Invariable Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Levels in Patients with Hereditary Hemochromatosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 1. George Washington University Hospital, USA
- 2. University of Notre Dame, USA
- 3. Geisel School of Medicine, USA
- 4. Department of Rheumatology, The Altoona Center for Clinical Research, USA
Abstract
Hereditary Hemochromatosis (HH) is a disorder known to increase iron levels in the body due to dysfunction in the HFE gene and thus iron studies are generally used in order to diagnose HH. HH can cause a wide variety of clinical manifestations including arthropathy but currently there are no lab studies that can be performed in order to distinguish Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) from HH. This relationship of concurrent RA and HH was further explored. HH has several different allele types including 365C, H63D, and C282Y and each of these allele types were assessed in relation to RA using various bio markers. These studies demonstrate that patients with specific allele types of HH and concurrent RA actually have normal anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP). Anti-CCP is generally elevated in patients with RA and thus warrants an alternate method of diagnosis in patients with HH and possible RA.
Keywords
• Hereditary hemochromatosis
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody
• Arthropathy
Citation
Awan SF, Murphy KG, Bodziok GM, Kivitz AJ, Murphy FT (2016) Invariable Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Levels in Patients with Hereditary Hemochromatosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. JSM Arthritis 1(1): 1006
ABBREVIATIONS
HH: Hereditary Hemochromatosis; Anti-CCP: Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide; RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis; RF: Rheumatoid Factor
INTRODUCTION
Hereditary Hemochromatosis (HH) is an autosomal recessive disorder that is associated with a mutation in the HFE gene [1]. This mutation can have many implications, but most notably it impairs the synthesis or function of hepcidin (hepatic bactericidal protein), which is a hormone produced by hepatocytes in response to increasing iron levels [5,7]. Hepcidin has many effects on iron metabolism. It causes enterocytes to remove ferroportin channels from their cell membrane, thus removing the main channel for iron absorption [7]. With impaired hepcidin in HH, enterocyte ferroportin channels are kept indefinitely open, leading to pathologically high iron levels. This early and progressive expansion of the plasma iron compartment leads to elevated transferrin saturation and progressive parenchymal iron deposition in the liver, endocrine organs, heart, and joints [5,6]. These changes lead to a wide array of clinical manifestations [2]. Among these, HH arthropathy is one of the earliest and most common afflictions, and it greatly deteriorates quality of life [1-8]. Furthermore, it can be difficult to diagnose because HH arthropathy closely mimics other inflammatory arthritides, particularly Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). HH arthropathy can cause true synovitis and frequently affects the metacarpophalangeal joints in a bilateral distribution. It has also been known to cause an elevated rheumatoid factor [1,2]. Additionally, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies have been used as a tool to distinguish HH arthropathy from RA, since patients with pure HH almost always have negative anti-CCP while patients with RA generally have positive anti-CCP. However, the literature has not addressed the implications for patients afflicted by both HH and RA concurrently [9]. Our study suggests that due to undescribed effects of HH on the immune system, patients with simultaneous HH and RA may have falsely negative anti-CCP. Due to HH being caused by several different genetic mutations with different implications, this hypothesis may only apply to certain HH alleles. If this hypothesis is indeed correct, the implication is that clinicians may be missing RA as a concurrent diagnosis in patients with HH, leading to under treatment and increased morbidity of RA.
METHODS
All patients with HH were seen at the Altoona Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center located in Altoona, PA from 2009 until 2015. 93 patients were found with HH and 121 patients were chosen at random as controls. Patients with HH were subdivided into three categories based on allele types- H63d, C282y, and 365C. Of 93 patients with HH, 8 patients are homozygous for 365C, 44 patients are C282Y, and 48 patients are H63d. (Seven of the 93 patients are heterozygous for alleles C282Y and H63d). All patients were diagnosed with HH based on genetic testing along with elevated serum iron studies. Control patients were randomly matched based on sex and age. These control patients were seen in the Altoona Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center in the same time period as those patients with HH. For both sets of patients (HH and control patients), serum transferases, serum iron studies, anti-CCP, and rheumatoid factor (RF) were determined.
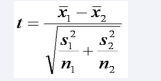
Comparisons between control group and disease group were analyzed using two-sample t-test. Two-sample t-test was used to determine if there was a statistically significant relationship between the control group in comparison to the HH subgroups-C282Y and H63D. In order to use the two-sample t-test, the means of all three groups were determined. The standard deviation of each group was calculated next in order to calculate the test statistic t. Initially, the control group was compared with the HH subgroup C282Y and the test statistic was calculated using the formula in Figure (1).
