In silico analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Human HFE Gene coding region
- 1. Department of Medical laboratory sciences, Sudan University of science and Technology, Sudan
- 2. Department of Medical laboratory sciences, Al-Neelain University, Sudan
ABSTRACT
Background: HFE gene is a HLA class1-like molecule, expressed in the different cells and tissues, mutations on this gene reported to cause about 80-90% of Hereditary haemochromatosis (HHC) and it is increasing the risk of different diseases. In this study; we aimed to analysis the SNPs in HFE gene by using different computational methods.
Methodology: We obtained HFE gene nsSNPs from dbSNP/NCBI database, Deleterious nsSNPs predicted by different bioinformatics servers including; SIFT, polyphen-2, I-mutant and SNPs & GO servers. Protein structure analysis done by using Project hope and RaptorX tools then visualized by Chimera software and function, interaction and network of HFE gene analysis done by Gene MANIA program.
Results: SIFT and Polyphen-2 servers predicted 75 deleterious nsSNPs and nine polymorphisms from them predicted as highly damaging and disease associated.
Conclusion: In silico analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms is better for understanding different genetic disorders, and give helpful information for future candidate studies.
KEYWORDS
• In silico
• HFE gene, Polyphen-2
• I mutant
• Project hope
CITATION
Bahereldeen AI, Alfadil RG, Ali HM, Nasser RM, Eisa NT, et al. (2020) In silico analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Human HFE Gene coding region. J Bioinform, Genomics, Proteomics 5(1): 1040
ABBREVIATIONS
HFE: Human Factor Engineering, HHC: Hereditary Haemochromatosis; nsSNPs: Non-synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphism; dbSNPs: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database; NCBI: National Center of Bioinformatics; Polyphen: Polymorphism Phenotype; HLA: Human Leukocyte Antigen; GWAS: Genome-Wide Association Studies; CHD: Coronary Heart Disease; SNP: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism; DDG: Free Energy Change Value; RI: Reliability Index
INTRODUCTION
Homeostatic iron regulator (HFE) gene on the short arm of the chromosome 6 in position 6p22.2 within the extended HLA class I region, encode for membrane protein, associated with beta-2 micro-globulin, this protein located on the surface of intestinal cells, liver cells and other cells, it interacts with different proteins to discover the iron levels [1-4]. Mutations in HFE gene associated with more than 80% of Hereditary haemochromatosis (HHC) disorder [1], HHC is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by increasing iron absorption by the intestinal tract and abnormal deposition in parenchymal organs, without treatment, this condition can cause severe diseases [5,6]. Several genome-wide association studies (GWAS) performed to investigate the effect of HFE genes mutations on body iron concentration [7-10], HFE gene mutations were frequently found in patients suffering from one of the most common types of porphyria known as porphyria cutanea because of abnormal deposition of iron in the body may cause iron toxicity which cause an abnormal building up of porphyrins [11,12], also HFE gene variants increase the risk of; a coronary heart disease (CHD) [13], Alzheimer disease [14] and increase the risk of the hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, colorectal cancer and others types of cancers [15-19].
Numbers of databases used to store the SNPs, like dbSNP Database from NCBI, which containing a large number of a discovered SNPs in a human genome and other domains [20], also tools such as SIFT, Polyphen2 and others used to analysis of functional and structural effects caused by the genetic polymorphisms and to study the roles of SNPs on various human diseases to help researchers and aid them in analysis and further studies of different diseases [21-27]. Therefore, this study focuses on analysis of non-synonymous missense SNPs of HFE gene by using computational tools to highlight deleterious mutations and to predict the structural and functional consequences of these polymorphisms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
