Molecular Docking Studies and In silico Admet Screening of Some Novel Heterocyclic Substituted 9-Anilinoacridines as Topoisomerase ii Inhibitors
- 1. Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, JSS University, India
Abstract
The derivatives of 9-aminoacridine are generally inhibiting DNA Topoisomerase II (topo II), because of the ability of acridine nucleus to intercalate into DNA base pair. In the present study, an attempt is made to identify potent ligands from heterocyclic substituted 9-anilinoacridines which target against Topoisomerase II (1ZXM) by molecular modelling and docking studies using Schrodinger suite-2011 Maestro 9.2 version. The binding affinity of the designed compounds towards Topoisomerase II (1ZXM) was calculated based on the GLIDE score due to various interactions. Many of the designed compounds have good Glide score due to strong hydrogen bonding interactions, hydrophobic interactions and other parameters.. The N-Phenyl pyrazole substituted 9-anilino acridine derivatives 1a- 1x have good binding affinity with topo II with Glide score in the range of -5.58 to -7.78 when compared with the standard ledacrine (-5.24). The in silico ADMET screening of these compounds also performed by qikprop module of Schrodinger suite and the values of all the properties are within the recommended values. So it is worthwhile to synthesis the designed compounds for their antibacterial and cytotoxic activities against Topoisomerase II.
Keywords
Topoisomerase II; Acridine; N-Phenyl Pyrazole; Cytotoxic; Docking studies; In silico ADMET screening I
Citation
Kalirajan R, Gowramma B, Jubie S, Sankar S (2017) Molecular Docking Studies and In silico Admet Screening of Some Novel Heterocyclic Substituted 9-Anilinoacridines as Topoisomerase ii Inhibitors. JSM Chem 5(1): 1039.
INTRODUCTION
The 9-aminoacridine derivatives are inhibiting DNA Topoisomerase II (topoII), due to their ability to intercalate into DNA base pair, stabilizing the DNA–topoII cleavable complex, and ternary complex is formed. The topoII activity is inhibited by the double-strand breaks in DNA, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The planar aromatic ring system of the acridine moiety has intercalative property.
In the same context, acridines have various biological activities like antimicrobial [1], antioxidant [2], anticancer [3-5], antimalarial [6], analgesic [7], antileishmanial [8], antinociceptive [9], acetyl cholinesterase inhibitors [10] and antiherpes [11] etc. Amsacrine is the known compound of 9-anilinoacridines series, which was the first DNA-intercalating agent to be considered as Topoisomerase II inhibitor. Several detailed SAR studies of acridine-based DNA-intercalating agents suggest that, the mode of binding is important and the chromophore intercalate with DNA base pairs. The chemical modifications of 9-aminoacridines by the introduction of various substitutions were allowed expansion of research on the structure activity relationship to afford new insight into molecular interactions at the receptor level [12]. In fact, it is well established that slight structural modification on 9-anilinoacridines may bring various pharmacological effects. Similarly pyrazole derivatives are also reported for various biological activities [13,14] like antimicrobial, anticancer etc. In continuous of our previous research work [15-18], on searching new potent antimicrobial and cytotoxic agents, we have designed 9-anilinoacridine analogues bearing the N-Phenyl pyrazole residue on anilino rings for Topoisomerase II inhibition by molecular docking studies by using by using Schrodinger suite-2011 Maestro 9.2 version. The results revealed that the newly designed heterocyclic substituted 9-anilinoacridine analogues exhibited good inhibition with topo II. Generally the Topoisomerase II inhibitors exhibit antibacterial and cytotoxic activities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Protein preparation
The crystal structure of protein Human Topoisomerase IIa (PDB ID: 1ZXM) at 1.87A° was obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and used for this study. In general, the protein structures are refined for their bond orders, formal charges and missing hydrogen atoms, topologies, incomplete and terminal amide groups using protein preparation wizard of Schrödinger suite [16].
The water molecules beyond 5A° were removed. The possible ionization states were generated in the protein structure and the most stable state was chosen. The hydrogen bonds were assigned and orientations of the retained water molecules were corrected. Finally, a minimization of the protein structure was carried out using OPLS2005 force field to reorient side-chain hydroxyl groups and potential steric clashes. The minimization is restrained to the input protein coordinates by a predefined Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) tolerance of 0.3A°
Ligand preparation
The ligands structures were generated in the CDX format using Chem Draw ultra version 8.0. These ligands were then converted to the mol2 format and the ligands were prepared by LigPrep module of Maestro in the Schrodinger suite 2011. The 2D structures are converted to 3D structures by including stereo chemical ionization, tautomeric variations. Then their energy was minimized and optimized for their geometry, desalted and corrected for their chiralities and missing hydrogen atoms. The bonds orders of these ligands were fixed and the charged groups were neutralized. The ionization and tautomeric states were generated between pH of 6.8 to 7.2 using Epik module. In the LigPrep module, the compounds were minimized by Optimized Potentials for Liquid Simulations-2005 (OPLS-2005) force field in Schrodinger suit until a RMSD of 1.8A° was achieved. A single low energy ring confirmation per ligand was generated and the optimized ligands were used for docking analysis.
