Repurposing Low Dose Fractionated Radiation Therapy to Induce Synthetic Lethality
- 1. Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Maryland, USA
EDITORIAL
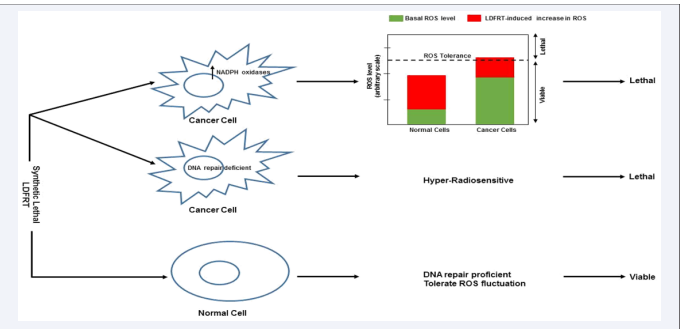
Synthetic lethality refers to the concept of combining two genetic perturbations that have no lethal potency on their own but lead to cell death when occurring in the same cell [1]. This principle has several potential benefits for cancer treatments since it can facilitate the targeting of cancer cells and consequently enhance the therapeutic ratio. This concept is best exemplified by the development of clinical trials aiming at treating breast cancer patients harboring mutations for the tumor suppressor BReast CAncer genes (BRCA1-2) with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors [1]. PARP1 is an enzyme required for efficient DNA single-strand break repair (SSBR)/base excision repair (BER). When PARP is impaired (inhibitors) this leads to accumulation of unrepaired SSB that are converted into DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) during replication. Because BRCA proteins are essential for DNA DSBs repairs by homologous recombination (HR), PARP inhibitors (PARPi) induce synthetic lethality in BRCA deficient cells. An obvious advantage of such a model is that the PARPi are not expected to affect normal cells harboring functional BRCA genes. This is a concept that is gaining momentum clinically but is still in needs of optimization since toxicity, although milder than the standard of care chemotherapies, is still significant and drug resistance often develops. Nonetheless, the concept of inducing synthetic lethality could also be expanded to modalities other than chemotherapies. For example it is well established that ionizing radiation can induce Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) [2]. Although ROS are pro-tumorigenic they are also toxic above a certain threshold level that could be exploited for therapeutic gain [3]. This is because normal cells have a robust capacity to tolerate a sizeable fluctuation in ROS levels due to their lower endogenous ROS levels and antioxidant capacity while relatively subtle increase in ROS level could readily reach toxic levels in cancer cells [3,4]. This vulnerability to ROS levels could thus be exploited to induce synthetic lethality in cancer cells (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Low Dose Fractionated Radiation (LDFRT) induces synthetic lethality in cancer cells. LDFRT can increase ROS production by up-regulating members of the NOX family of NADPH oxidases. Normal cells can tolerate sizeable fluctuations in ROS levels due to their lower endogenous ROS levels and antioxidant capacity. On the other hand relatively subtle increase in ROS level could readily reach toxic levels in cancer cells and lead to cell death. LDFRT could also induce synthetic lethality in DNA repair deficient cancer cells that are hyper-radiosensitive. Normal cells have functional DNA repair machinery and tolerate LDFRT and ROS fluctuation (see text for details).
For instance, we recently identified DualOxidase2 (DUOX2), an enzyme involved in the production of hydrogen peroxide, as a key mediator of human gastric cancer cells death in response to Low Dose Fractionated Radiation Therapy (LDFRT) [5]. In these cells, doses of radiation as low as 0.15 Gy, a dose more than ten times lower than the conventional 2 Gy per fraction, resulted in DUOX2 upregulation, ROS production and cancer cells death. Down regulation of DUOX2 abrogated this effect and LDFRT did not upregulate DUOX2 in normal cells [5]. LDFRT is a modality classically used as a chemosensitizer to allow full-dose drug therapy to improve efficacy without adding to the toxicity of the systemic treatment. In the setting of diseases that requires both local control as well as systemic dosing of chemotherapy, this offers the benefits of effective combined modality treatment that was hitherto considered not deliverable without additional toxicity associated with irradiating larger surface of disseminated disease with conventional radiation doses. Nonetheless, chemopotentiation by LDFRT has been met with varying degrees of success in different clinical settings due in part to a still poor understanding of the basic mechanisms underlying this effect. In vitro studies have established a link between Hyper-radiosensitivity (HRS) induced by LDFRT and evasion of the early G2/M cell cycle checkpoint. However, it has also been suggested that mechanisms other than a failure to arrest in early G2 can lead to HRS since some cells lacking the capacity to arrest in G2 following LDFRT are also negative for HRS [6]. In fact, as mentioned above, we have demonstrated that DUOX2 and ROS production are critical mediators of HRS in response to LDFRT in human gastric cancer cells. Still, DUOX2 is not expressed in all cancer cells and it is likely that other members of the NOX family of NADPH oxidases may be involved in a tissue specific manner. Based on these observations it seems reasonable to repurpose LDFRT to increase ROS beyond a tolerable level in cancer cells and induce synthetic lethality in these cells. In addition, LDFRT could also be repurpose to induce synthetic lethality in DNA repair deficient cancer cells that are HRS. For example, Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM) deficiency is associated with extreme radiosensitivity due to defective cell cycle checkpoints [7]. ATM is a serine/threonine kinase that underlies the symptoms associated with the Ataxia Telangiectasia syndrome. Germ line biallelic ATM mutations would however preclude any form of Radiation Therapy (RT) including LDFRT due to toxic effect on normal tissues. On the other hand, disease harboring ATM somatic mutations such as Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) [8] would be suitable to this approach of inducing synthetic lethality by LDFRT in ATM deficient MCL cells while sparing normal tissues. The concept of inducing synthetic lethality with LDFRT in cancers has not been exploited yet for therapeutic gain but could be applied to cancer cells expressing radiation responsive members of the NOX family of NADPH oxidases or to Hyper-radiosensitive cells harboring DNA repair deficiencies. It is expected that such an approach could improve the current therapeutic index and decrease adverse effects associated with existing therapies.
Citation
Carrier F (2018) Repurposing Low Dose Fractionated Radiation Therapy to Induce Synthetic Lethality. JSM Clin Oncol Res 6(1): 1060.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by a Veterans Affairs Merit Award (I01BX003437) from the United States Department of Veterans Affairs Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development Service and the National Institutes of Health (RO1CA177981-01).
US GOVERNMENT DISCLAIMER
The contents do not represent the views of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.