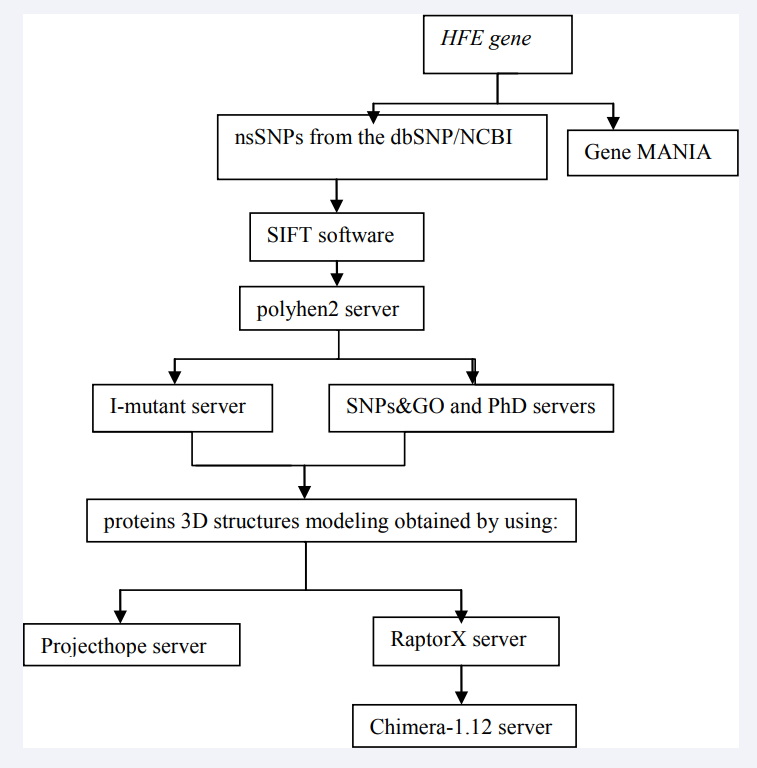
We have obtained HFE gene SNPs from dbSNP database, one of the largest websites canting wide collection of single nucleotide variations, available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih gov/snp and FAST format of the HFE proteins has obtained from ensemble database: https://feb2014.archive.ensembl.org then the analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms done by using various Bioinformatics tools (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Software used in HFE gene SNPs analysis.
SIFT software [SIFT Predict effects of nonsynonymous/ missense variants]
One of the firsts online Bioinformatics website, available at; http://sift.bii.astar.edu.sg/, used to predict the effect of damage caused by SNPs in a particular gene, SIFT is working by taking a query sequence from protein sequence database and making several comparisons at the mutant amino acids to predict if this mutation tolerated or not depending on the specific score determined between 0-1 [21]. We have submitted dbSNP reference numbers (rs numbers) of HFE gene as batch into the server, the results with SIFT score of ≤ 0.05 predicated as deleterious and those with SIFT score > 0.05 predicted as tolerance.
PolyPhen-2[Polymorphism phenotyping v2]
Is a free online Bioinformatics website available at http:// genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/index.shtml, used to predict the effects of amino acids changing on the structural and function of the proteins, it depends on several proteomics databases to search for protein 3D structure and makes multiple alignments between the homologous sequences and newly-formed amino acid then determines the difference in amino acid properties and calculates the position-specific independent count scores (PSIC) for each substitution, which indicate the possibility of the damage [22]. We have submitted protein query sequence in FASTA format with each mutations position separately to the server then the results predicated as probably damaging if the PSIC score equal 2.00 or more, possibly damaging if PSIC score between (1.40–1.90), potentially damaging if PSIC score between (1.0–1.30) and benign when PSIC score between (0.00–0.90).
I-Mutant suite [I mutant 3.0]
Is an online Bioinformatics server available at http://gpcr2. biocomp.unibo.it/cgi/predictors/I-Mutant3.0/I-Mutant3.0.cgi, it depends on numbers of data set including; Gibbs frees energy change, enthalpy change, transition temperature and heat capacity change which obtained from thermodynamic databases, to predict the effect of the amino acid changed on protein stability and predication of their result depending on the reliability index (RI), which is ranging from (0-10) [28]. We have submitted HFE protein sequence and mutations to predict the effects of damaging nsSNPs on protein stability, all tests done at temperature 25C° and pH 7.0 and the results predicated as decrease or increase in protein stability.
SNPs & GO [SNPs&GO3d]: [predictor of Human Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms]
Online database http://snps.biofold.org/snps-and-go/ snps-and-go.html, acts to drive collection of unique framework information about protein sequence, evolutionary information and function as encoded in the Gene Ontology terms, and automatically do other available tests methods to predicate if the change of amino acid on protein sequence was disease related or neutral [29,30]. We have submitted HFE protein sequence and mutations then selected all Methods to option the server to do predictions using S3D-PROF, SNPs & GO and PhD-SNPs methods.
Gene MANIA
Is a cytoscape server available at http://www.genemania.org, used for Function, interaction and network of gene analysis; it acts on numbers of functional association information including physical interactions, genetic interactions, pathways, co-expression, phylogenetic profiles, protein domain and other data obtained from the different biological database [31].