Figure 1 Formula used to determine t statistic. x1 is the mean of control group, x2 is the mean of HH subgroup (C282Y or H63D), s1 is standard deviation of control group, s2 is standard deviation of HH subgroup, and n1 is number of patients in control group and n2 is the number of patients in HH subgroup
Similarly, the test statistic was calculated for the control group and HH subgroup H63D. The t statistic was then used to determine the p-value [11].
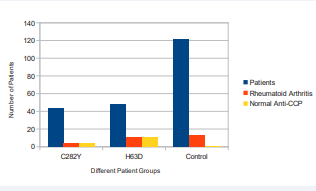
Unfortunately this provided us with a p-value for both subgroups that was not statistically significant. Consequently, instead of using t statistic and p value, calculation of percents were used to determine the percent of patients with RA who have normal anti-CCP levels. The results are displayed in Figure (2).
Figure 2 Different patient groups (C282Y, H63D, and Control) with Rheumatoid Arthritis and normal Anti-CCP levels
RESULTS
The 8 patients with allele type 365C were excluded from the study due to inadequately small sample size and because none were diagnosed with RA. 4 of the 44 patients with allele type C282Y had previously been diagnosed with RA, and all 4 had normal anti-CCP levels upon presentation of RA symptoms. Although the 4 patients with allele type C282Y who also have RA make up only 9% of the C282Y allele type patients in our study, 100% of the 4 patients were determined to have normal levels of anti-CCP. Patients with RA generally have levels of anti-CCP above 20 u/ml. Of 48 patients with allele type H63D, 11 patients (23%) were diagnosed with RA and all 11 patients had normal levels of anti-CCP. Taking a look at the patients in the control part of our study, of 121 control patients, 13 patients had RA and of 13 patients, 12 patients (92%) had elevated levels of anti-CCP at presentation of symptoms. These results are further shown in Figure (2).
Figure (2) shows the total number of patients (blue) in each subgroup. Further, the orange bar represents the patients who are part of the subgroup and were diagnosed with Rheumatoid Arthritis. The yellow bar shows the number of patients from the RA subgroup that had normal Anti-CCP levels.
DISCUSSION
HH is divided into three different allele types, including 365C, C282Y (most common), and H63D. At our study facility – Altoona Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center – there were a limited number of patients with HH. Allele type 365C only produced 8 patients which was not enough patients to have overlap of patients with HH and RA. Thus, we decided to not further pursue analysis of 365C however if we were able to add other research centers we may be able to find some patients with both HH allele 365C and RA
Allele types C282Y and H63D both yielded enough patients to find a possible relationship between HH and RA. For allele type C282Y, 4 (9%) of the patients had RA but all 4 showed normal levels of anti-CCP. Quite similarly, 100% of patients with allele type H63D and RA had normal levels of anti-CCP. Although these results are not enough to produce statistical significance, there is a level of probable clinical significance that lies in these findings.
Our data supports the hypothesis that patients with HH due to the most common allele mutations may have normal levels of anti-CCP despite co-occurrence of RA. HH is known to have elusive immunological effects [10], and we believe the disease is causing falsely lowered anti-CCP levels in patients with concurrent RA through an unknown mechanism. In support of this, our data suggests that anti-CCP would not be an accurate test to rule out RA in patients with HH.
Anti-CCP is generally used as one of the serum tests that help to rule out a diagnosis of RA (if the result is negative), but based on our results, anti-CCP may need to be used more cautiously in patients with HH. Thus, this group of patients would benefit from additional testing to rule out RA. Although future studies with higher statistical significance are needed to confirm our hypothesis, the preliminary data is compelling and warrants further investigation.
CONCLUSION
Hereditary hemochromatosis may cause negative anti-CCP in patients with concurrent RA. Due to the normal levels of anti-CCP antibodies in HH patients, anti-CCP antibody levels cannot solely be used in patients with HH to determine if a patient may have RA. HH patients with arthropathy suspicious for RA would benefit from additional diagnostic testing in order to begin disease modifying treatment. Further testing is needed to confirm our hypothesis, but the preliminary data is very promising
REFERENCES
2. Mazza, Joseph. Manual of Clinical Hematology. Lippincott Williams and Watkins. Third Edition, 118.
7. Zhao N, Zhang AS, Enns CA. Iron regulation by hepcidin. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123: 2337-2343.
8. Schumacher HR Jr. Arthropathy in hemochromatosis. Hosp Pract (1995). 1998; 33: 81-86, 89-90, 93.
11. Larsen R, David. “Testing differences between two samples.” Natural Resource Biometrics. 2010.