Insilico Molecular Docking of Some Isolated Selected Compounds of Phoenix sylvestris (L.) Against Diabetes
- 1. Department of Pharmacy, BGC Trust University Bangladesh, Bangladesh
ABSTRACT
Phoenix sylvestris is a very graceful palm which is also known as Wild date palm, Silver date palm, date sugar palm and belongs to the family Arecaceae. The various parts of plant reported possessing diuretic, analgesic effect, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and neuropharmacological activities. Phoenix sylvestris is traditionally claimed to have antidiabetic, antidiarrheal, anti-dysentery activity and used in the treatment of a toothache, menstrual complaint. Our aim of the study to performed molecular docking studies to identify potential binding affinities of the phytocompounds from Phoenix sylvestris, namely 4-methylcatechol towards α-amylase for searching of the lead molecule against diabetes. A wide range of docking score found during molecular docking by Schrodinger. 2, 3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one and 4-methylcatechol showed the docking score respectively -5.044 kJ/mol and -5.303 kJ/mol against α-amylase. Between all the compounds 4-methylcatechol showed the best docking score towards α-amylase. So, 4-methylcatechol is the best compound for α-amylase enzyme inhibition, as it possessed the best value in Molecular Docking. Further, in vivo investigation need to identify α-amylase enzyme inhibitory activity of isolated compounds from Phoenix sylvestris.
KEYWORDS
• Phoenix sylvestris (L.)
• Alpha-amylase
• Molecular docking
• 4-Methylcatechol
CITATION
Barua J, Barua L, Hossen M, Absar N, Zohra FT, et al. (2019) Insilico Molecular Docking of Some Isolated Selected Compounds of Phoenix sylvestris (L.) Against Diabetes. J Bioinform, Genomics, Proteomics 4(1): 1039.
INTRODUCTION
The term Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder of multiple etiology characterized by abnormal fat, carbohydrate and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both [1,2]. It is one of the most challenging heterogeneous diseases, can be simply classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus [3,4]. Historically, the excellence between type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus has largely depended on the clinical presentation, such as age at disease onset, the presence of ketosis and also the dependence on insulin secretion. Type 1 diabetes mellitus, appearing mainly in childhood or young adulthood, is characterized by T cells-mediated autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islet b-cells, rendering the pancreas unable to synthesize and secrete insulin [5]. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, mainly appearing in adulthood, is the result of insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have a higher risk of cancer involving the breast, endometrium, stomach, colorectum, liver, pancreas, urinary bladder, and lymphoid tissue [6,7]. The mechanisms of increased cancer risk of diabetic patients may be related to insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, proinflammatory status and increased oxidative stress [4,8].
Diabetes is a common disease. The current worldwide prevalence is assessed to be approximately 250 x 106, and it is expected to reach 380 x 106 by 2025. In recent years, the prevalence of diabetes is increasing in Bangladesh in both urban and rural areas [9]. A recent study reported that majority adults with type 2 diabetes in Bangladesh have uncontrolled diabetes with a high prevalence of hazard factors crediting to early advancement of inconveniences [10]. One such enzyme, human pancreatic α-amylase (HPA, α1,4-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase, E.C. 3.2.1.1) plays a vital role in DM. It catalyzes the initial step in the hydrolysis of starch to maltose which is eventually degraded to glucose by α-glucosidases. Hence, retardation of starch digestion by HPA inhibition plays a key role in the control of postprandial hyperglycemia in type II DM [11] . By inhibiting HPA in the small intestines, the rate of hydrolysis of starch is decreased delaying the digestion process. This spreading of the digestion process reduces the amount of glucose generated and released in the blood and is one of the effective strategies for lowering post prandial hyperglycemia [12].
The use herbal medicine is gaining support and recognition across the world because most of these products are believed to have bioactive compounds responsible for healing various diseases without any side effects and at a lower cost. Phoenix sylvestris is a very graceful palm which is also known as Wild date palm, Silver date palm, date sugar palm and belongs to the family Arecaceae. Phoenix sylvestris is a very graceful palm which is also known as Wild date palm, Silver date palm, date sugar palm and belongs to the family Arecaceae.In Bangladesh, is known as Khejur. It is a palm tree cultivated for its syrupy juice and edible fruit in Bangladesh [13]. In Bangladesh, Khejur palm is produced as a homestead crop; however, it grows naturally or is cultivated in fallow lands, around homesteads, farmland boundary and even in the marginal lands along the roads and canals [14]. Fruits of the plant are used to treat back pain, stomachache, toothache, headache, arthritis, pain of buttocks, fever, piles, nervous debility, and as nervine tonic, restorative, sedative in ethno medicine [13,15]. The sap of Khejur palm is a good source of vitamins of the B group and contains, in addition, a variable amount of ascorbic acid [16], freshly harvested sap consists of sucrose around 10%, minimal invert sugar of <0.5% and a small amount of protein, gums, and minerals. Phoenix sylvestris leaves are traditionally claimed to have antidiabetic, antidiarrheal, anti-dysentery activity and used in the treatment of a toothache, menstrual complaint [17,18].
Computational simulations of drug-target interactions using in silico molecular docking and molecular dynamics approaches are commonly used for the rational design and screening of drugs [19]. Molecular docking has become a major computational method for the prediction of ligand–receptor interactions [20]. A productive docking strategy must have the ability to adequately envision the local ligand represent the receptor limiting site (i.e.to find the trial ligand geometry inside a particular resistance confine and the related physical-compound submolecular affiliations [21-24].