HFE protein 3D structure modeling and analysis programs
Project hope [Version0.4.1]: Is an online proteomic database developed at the center of molecular and biomolecular informatics (CMBI) at Radboud University in Nijmegen, the program available at http://www.cmbi.ru.nl/hope/, it works by obtaining structural information from different sites, including 3D structure of protein, sequence annotations in UniProt and predictions from DAS-servers, to analysis the impact of the amino acid change on the protein structure [32]. We have submitted nsSNPs that predicted as highly damaging by both SIFT and Polyphen-2 databases to project hope server as protein sequence in FASTA format with position of each mutation, native amino acid and the new substituent, than the server provided us with the complete report about the effect of each SNPs on the structure of HFE protein.
RaptorX [RaptorX Structure Prediction]: Online free server for protein structure and function prediction available at http://raotorx.uchicago.edu/ [33], we have submitted the HFE protein sequence into the RaptorX server, then it provided us with secondary and tertiary structures in addition to contact map, solvent accessibility, disordered regions, binding sites for the given sequence and reliability scores. The tertiary structures of HFE gene that was given by RaptorX treated by Chimera-1.12 Bioinformatic server which is the program of high quality used for visualization and investigation of molecular assemblies and related data, it designed by University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) available at: http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera [34].
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Two missense mutations; C282Y (rs 1800562) and H63D (rs 1799945) reported as common HFE gene mutations, C282Y is the most common in Northern European populations and H63D has a global distribution and case about 40-70% HFE non-C282Y haemochromatosis, a new HFE amino acid variant S65C/rs1800730 that reported in position 193 of the HFE gene exon 2, is the third common HFE gene mutation involved in the pathogenesis of haemochromatosis [35-38]
In this study a total of 1443 Homo sapiens HFE gene SNPs, obtained from dbSNP/NCBI in September 2018 , for computational analysis; 163 SNPs of them were missense, 12 nonsenses, eight frame shift and 236 in 3’UTR, 31 in 5’UTR and the remaining were other types. We have selected only non-synonymous coding SNPs for our investigation.
Functional analysis of polymorphism in HFE gene coding region by using SIFT and Polyphen-2 servers
SIFT software predicted 84 deleterious SNPs, 75 nsSNPs of them predicated as damaging by Polyphen2 server and nine mutations identified as highly damaging by both servers, all the nine mutations were replacing the Cysteine residue to Tyrosine in different positions(194, 282, 102, 190, 176, 259, 279, 180, 268)/ (rs 1800562) (Table 1 and Appendix Table 1).
Table 1: Highly damaging nsSNPs results obtained by; PolyPhen-2, SIFT, I-Mutant and SNPs&GO servers.
| Amino acid Change | PolyPhen-2 | SIFT | I MUTANT | PhD-SNP | SNPs&GO | ||||||||
| Effect | Score | Prediction | Index | DDG | RI | Predation | Predation | probability | RI | Predation | probability | RI | |
| C194Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.844 | 7 |
| C282Y | Probably damaging | 0.999 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.845 | 7 |
| C102Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.87 | 7 |
| C190Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.87 | 7 |
| C176Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.876 | 8 |
| C259Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.845 | 7 |
| C279Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.845 | 7 |
| C180Y | Probably damaging | 1 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.843 | 7 |
| C268Y | Probably damaging | 0.999 | Deleterious | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | Increase | Disease | 0.977 | 10 | Disease | 0.425 | 2 |
Note: All 84 nsSNPs that predicted as intolerant by SIFT server, used for farther investigation as fallow:
Prediction of the protein’ s stability by I MUATANT server
It results are 69 SNPs as decrease stability of HFE proteins (Appendix Table 2) and fifteen SNPs increase stability of HFE protein (Table 1 and Appendix Table 2).
Table 2: GeneMANIA results of genes co-expression and share domain with HFE gene.
| Gene symbol | Description | Co-expression | shared domain |
| ATF2 | activating transcription factor 2 | Yes | No |
| TFRC | transferrin receptor | Yes | No |
| B2M | beta-2-microglobulin | Yes | Yes |
| TFR2 | transferrin receptor 2 | Yes | No |
| MR1 | major histocompatibility complex, class I-related | Yes | Yes |
| GALNS | galactosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase | Yes | No |
| HLA-E | major histocompatibility complex, class I, E | Yes | Yes |
| ID3 | inhibitor of DNA binding 3, HLH protein | Yes | No |
| IGFBP4 | insulin like growth factor binding protein 4 | Yes | No |
| TPP1 | tripeptidyl peptidase | Yes | No |
| HLA-B | major histocompatibility complex, class I, B | Yes | Yes |
| MICA | MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A | Yes | Yes |
| HLA-C | major histocompatibility complex, class I, C | Yes | Yes |
| TPMT | thiopurine S-methyltransferase | Yes | No |
| IL13RA1 | interleukin 13 receptor subunit alpha 1 | Yes | No |
| DSE | dermatan sulfate epimerase | Yes | No |
| CFI | complement factor I | Yes | No |
| CD44 | CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) | Yes | No |
| PRICKLE3 | prickle planar cell polarity protein 3 | Yes | No |
| HLA-F | major histocompatibility complex, class I, F | Yes | Yes |
Investigation of disease-mutations association
It done by PhD-SNP method that predicated 43 nsSNPs as disease associated and SNP&GO method that predicated only 27 nsSNPs as disease associated, all the highly damaging nine mutations on (rs 1800562) predicated as disease associated by both methods (Table 1 and Appendix Table 2).
