Hemolytic Disease of Newborn due to ABO Incompatibility between O Blood Group Mother and A Blood Group Neonate: Do we need to screen ABO blood group antibody in ante-natal care?
- 1. Professor and Head/ Senior Consultant Physician and Nephrologist, Department of Medicine/Nephrology, Defence Services Medical Academy/ No. (1) Defence Services General Hospital (1000-Bedded), Yangon, Myanmar.
- 2. Senior Consultant Physician, No. (1) Defence Services General Hospital (1000-Bedded), Yangon, Myanmar
- 3. Consultant Hematologist, No. (1) Defence Services General Hospital (1000-Bedded), Yangon, Myanmar.
- 4. Consultant Physician, No. (1) Defence Services General Hospital (1000-Bedded), Yangon, Myanmar
Abstract
ABO incompatibility between O blood group mother and non-O blood group neonate is common. It rarely causes anemia and hyperbilirubinemia in neonate, requiring invasive management. We reported a case of incompatibility in a O blood group primigravid mother and A blood group neonate; the neonate had severe jaundice 12 hour after elective cesarean section. She was managed with phototherapy. It highlighted the need for screening antibodies to both ABO and Rh group in antenatal care and awareness among health care personnel but also in general public.
Keywords
Hemolytic disease of newborn (HDN), Hyperbilirubinemia, ABO incompatibility
Citation
Pyar KP, Myint MZ, Kyaw AP, Tun ZM, Aung A, et al. (2023) Hemolytic Disease of Newborn due to ABO Incompatibility between O Blood Group Mother and A Blood Group Neonate: Do we need to screen ABO blood group antibody in ante-natal care?. JSM Clin Case Rep 11(2): 1215.
BACKGROUND
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is commonly caused by the incompatibility of the mother’s and the baby’s blood; it leads to fetal death rate in 1% of all pregnancies (1). It results from either ABO or rhesus (Rh) mismatch. ABO mismatch affects 15 to 25% of all pregnancies; nonetheless, only 1% of people will develop HDN. HDN caused by ABO incompatibility (ABO HDN) is usually mild form and it is very rarely severe (2); it is due to the expression of ABO blood type antigens and their presentation in several organs. Similarly, one study reported the risk of ABO HDN as 4.3% of deliveries and moderately severe to severe hemolysis as 2.7% (3). However, the finding from another study was not supportive to them; severe hemolytic disease in neonates born to group O (+) woman was not more likely in group A or B neonates than in controls (group O) (4).
Regarding the prevalence of ABO HDN among pregnant mothers, it occurs almost exclusively in the offspring of women of blood group O; it rarely develops in group A mothers with high? titre anti? IgG. Haemolysis due to anti?A is more common (1 in 150 births) than that to anti? B immune antibodies.
Clarity in diagnosis of ABO HDN was suggested by some researchers; ABO incompatibility, significant neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, and a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) (5). Nonetheless, it was challenging to do all the tests in developing countries.
Prevention is still essential in decreasing morbidity and mortality of HDN although fetal death rate is very low (1). Early screening and preventative strategies during prenatal care are essential. Moreover, sensitizing procedures including abortion, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling should be followed with anti-D immunoglobulin prophylaxis.
CASE PRESENTATION
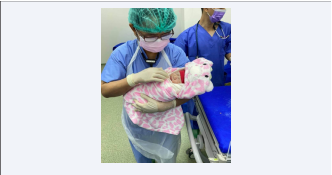
A term female neonate weighing (6lb 12oz) 3.1kg delivered by lower segment cesarian section at 38 week to a O RhD-positive primigravida mother developed jaundice on day 1 (12 hours after delivery); total serum bilirubin was 12.0 mg/dL. (Photo 1 & 2) On complete blood count,
Figure 1: Baby immediately after delivery reveals normal.