The aim of the study to find the mechanism of action of the isolated compounds from Phoenix sylvestris was explored the anti-diabetic activity by molecular docking analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Insilico molecular docking protein preparation
silico molecular docking protein preparation The 3D coordinates of the crystal structure of alpha-amylase (PDB:1PPI) were downloaded from the RCSB protein data bank(http://www.rcsb.org/pdb) [25]. It is a worldwide repository of information about the 3D structure of biological molecules, including proteins and nucleic acids. Then water molecules were removed from the protein PDB: 1PPI. The protein structure was corrected by the utilization of alternate conformation. The resultant protein file was subjected to energy minimization by force field. After the energy minimization, the protein file was subjected to define and edit binding site option available on the tools panel to explore the plausible binding site within the protein (1PPI). Using force field OPLS_2005, minimization was carried out setting maximum heavy atom RMSD (root-mean-square-deviation) to 0.30 Å.
Ligand preparation
The structures of six major representative compounds i.e., Diethylnitrosamine (CID: 5921), 2, 3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6- methyl-4H-pyran-4-one (CID: 119838), 4-methylcatechol (CID: 9958), 2,4-Di-tert-butyl phenol (CID: 7311), and Diethyl Phthalate (CID: 6781) were obtained from PubChem database. The ligands were prepared with LigPrep tool embedded in Maestro 2015, neutralized at pH 7.0 ± 2.0 using Epik and minimized by force field OPLS_2005.
Receptor grid generation
Receptor grids were calculated for prepared proteins such that various ligand poses bind within the predicted active site during docking. In Glide, grids were generated keeping the default parameters of van der Waals scaling factor 1.00 and charge cutoff 0.25 subjected to OPLS 2005 force field. A cubic box of specific dimensions centered around the centroid of the active site residues (Reference ligand active site) was generated for the receptor. The bounding box was set to 14 ? × 14 ? × 14 ? for docking experiments.
Glide Standard Precision (SP) ligand docking
SP flexible ligand docking was carried out in Glide of Schrödinger-Maestro v 10.1 [26]. Within which penalties were applied to non-cis/trans amide bonds. Van der Waals scaling factor and partial charge cutoff were selected to be 0.80 and 0.15, respectively for ligand atoms. Final scoring was performed on energy-minimized poses and displayed as Glide score. The best-docked pose with lowest Glide score value was recorded for each ligand.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Insilico molecular docking analysis
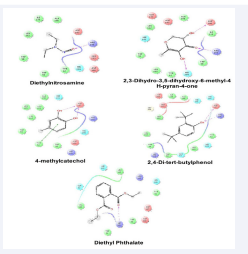
In this study, the binding mode of the α-amylase enzyme was investigated by doing computational analysis, glide docking. Both glide standard (SP) and extra precision (XP) mode had been introduced, where extra precision mode used for cross-validation purpose [27]. Grid-based docking study was used to analyze the binding modes of molecules with the amino acids present in the active pocket of the protein. To identify the potential antidiabetic lead molecule, we have subjected the docking analysis of the active compounds of Phoenix sylvestris (L.) to the active site of BACE1. In order to study the interaction of the compounds with alpha-amylase (PDB id: 1PPI). We performed Glide docking analysis by Schrodinger suite v10.1, where among of these compounds 4-methylcatechol shows highest docking score against both of the enzymes. Docking Score suggested that 4-methylcatechol had the highest affinity to the alpha-amylase corresponding to the other compound. The results of docking analysis were described in Table (1) and the docking figure showed in Figure (1).
Table 1: Docking results of compounds diethylnitrosamine (CID 5921), 2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one (CID 119838), 4-methylcatechol (CID 9958), 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol (CID 7311) and diethyl phthalate (CID 6781) with alpha-amylase (PDB id: 1PPI).
| Compound Name | Compound Id | Docking Score | Glide Energy |
| Diethylnitrosamine | 5921 | -3.571 | -15.042 |
| 2, 3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one | 119838 | -5.044 | -27.276 |
| 4-methylcatechol | 9958 | -5.303 | -25.993 |
| 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | 7311 | -4.873 | -26.658 |
| Diethyl Phthalate | 6781 | -4.62 | -30.352 |
Figure 1: Schematic representation of the interactions between the best pose found of the selected compounds with alpha-amylase (PDB ID: 1PPI).
The colors indicate the residue (or species) type: Red-acidic (Asp, Glu), Green-hydrophobic (Ala, Val,Ile, Leu, Tyr, Phe, Trp, Met, Cys, Pro), Purple-basic (Hip, Lys, Arg), Blue-polar (Ser, Thr, Gln, Asn, His, Hie, Hid), Light gray-other (Gly, water), and Darker gray-metal atoms. Interactions with the protein are marked with lines between ligand atoms and protein residues: Solid pink—H-bonds to the protein backbone, Dotted pink-H-bonds to protein side chains, Green—pi-pi stacking interactions, Orange-pi-cation interactions. Ligand atoms that are exposed to solvent are marked with gray spheres. The protein “pocket” is displayed with a line around the ligand, colored with the color of the nearest protein residue. The gap in the line shows the opening of the pocket.
CONCLUSION
From the study, it was found that Phoenix sylvestris (L.) could be a great source of new alpha-amylase activity. Insilco model support that all the isolated compound from P. sylvestris might be an alpha-amylase inhibitor. Further invivo investigation needs to identify the potential inhibitory activity of isolated compounds from P. sylvestris.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thankful Mr. Arkajyoti Paul for providing the software and helping in manuscript writing.