Iatrogenic Cushing
- 1. Department of Medicine, Olive View-UCLA Medical Center, David Geffen School of Medicine, USA
Abstract
Background: Intake of glucocorticoids (GCs) may result in iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome.
Objective: To describe a case of severe iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome caused by administration of a non-prescription drug adulterated with dexamethasone, and to alert physicians and public about harm associated with this product.
Methods: Pubmed and internet search up to June 27, 2022. Search terms are Cushing’s, glucocorticoids, adulteration, iatrogenic. Case reports, case series and review articles are included.
Case presentation: A 54-year-old man presented with severe Cushinoid features. Laboratory work-up was consistent with exogenous source of GCs. Patient denied previous or current intake of GCs but reported taking a health product called “Artri-King” for knee pain. Inspection of this drug did not reveal any GCs among its ingredients. Yet, laboratory analysis performed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) confirmed that this drug contains dexamethasone, which was not listed on the product label. Review of literature reveals that GC adulteration in Chinese health products is common occurring in 47.5% of patients consuming these products. Most subjects (62.3%) taking products with undeclared GCs had one or more complications attributed to GCs, 11.5% required admission to intensive care, and 3.3% died. In another series, iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome was the second clinical presentation of use of adulterated Chine medicines occurring in 10.6% of cases, whereas psychosis was the first most frequent presentation (12.9% of cases).
Conclusion: In any case of iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome, discontinuation of supplemental health products is essential because many of these products may include undeclared GCs.
Keywords
Cushing’s, Iatrogenic, Adulteration, Artri-King, FDA
Citation
Mikhail N, Kurator K, Martey E, Gaitonde A, Cabrera C, et al. (2022) Iatrogenic Cushing’s Syndrome Caused by Adulteration of a Health Product with Dexamethasone. JSM Clin Case Rep 10(2): 1201.
INTRODUCTION
A common belief among public is that supplemental health products or complementary medicines are “natural” and therefore “safe”. However, rigorous control of these products by governmental agencies is lacking. Thus, they may include unknown concentrations of synthetic drugs and chemicals causing serious health problems. Moreover, product label may not reflect the true product ingredients and may be adulterated with harmful substances. A large retrospective study (n=404, median age 51 years, 58% females) of Chinese health products identified 1,234 adulterants that consisted of approved and banned drugs, drug analogues and animal thyroid extracts [1]. In this Chinese study, 65.1% of subjects reported adverse effects attributed to adulterated products, including 14 severe and 2 fatal cases [1]. Thus, health products are neither natural nor safe. We herein report a case of severe iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome as result of intake of a health product that contained undeclared and unknown amounts of dexamethasone.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 54-year-old man presented with shortness of breath. On physical exam, he exhibits severe Cushinoid features including central obesity, moon facies, dorsocervical hump, abdominal striae, and fungal skin widespread rash (Figure 1). Computed tomography (CT) showed bilateral multiple acute, sub-acute and chronic rib fractures indicative of severe osteoporosis. Furthermore, CT of the spine demonstrated multiple severe compression deformities of 4th and 6th thoracic vertebral bodies. Serum AM cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), both came back undetectable consistent with exogenous exposure to GCs [2]. Patient’s list of prescribed medications did not include any current or past use of GCs. However, on further asking, patient reported the use of a supplemental drug called “Artri-King” bought from a local store to relieve knee pain in a dose of 2 tablets 3 times daily for approximately 1 year. Inspection of ingredients of this product did not reveal any type of GCs. However, a recent analysis by the FDA in April 2022 confirmed that this product contained 2 hidden ingredients, namely dexamethasone (a potent synthetic GC) and diclofenac (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) [3]. In addition, the FDA advised consumers not to purchase or use Artri-King [3]. Accordingly, on June 2, 2022, Walmart recalled all lots of ArtriKing Supplements [4].
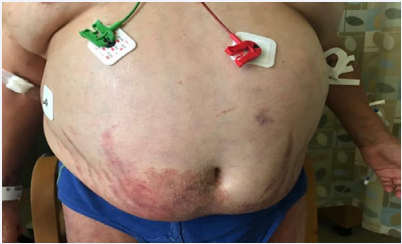
Figure 1: Severe abdominal obesity, abdominal stria and fungal skin infections reflecting severe iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome.
DISCUSSION
This report illustrates the profound harm caused by GC adulteration of a popular health product Artri-King used for pain relief. In fact, GC adulteration of supplemental medicines is not uncommon. Chong et al. [5], reported on the safety of confirmed GC-adulterated Chinese medicines among 61 patients who consumed such medicines. Dexamethasone was the most common GC implicated in 47.5% of subjects followed by prednisone 39.3% and betamethasone 8.2% [5]. Among these 61 subjects, 62.3% had one or more complications related to exogenous GCs, 29.5% had documented Cushing’s syndrome, 11.5% required admission to intensive care, and 3.3% (2 patients) died within 30 days of admission [5].
In the large series of Ching et al. [1], iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome emerged as the second most common presentation of adulterated Chinese medicines occurring in 10.6% of subjects, only preceded by psychosis occurring in 12.9% of individuals [1]. Psychosis was presumably attributed to the banned anorectic drug sibutramine, which was the most common adulterant found in this series [1]. The most likely reason for adding GCs to pain-relief supplemental products is to increase their analgesic effects thanks to the anti-inflammatory of GCs [5]. However, it is unclear why the manufacturer of Artri-King did not declare dexamethasone (and diclofenac) among the product ingredients.
To the best of our knowledge this the first case of iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome reported in relation to Atri-King. Fortunately, the timely FDA warning about the inclusion of undeclared dexamethasone in this product alerted us to stop it. Despite the risk of development of clinically manifest adrenal insufficiency after sudden discontinuation of this product, we elected not to taper of GCs because of the following 2 reasons. First, patient was followed closely in our hospital after stopping Artri-King and did not show any symptoms or signs of adrenal insufficiency such as hypotension, vomiting, diarrhea. Second, patient had already severe Cushing’s syndrome complicated by widespread osteoporotic fractures due to dexamethasone. Thus, we did not like to prolong the duration of GC administration further. However, it should be emphasized, that patient was instructed to call his medical doctor or go the emergency department should he experience any of symptoms of adrenal insufficiency.
CONCLUSIONS
We presented a case of severe iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome due to undeclared dexamethasone in a popular pain-relief nonprescription drug called Artri-King. While the FDA laboratory analysis unraveled the presence of dexamethasone and diclofenac adulteration in this product, it is likely that other supplemental medicines suffer from similar problem. Therefore, in any case of iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome, drug history should not be limited to GC-containing prescription drugs. Rather, physicians should inquire about intake of any supplemental medicine. The latter should be stopped since undeclared GCs could be one of the product components. Lessons learnt from this case were summarized in Table 1.
| 1. Adulteration of health products with undeclared glucocorticoids is common. |
| 2. In patients with iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome, taking a careful drug history, including history of intake of any food supplements, is essential. |
| 3. Inspect ingredients of non-prescription drugs and check ?for any glucocorticoid among ingredients. |
| 4. Even in absence of evidence of any product adulteration, discontinue the supplemental product as there may be a potential for glucocorticoid adulteration unless proved otherwise. |
| 5. The decision of glucocorticoid tapering after stopping the implicated product to avoid clinical adrenal insufficiency should be individualized. |
| 6. Close supervision should be undertaken for any symptoms or signs of adrenal insufficiency after discontinuation of the suspected product. |








































































































