Receptor grid generation
The ligand ANP (phosphoamino phosphonicacid adenylate ester) was retained in the crystal structure of the prepared protein which was used for the receptor grid construction. The binding box dimensions (within which the centroid of a docked pose is confined) of the protein was set to 14A° x 14A° x 14 A°.
Validation of the docking programme
The accuracy of the docking studies are determined by finding how closely the lowest energy pose of the co-crystallized ligand predicted by the object scoring function, Glide score (G Score), resembles an experimental binding mode as determined by X-ray crystallography. The Glide docking procedure was validated by removing the co-crystallized ligand from the binding site of the protein and redocking the ligand with its binding site. The hydrogen bonding interactions and the RMSD between the predicted conformation and the observed X-ray crystallographic conformation were used for analyzing the results.
Glide ligand docking
The glide docking of the designed molecules was performed by using the receptor grid and the ligand molecules. The favourable interactions between ligand molecules and the receptor were scored using Glide module of ligand docking program. The docking calculations were performed using extra precision (XP) mode. The docking process was run in a flexible docking mode which automatically generates conformations for each input ligand. The ligand poses generated were passed through a series of hierarchal filters that evaluate the ligand’s interaction with the receptor. The spatial fit of the ligand to the active site, examines the complementarity of the ligand-receptor interactions using grid-based method by the empirical ChemScore function. This algorithm recognizes favourable hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic, metal-ligation interactions and penalizes steric clashes. The Poses that pass these initial screens enter in to the final stage of the algorithm, which involves evaluation and minimization of grid approximation, OPLS non bonded ligand-receptor interaction energy. Finally, the minimized poses were re-scored using Glide Score scoring function.
The XP-Glide score of active compounds were summarized and the fitness scores for each ligand in Topoisomerase II are compared. When compared with the G-score of standard compound containing acridine derivative ledacrine which is used as anti tumour agent, as well as potent Topoisomerase, most of the proposed compounds have good Glide scores [19].
The in silico ADMET properties of the proposed compounds were determined by qikprop module of Schrodinger suite maestro 9.2 version.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The molecular docking studies of the ligands to protein active sites were performed by an advanced molecular docking program Schrodinger suite Maestro-9.2 version to determine the binding affinities. The docking of the compounds are performed towards the Topoisomerase II (1ZXM) in order to ascertain their topo II inhibition activity. The Glide score of the compounds 1a-x are higher than the standard ledacrine, showed good affinity to the receptor (Figure 1)
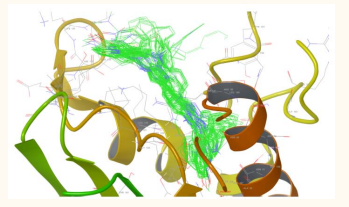
Figure 1: Cluster of compounds 1a-x with Topoisomerase II (1ZXM)
Out of these compounds, 1c, 1p, 1r and 1t have more Glide scores due to higher lipophilic character, 1t has more Glide scores due to hydrogen bonding and 1h has more Glide scores due to higher electrostatic evidence. The results are summarized in the Table (1)
Table 1: Docking studies for compounds 1a-x with topoisomerase II (1ZXM).