Function, interaction and network of HFE gene analysis by using GeneMANIA software
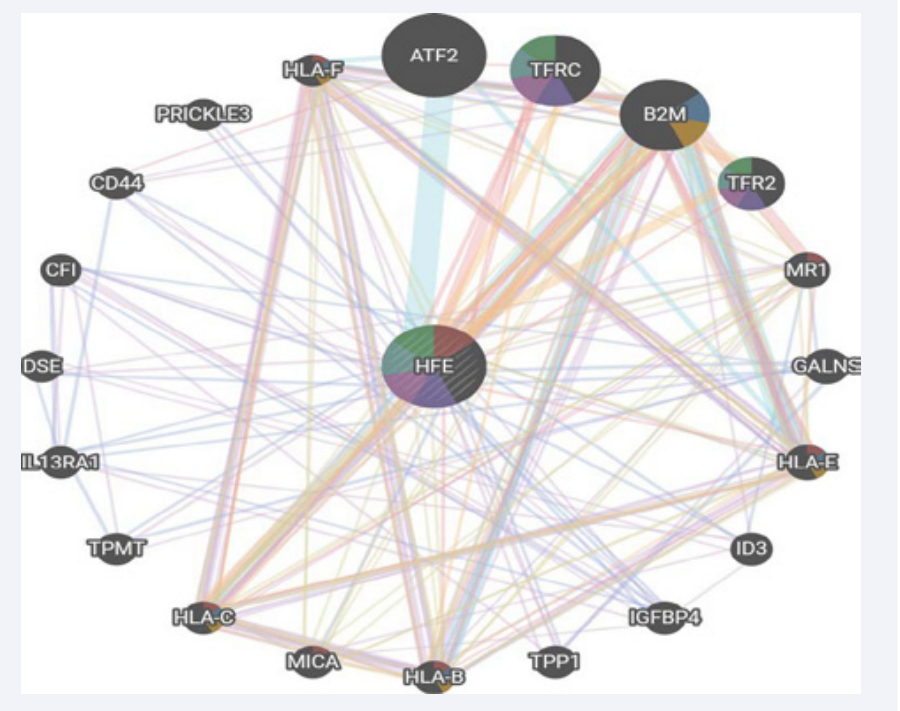
Gene MANIA server detected that HFE gene was co-expressed with twenty genes and shares the same protein domain with seven of them (Figure 2 and Tables 2 and 3).
Figure 2: GeneMANIA result of functional interaction between HFE gene and its related genes.
Table 3: GeneMANIA results of HFE gene functions and its appearance in network and genome.
