigation, allelopathic effects of yarrow’s (Achillea millefolium) different organs aqueous extract were examined on germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum). This examination was conducted as completely randomized design with three replications in the University of Tabriz, Iran during summer 2017. All of the experiments were done in the lab condition and Petri dishes. The results indicated that the leaf, flower and whole plant extract caused a reduction in germination and growth of wheat seedlings. The highest reduction values in germination percentage and index, shoot, root and seedling length, shoot and root fresh weight and shoot and root dry weight were recorded at about 39, 43, 74, 78, 73, 66, 25, 56 and 33%, respectively. In contrast, the stem and root extract increased the mentioned parameters except germination percentage and germination index, about 11, 47, 26, 54, 220, 68 and 62%, respectively. The results showed that different organs of yarrow had dual allelopathic effects (both stimulatory and inhibitory effects) on wheat germination.
Keywords
• Allelopathy
• Aqueous extract
• Yarrow; Wheat; Growth
Citation
Pouresmaeil M, Motafakkerazad R (2018) Dual Allelopathic Effects of Yarrow’s Different Organs Extract on Germination and Seedling Growth of Wheat. Int J Plant Biol Res 6(1): 1083.
INTRODUCTION
Allelopathy is a natural phenomenon and an important interaction among plants with releasing biochemical compounds that called allelochemicals which found the different parts of plants such as root, flower, leaves, and stem. Volatilization from aerial parts, leaching, root exudates and decomposing of plants are well-known releasing ways of allelochemicals into the environment. Allelochemicals have direct and indirect useful or harmful effects on growth and physiological parameters of received plants [1-3].
Achillea millefolium (Asteraceae) is an aromatic plant which is native to Europe and Western Asia [4]. A little study was done about Achillea species allelopathic effects on other plants. Abu-Romman [5], who indicated that the leachate of Achillea biebersteinii has an inhibitory effect on growth parameters of pepper such as germination percentage and rate, shoot and root length as well as a reduction in chlorophyll and protein content. Also, different concentrations of Achillea millefolium leachate decreased growth parameters of corn weeds [6]. Wheat is an important, economic and most cultivated crop species in Iran. Also, the yarrow is visible in the wheat farms. Therefore, it is probable which this weed interferes with wheat. Thus, this study was conducted to identify the allelopathic effects of Achillea millefolium (yarrow) different parts on the germination and growth of wheat through leaching method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental design and treatments
All of the experiments were conducted in the Faculty of Natural Sciences of the University of Tabriz with three replications and based on completely randomized design (CRD) in Petri dishes in 25-30° C. According to the results of the previous study [6], the 5% concentration was chosen as a proper concentration toevaluating its allelopathic effects. Therefore, 5% aqueous extract (extract) of each organ of yarrow including root, stem, leaf, flower and whole plant were prepared.
Plant sampling and leachate preparation
The fresh materials of Achillea millefolium were collected in the flowering stage around Jajan village in the East-Azerbaijan province, Iran. The seeds of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. “Mihan”) were obtained from “East Azerbaijan Research and Education Centre for Agricultural and Natural Resources”. The yarrow was separated into four parts including leaf, root, flower, and stem and air-dried sufficiently. The dried materials of different parts of yarrow were powdered by an electric mill. The 5% leachate was prepared by dissolving 5g of each sample into the 100 ml double distilled water and suspended by a shaker for 48 hours and then filtered through cheesecloth. Double distilled water was used as control (0%) [7].
Plant cultivation
The seeds of wheat were sterilized before experiment by sodium hypochlorite 10% for 5 minutes. Five seeds of wheat were placed in Petri dishes (80 mm) with two-layer filter paper and then 5 ml of extracts were added into the Petri. The Petri dishes were caulked by parafilm and then placed in darkness until germination. After 10 days, all seedlings were harvested for analyzing.
Measurement of growth parameters
The growth parameters of wheat consist of germination percentage and index, shoot, root and seedling length, shoot and root fresh and dry weight were measured by ruler (with 1 mm accuracy) and a digital scale (with 0.001 gram accuracy). Germination percentage and germination index were calculated by following formula:
Where, total seeds are five seeds in each petri dish. Day of the first count is 1 and day of the final count is 10.
Statistical analysis
All data were processed by Microsoft Excel 2010 and analyzed using SPSS ver. 22 by Duncan’s multiple tests at 5% level of significance and general linear model (GLM) method.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Germination percentage and index
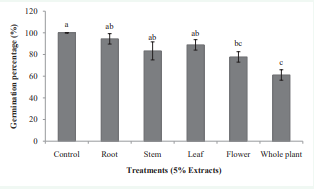
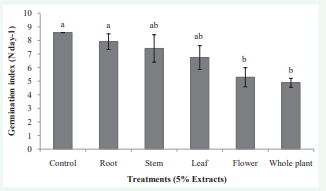
The effect of yarrow’s extract was clearly visible on the morphology of wheat (Figure 1). Flower and whole plant extract caused significantly (p ≤ 0.05) reduction in germination percentage (Figure 2) and germination index (Figure 2) of wheat. Highest reduction in both parameters occurred in whole plant aqueous extract of about 39 and 43% respectively in comparison with control. The investigated reports in allelopathic studies exhibited that effects of different organs of plant species are not same. Saadaoui et al. [8], reported that leaves and pericarp extract of Ricinus communis had inhibitory effect on germination of the six studied plant species. Also, the inhibitory effect of Parthenium hysterophorus leaf and flower extracts on Eragrostis tef was reported [9]. Different extractions of Achillea biebersteinii caused inhibition of pepper germination especially in the highest concentration [5].