| Compound | GScore | Lipophilic EvdW | HBond | Electro | LowMW | RotPenal |
| 1h | -7.78 | -5.98 | -0.44 | -1.36 | 0 | 0 |
| 1r | -7.72 | -6.6 | -0.7 | -0.42 | 0 | 0 |
| 1c | -7.57 | -6.55 | -0.7 | -0.32 | 0 | 0 |
| 1n | -7.54 | -5.1 | -1.81 | -0.63 | 0 | 0 |
| 1t | -7.5 | -6.42 | -0.7 | -0.38 | 0 | 0 |
| 1p | -7.35 | -6.25 | -0.7 | -0.37 | 0 | 0 |
| 1l | -7.17 | -6.1 | -0.7 | -0.35 | 0 | 0 |
| 1j | -6.91 | -5.86 | -0.7 | -0.38 | 0 | 0 |
| 1d | -6.88 | -5.8 | -0.7 | -0.39 | 0 | 0 |
| 1v | -6.85 | -5.82 | -0.7 | -0.37 | 0 | 0 |
| 1g | -6.85 | -5.75 | -0.7 | -0.35 | 0 | 0 |
| 1a | -6.84 | -5.78 | -0.7 | -0.38 | 0 | 0 |
| 1s | -6.78 | -5.67 | -0.7 | -0.3 | -0.03 | 0 |
| 1i | -6.77 | -5.62 | -0.7 | -0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| 1x | -6.76 | -5.67 | -0.7 | -0.36 | 0 | 0 |
| 1q | -6.75 | -5.67 | -0.7 | -0.38 | 0 | 0 |
| 1m | -6.71 | -5.91 | -0.5 | -0.29 | 0 | 0 |
| 1e | -6.65 | -5.56 | -0.7 | -0.39 | 0 | 0 |
| 1u | -6.45 | -6.35 | 0 | -0.03 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 1f | -6.38 | -5.58 | -0.7 | -0.11 | 0 | 0 |
| 1b | -6.37 | -5.34 | -0.69 | -0.34 | 0 | 0 |
| 1k | -6.3 | -5.68 | -0.35 | -0.28 | 0 | 0 |
| 1w | -6.21 | -5.21 | -0.7 | -0.29 | 0 | 0 |
| 1o | -5.58 | -5.74 | 0 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 |
| Ledacrine(std) | -5.24 | -2.94 | -0.22 | -1.66 | -0.42 | 0 |
The best affinity modes of the docked compounds (1c, 1r, 1h) with Topoisomerase II with good Glide score are shown in Figure (2)
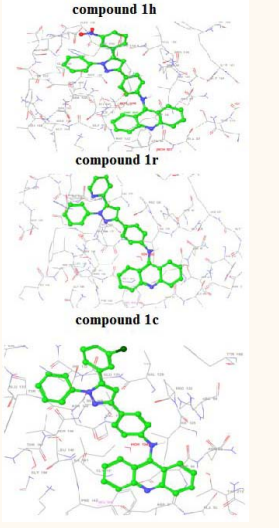
Figure 2: Best affinity mode of docked compounds 1h, 1r & 1c with topoII (1ZXM).
The ADMET properties for the proposed compounds can be determined in silico by using qikprop module of Schrödinger suite 2011. The computed dipole moment of the molecule are in the range of 2.3 -6.1. Estimated number of hydrogen bonds that would be donated by the solute to water molecules in an aqueous solution of the compounds are in the range of 1-2. Estimated number of hydrogen bonds that would be accepted by the solute from water molecules in an aqueous solution of the compounds are in the range of 2.5-4. Predicted octanol/water partition coefficient values of the compounds are in the range of 7.7-9.6. The compounds have highest QPlogP value. Numbers of likely metabolic reactions of the compounds are in the range of 2-4. Predictions of binding to human serum albumin for the compounds are in the range of 1.8-2.4. Number of violations of Lipinski’s rule of five is 1-2. Many of the compounds have 100% Human Oral Absorption Figure (3)
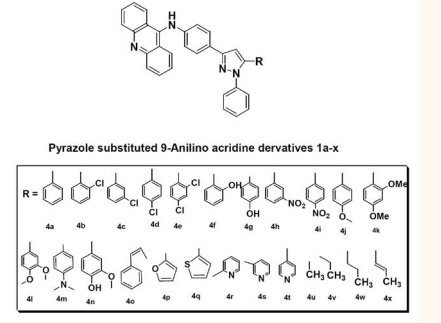
Figure 3: Structure of most active compounds 1a-x.
Almost all the properties except QPlogP and binding to human serum albumin of the compounds are within the recommended values. The details of the in silico ADMET properties for the compounds 1a-x are shown in the Table (2).