Figure 2: Baby immediately after delivery showing normal facial skin.
hemoglobin was 13.0g/dL; total WBC count was normal; platelet count was normal; and, thyroid profile was within normal limits. Fire-fire Photo therapy was initiated within 24 hours after delivery. TORCH screen was negative. The blood group of neonate was “A” Rh positive; her mother was ‘O’ Rh positive and her father was ‘A’ Rh positive. There was no history of sensitizing procedures: abortion, blood transfusion, bleeding in early pregnancy and ante-partum hemorrhage in mother. Photo therapy was given for 5 days. Serum bilirubin on Day 3 was 13 mg%; Day 7 was 12 mg%; Day 10 was 11 mg%. The baby was afebrile; her bowels opened well and there was no sepsis. The baby was fed initially with bottle feeding; breast feeding was initiated on Day 3. She was discharged on Day 6 after delivery. Total serum bilirubin was 11 mg/dL on Day 10. The baby was doing well. As shown in photo taken on one month after delivery, the baby had yellowish staining of skin.
Figure 3: Baby at one month still having jaundice in face and darkening of legs due to phototherapy.
DISCUSSION
Thorough history taking and physical examination are important in predicting diagnosis as well as prevention of HDN. There are two main mechanisms by which maternal antibodies target fetal or newborn RBC antigens: ABO incompatibility and fetomaternal hemorrhage. ABO incompatibility is a congenital, inherent mismatch between maternal and fetal blood types. Conversely, alloimmunization due to fetomaternal hemorrhage (FMH) is an acquired immune-mediated mechanism that typically affects subsequent pregnancies rather than the pregnancy in which the FMH happens. In almost all of the cases of HDN, the underlying cause is usually Rh or ABO incompatibility between the mother and the fetus. In the event of alloimmunization, the maternal antibodies start attacking fetal red blood cells. Maternal antibodies, IgM antibodies, cannot cross the placenta; thus, they cannot reach the fetus. On the other hand, maternal antibodies, IgG antibodies, reach the fetus. Antibody isotype switching from IgM antibodies to IgG antibodies is caused by fetus-maternal hemorrhage. In this case, the mother was primigravida and there was no prior history of HDN or hydrops fetalis, chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, antepartum hemorrhage, miscarriages, abortions, and maternal blood transfusions. Therefore, ABO incompatibility must be the cause for HDN. One systematic review found that HDN was rare; and most births occured at a late preterm gestational age (6). This case was born at term; one reason for case sharing.
Data on hemolysis indexed by carbon monoxide (CO) levels in expired air (ETCOc) and blood (COHbc) support an essential role for a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) in making a more precise diagnosis of ABO HDN. ABO incompatibility, significant neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, and a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) were required to diagnose ABO HDN clearly (5). In this case, DAT test could not be done. Being poor resource setting, clinical diagnosis of ABO HDN was made with ABO incompatibility, significant neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, with normal thyroid function, without sepsis and without congenital abnormality in hepatobiliary tree.
In contemporary neonatal practice, HDN should be considered in the fetus or neonate where there is one or more of the following: rapidly developing or severe hyperbilirubinaemia not predicted by maternal antenatal antibody screening; positive maternal antenatal antibody screening and/or diagnosis of a severely anaemic/hydropic fetus; a positive direct anti-globulin test (DAT); haemolysis detected on blood film examination; and prolonged hyperbilirubinaemia (7). In this case, the serum bilirubin level was still high on day ‘10’ after delivery though the neonate was very alert and eating well. Therefore, the finding in this case, sudden onset of severe hyperbilirubinaemia proved their practice. As shown in photo, yellowish staining in the skin of the baby persisted till one month after delivery; it provided the evidence to population-based study. They found that cholestasis was common in infants with severe HDN and they recommended early and repeated screening for conjugated hyperbilirubinemia in the first week of life to ensure adequate management (8).
This neonate had severe jaundice shortly after delivery and the level of serum bilirubin was high, more than 10 times normal. Therefore, the case proved the other study done over 13 years; they reported that severe hemolytic disease in neonates born to group O (+) woman was not more likely in group A or B neonates than in controls (group O) (4). Therefore, HDN caused by ABO incompatibility may be severe like this case and early diagnosis is important to get timely treatment. It is second for reporting.