Figure 1 The effects of yarrow’s different organs aqueous extract on the morphology of wheat seedlings.
Figure 2 The effect of yarrow’s different organ aqueous extracts on germination percentage of wheat. Significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences of means in each column followed with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple tests.
Shoot, root and seedling length and weight
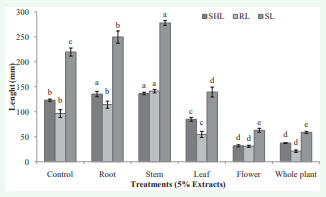
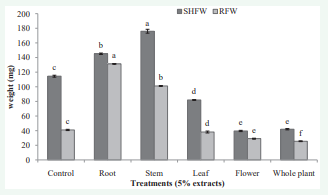
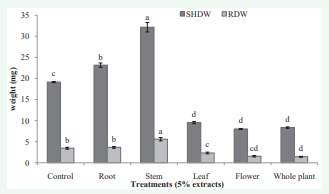
The allelopathic effects of yarrow’s different organs extract had various impacts on the length parameters of wheat seedlings. Leaf, flower and whole plant extract caused are duction in shoot, root and seedling length of wheat. In contrast, root and stem extract caused significantly (p ≤ 0.05) increase in the length parameters of wheat (Figure 3,4). Highest reduction in shoot, root and seedling length was recorded at flower and whole plant extract. The results show that the reduction rate of whole plant extract on the mentioned parameters of wheat were about 74, 78 and 73% respectively and the highest increase of all parameters were recorded in the stem extract at about 11, 47 and 26% respectively in comparison with control. The effects of different organs extract of yarrow varied on the shoot and root fresh and dry weight (Figure 5,6). The root and stem extract caused stimulation in the shoot and root fresh and dry weight. In contrast, other organs extract significantly (p ≤ 0.05) decreased weight parameters of wheat seedlings. The highest increase in shoot fresh weight, and root fresh weight, shoot dry weight and root dry weight were recorded at stem, root, stem and stem extract about 54, 220, 68 and 62% respectively in comparison with control. The highest reduction in shoot fresh weight, root fresh weight, shoot dry weight and root dry weight was recorded at flower, whole plant; flower and whole plant extract about 66, 25, 56 and 33% respectively in comparison with control.
Figure 3 The effect of yarrow’s different organ aqueous extracts on germination index of wheat. Significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences of means in each column followed with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple tests
Figure 4 The effect of yarrow’s different organ aqueous extracts on shoot length (SHL), root length (RL) and seedling length (SL) of wheat. Significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences of means in each column followed with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple tests.
Figure 5 The effect of yarrow’s different organ aqueous extracts on shoot fresh weight (SHFW) and root fresh weight (RFW) of wheat. Significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences of means in each column followed with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple tests.
Figure 6 The effect of yarrow’s different organ aqueous extracts on shoot dry weight (SHDW) and root dry weight (RDW) of wheat. Significant (p ≤ 0.05) differences of means in each column followed with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple tests.
In this investigation, dual allelopathic effects of different organs extract of yarrow were recorded. Generally, stem and root extract promoted and other extracts reduced wheat seedlings growth. The lemon’s different parts extract were examined on germination and growth of lettuce and cabbage; Based on the mentioned results it has been showed that the flower extract has a stimulatory effect on cabbage shoot length. Also, other different organs extract of lemon decreased the lettuce’s shoot and root length [10]. The allelopathic effects of litter aqueous extracts of slash pine were examined by da Silva Rodrigues-Corrêa et al. [11], who reported that the litter extract of slash pine promoted lettuce growth but the fresh slash pine needle extract inhibited lettuce growth, especially in high concentration.
Increasing the seedlings growth probably relate to several growth-promoting substances of plants that are investigated in allelopathic research [12]. Other allelochemicals are found in plants are candidates for growth inhibitor substances that their phytotoxic effects and molecular characterization were distinguished [13-17].
It seems that study of allelopathic effects of each organ as separately makes it possible for understanding their effects on plant growth. Therefore, it offers a good future perspective to identify and isolate the yarrow’s growth-promoting substances and inhibitors. Since the results indicated that the stimulatory effects of some organs on weight weren’t related to water uptake (because the dried biomass of wheat at root and stem extract treatment was higher than control), it showed that probably the root and stem of yarrow is full of real growth stimulant. In our work, the stimulatory effects of some organs was an interesting finding, because the inhibitory effects of other plant extracts were reported in most studies. Also, it can be the best suggestion for future studies about organic fertilizer. Based on the presented results; it seems that more research is necessary to fully understand the mechanism of allelopathic regulation.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the stem and root aqueous extract of yarrow promoted wheat seedling growth but the other organs including flower, leaf, and whole plant aqueous extract caused growth reduction of wheat seedlings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are thankful to Dr. Seyedyahya Salehi-Lisar, Ms. Rogayyeh Abbasi and East Azerbaijan Research and Education Centre for Agricultural and Natural Resources for preparation of plant materials, technical guide for experiments design and seeds supplying.