Table 2: In silico ADMET screening for designed compounds 1a-x.
| Compound | dipole | Donor HB | Accpt HB | logP o/w |
# metab |
QPlog Khsa | Rule of Five |
% Human Oral Absorption |
| 1a | 4.639 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.75 | 2 | 2.299 | 1 | 100 |
| 1b | 5.466 | 1 | 2.5 | 9.165 | 2 | 2.409 | 2 | 100 |
| 1c | 3.674 | 1 | 2.5 | 9.253 | 2 | 2.424 | 2 | 100 |
| 1d | 2.314 | 1 | 2.5 | 9.257 | 2 | 2.425 | 2 | 100 |
| 1e | 3.507 | 1 | 2.5 | 9.666 | 2 | 2.534 | 2 | 100 |
| 1f | 3.115 | 2 | 3.25 | 8.013 | 3 | 2.029 | 2 | 100 |
| 1g | 4.848 | 2 | 3.25 | 7.914 | 3 | 2.041 | 2 | 100 |
| 1h | 5.549 | 1 | 3.5 | 8.036 | 3 | 2.242 | 2 | 100 |
| 1i | 3.393 | 1 | 3.5 | 8.038 | 3 | 2.243 | 2 | 100 |
| 1j | 4.922 | 1 | 3.25 | 8.835 | 3 | 2.303 | 2 | 100 |
| 1k | 6.297 | 1 | 4 | 8.986 | 4 | 2.331 | 2 | 100 |
| 1l | 3.812 | 1 | 4 | 8.916 | 4 | 2.296 | 2 | 100 |
| 1m | 7.197 | 1 | 3.5 | 9.19 | 3 | 2.466 | 2 | 100 |
| 1n | 4.158 | 2 | 4 | 8.051 | 4 | 2.068 | 2 | 100 |
| 1o | 4.588 | 1 | 2.5 | 9.494 | 2 | 2.471 | 2 | 100 |
| 1p | 4.529 | 1 | 3 | 8.141 | 3 | 2.031 | 1 | 100 |
| 1q | 4.559 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.666 | 3 | 2.222 | 1 | 100 |
| 1r | 5.719 | 1 | 3.5 | 8.214 | 3 | 2.059 | 1 | 100 |
| 1s | 3.696 | 1 | 4 | 7.801 | 4 | 1.939 | 1 | 100 |
| 1t | 1.81 | 1 | 4 | 7.773 | 4 | 1.936 | 1 | 100 |
| 1u | 4.809 | 1 | 2.5 | 7.837 | 3 | 1.822 | 1 | 100 |
| 1v | 4.87 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.225 | 3 | 1.939 | 1 | 100 |
| 1w | 4.59 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.087 | 3 | 2.067 | 1 | 100 |
| 1x | 4.639 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.75 | 3 | 2.043 | 1 | 100 |
| Recommended values | 1-12.5 | 0-6 | 2-20 | -2-6.5 | 1-8 | -1.5-1.5 | max4 | >80% is high <25% is poor |
| Abbreviations: Dipole: Computed dipole moment of the molecule; donor HB: Estimated number of hydrogen bonds that would be donated by the solute to water molecules in an aqueous solution; accpt HB: Estimated number of hydrogen bonds that would be accepted by the solute from water molecules in an aqueous solution; QPlogPo/w: Predicted octanol/water partition coefficient; #metab: Number of likely metabolic reactions; QPlogKhsa: Prediction of binding to human serum albumin; Rule of Five: Number of violations of Lipinski’s rule of five; %Human-Oral absorption: Predicted human oral absorption on 0 to 100% scale. The prediction is based on a quantitative multiple linear regression model | ||||||||
CONCLUSION
9-aminoacridines are reported for various biological properties. A structure-based pharmacophore model was generated and validated to obtain active Topoisomerase II inhibitors from our self-compiled database of heterocyclic substituted 9-anilino acridine derivatives. The docking study revealed that N-Phenyl pyrazole substituted 9-anilino acridine derivatives showed better alignment at active site by interacting with all crucial amino acid residues. Thus, the in silico method was adopted in the present study helped to identify the lead molecules and also may explain their beneficial effect for further study to produce more significant antibacterial and antitumour drugs. On this basis, authors recently demonstrated that diverse compounds of the heterocyclic substituted 9-anilinoacridine series exerted Topoisomerase II inhibitor activity. Results observed in the present study clearly demonstrated that some of the heterocyclic substituted 9-anilinoacridine family may exert interesting antibacterial and antitumour activities. The compounds 1h, 1c, 1r and 1n have expected to be significant antibacterial and antitumour activity and also to be useful after further refinement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank All India Council for Technical Education, New Delhi for the financial support under Research Promotion Scheme. We also thank our Vice Chancellor Dr. B. Suresh, JSS University, Mysore, Our principal Dr. S.P. Dhanabal, JSS College of pharmacy, Ooty for the technical support






































































































