The likely reason for severe HDN in this case is postulated as follows. The blood group of her father is ‘A’; mother, is blood group ‘O’, the mother’s immune system was produced a large amount of antibodies anti-A IgG to ‘A’ antigen probably induced with short period of surgery, lower segment cesarean section. Severe destruction of neonate red blood cells within few hours led to severe jaundice and hyperbilirubinemia in first 24 hours after delivery. In fact, antibody level (ABO) screening with indirect anti-globulin test (IAT) and after that titration IgG antibody should be done to mother or neonate to prove our hypothesis (9).
Blood testing, antibodies to both ABO system and Rh system, throughout the first trimester is very important; it is recommended in ANC guidelines in developed countries. In resource poor setting, screening and monitoring of antibodies to both ABO system and Rh system is not accessible. At least, we can pay more attention to baby born from pregnant women with blood type O; close observation during and after birth. Moreover, the blood type of the baby should be identified as soon as possible after birth. Besides, serum bilirubin level should be closely monitored if the blood group of the baby is non-O type. This is another reason for sharing case to those living in developing countries. Red blood cell antibody screening programmes are required to detect maternal alloimmunization early in pregnancy to facilitate the identification of high-risk cases to timely start antenatal and postnatal treatment (10).
CONCLUSION
HDN should also be suspected in a neonate present with features of HDN born to both non-O group mother and O group mother. HDN due to ABO incompatibility (ABO HDN) may not be always benign as perceived. Although history (abortion, blood transfusion, neonatal jaundice in previous baby) is important, HDN can happen without history of sensitization in primigravida like this case. Routine screening of antibodies to both ABO and Rh blood group should be done in antenatal care though it may not be easy in low resource setting. Health education on awareness of HDN should be done to all pregnant mothers. A high index of suspicion of HDN among obstetric and gynecologists, neonatologists, physicians and nursing staffs is important. Early diagnosis, along with timely intervention and appropriate measures, can reduce neonatal morbidity and mortality.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank both parents for giving consent to this article. Also, to all doctors and nursing team for making great efforts in caring her. The authors acknowledged the following team; Professor Darli Aung for obstetric care, Professor Win Mar Aye for neonatal care, Professor Kyaw Sein Tun, Professor Myint Zaw, Professor Kyaw Zay Ya and Professor Ko Ko Lwin for administrative support.
Declaration of conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interests with respect to authorship and publication of this article.
Ethical approval
Our institution does not require ethical approval for reporting cases.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for publication of this article.
Informed consent
The informed consent for publication in this article was obtained from both parents.
REFERENCES
1. Myle AK, Al-Khattabi GH. Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn: A Review of Current Trends and Prospects. Pediatr Health Med Ther. 2021;12:491–8.
2. RA, Khan J, Andrews J, Mayock D, Billimoria Z, Pagano MB. Severe ABO Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn Requiring Exchange Transfusion. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019 Nov;41(8):632–4.
3. Akanmu AS, Oyedeji OA, Adeyemo TA, Ogbenna AA. Estimating the Risk of ABO Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn in Lagos. Wendel S, editor. J Blood Transfus. 2015 Sep 17;2015:560738.
4. Christensen RD, Baer VL, MacQueen BC, O’Brien EA, Ilstrup SJ. ABO hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: thirteen years of data after implementing a universal bilirubin screening and management program. J Perinatol. 2018 May 1;38(5):517–25.
5. Watchko JF. ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn: a need for clarity and consistency in diagnosis. J Perinatol Off J Calif Perinat Assoc. 2023 Feb;43(2):242–7.
6. de Winter DP, Kaminski A, Tjoa ML, Oepkes D. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: systematic literature review of the antenatal landscape. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Jan 7;23(1):12.
7. Neil A Murray, Irene A G Roberts. Haemolytic disease of the newborn. Arch Dis Child - Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007 Mar 1;92(2):F83.
8. Teng J, Wickman L, Reilly M, Nemeth A, Fischler B, Bohlin K, et al. Population-based incidence and risk factors for cholestasis in hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. J Perinatol. 2022 Jun 1;42(6):702–7.
9. Knight R. Haemolitic disease of the newborn or foetus (HDN). In: Transfusion and Transplantaion Science. Oxford University; 2012. p. 155–61.
10. De Haas M, Thurik FF, Koelewijn JM, Van Der Schoot CE. Haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Vox Sang. 2015 Aug;109(2):99–113.