| Feature | FDR | Genes in network | Genes in genome |
| Antigen binding | 3.44E-9 | 7 | 59 |
| Phagocytic vesicle membrane | 2.17E-7 | 5 | 22 |
| Antigen processing and presentation | 2.26E-7 | 8 | 216 |
| Interferon-gamma-mediated signaling pathway | 5.53E-7 | 3 | 76 |
| ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane | 5.55E-7 | 5 | 31 |
| ER to Golgi transport vesicle | 7.55E-7 | 5 | 35 |
| early Endosome membrane | 7.55E-7 | 5 | 35 |
HFE protein 3D structure modelling
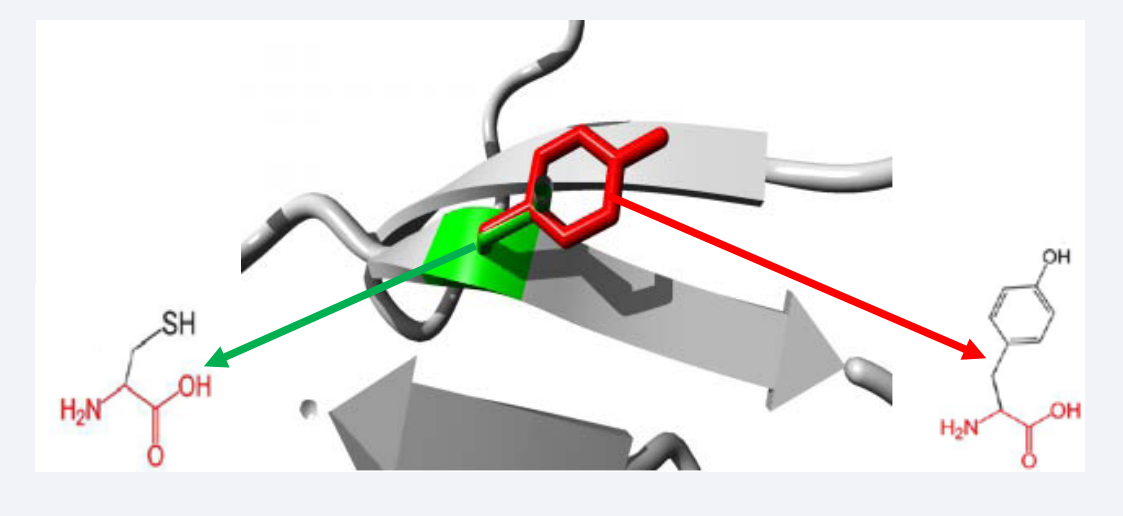
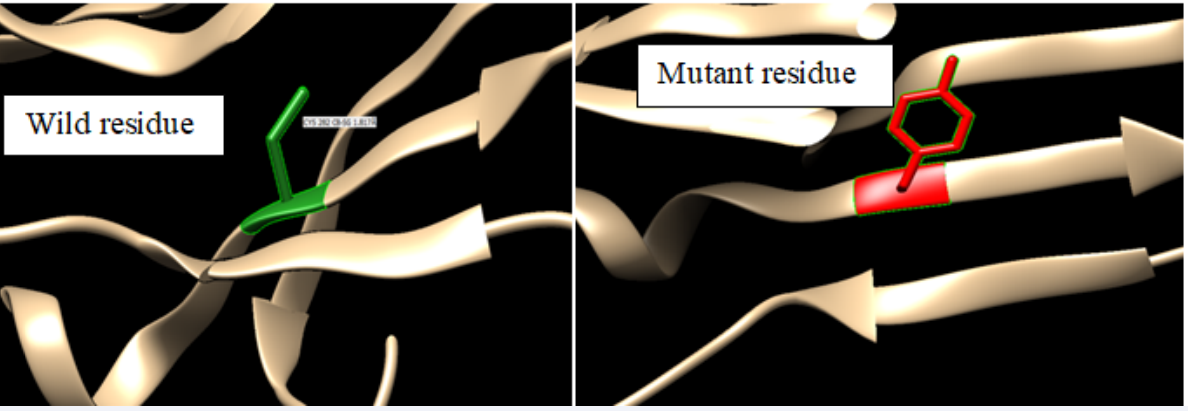
The effect of the amino acid changes on 3D structure of HFE protein ware explained by project hope software for all nine highly damaging mutations [Cysteine residue to Tyrosine in different positions(194, 282, 102, 190, 176, 259, 279, 180, 268)/ (rs 1800562)], the reports indicated that the mutations in 100% conserved region for all, the mutant residues were bigger than the wild-type residues and the wild-type residues were more hydrophobic than the mutant residues, the wild-type residues annotated in Uniprot to involve in a cysteine bridge, which is important for stability of the protein, the mutations causes’ loss of this interaction and have a severe effect on the 3D-structure of the protein and the variants annotated with severe disease (Figure 3), but C282Y mutation was not given report by project hope software and their protein 3D structure obtained from Raptor X server and treated by Chimera tool (Figure 3,4,5).
Figure 3: Project hope model for SNP ID: rs1800562/ C102Y.
Figure 4, 5: Protein 3D structure models by Chimera server for SNP ID: 1800562/C282Y.
CONCLUSION
HFE gene SNPs analyzed by using translation bioinformatics prediction tools; for functional and structural analysis of mutations in nonsynonymous coding region and to analysis functions and interaction of HFE gene with functional similar genes. Nine SNPs on (rs 1800562) predicted as highly damaging, increase the protein stability, have a severe effect on the 3D-structure of the protein and disease associated.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are acknowledgement; Dr. Hisham Noureldayem Altaib, Faculty of medical laboratories sciences, Sudan University of science and Technology for his guidance and support in this work.