Separate Effects of Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, or Minocycline on Microorganisms from Deep Caries
- 1. Division of Endodontics, College of Dental Medicine, Columbia University, USA
- 2. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, USA
Abstract
The study was carried out to evaluate antibacterial susceptibility of bacteria from deep carious lesions to 3 different antibiotics Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, or Minocycline that were tested at concentrations (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8µmg/ml) by the disk diffusion method. Carious, infected dentin close to the pulp was collected from teeth with deep cavities and cultured in thioglycolate and brain heart infusion broths for 48hrs anaerobically and aerobically.
The infected broths were tested for adequate growth and colony forming units against the McFarland Turbidity standard. It was then spread onto Brucella and Brain Heart Infusion Agar plates. Disks with the different concentrations were then placed on the agar surfaces. Each concentration was tested nine times. The control group consisted of agar plates infected with broth but without antibiotics. All agar plates were then placed in anaerobic or aerobic environments. The plates were checked for zones of inhibition after 48 hrs. All control groups had bacterial growth. A zone of inhibition was seen for all Ciprofloxacin concentrations tested under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Metronidazole and Minocycline did not show any zones of inhibition. Ciprofloxacin shows promise as an antibacterial agent against bacteria from deep caries.
Citation
Jha D, Prateepchinda S, Lu HH, Hasselgren G (2021) Separate Effects of Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, or Minocycline on Microorganisms from Deep Caries. JSM Dent 9(1): 1136.
Keywords
- Caries bacteria
- Antibiotics
- Ciprofloxacin
- Metronidazole
- Minocycline
INTRODUCTION
Pulp regeneration makes it possible to restore the vitality of an immature tooth and also to obtain root growth and increased dentin formation [1-5]. In order for this treatment to be successful freedom from infection is a prerequisite [6]. The most common source of pulp disease is caries and the flora from deep carious lesions is poly-microbial in nature and predominantly anaerobic [7-9]. When regenerative procedures are planned it is therefore necessary to use antibiotics with a wide spectrum to make sure that no microorganisms remain even after caries excavation. A combination of three antibiotics - Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, and Minocycline – has been introduced by Hoshino and collaborators [10] to be effective against bacteria stemming from caries. The three antibiotics mixture has been used for pulp regeneration [11-16] and also in pediatric patients against endodontic infections [17]. Only one of the three antibiotics, Metronidazole, has been tested separately for its effect on bacteria from caries [18,19]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to test the effects of all three antibiotics Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, and Minocycline separately on microorganisms from deep caries under anaerobic and aerobic conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Information about commercial products used in the study is summarized below. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Carious dentin was collected from nine teeth with deep carious lesions in seven patients (4 female, 3 male) ages 25 to 72. When the caries excavation came very close to the pulp the cavity, surrounding tooth structure, rubber dam and slow speed hand piece were wiped with small gauze soaked in 5% sodium hypochlorite solution and a new sterile round bur replaced the old one in the hand piece. Carious dentin was collected from the flutes of the round bur after excavation of the deepest layer and transferred to Brain Heart Infusion and Thioglycolate broths. The mediums were incubated at 37º C in aerobic and anaerobic environments. After 48hrs the infected broths were used to infect fresh broths and also matched to the McFarland standard to approximate colony forming units. The infected broths were then plated on Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) or Brucella agar plates. Solutions of Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, or Minocycline were prepared at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8µgm/ml concentrations. The disk diffusion method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, PO Box 633 Annapolis Junction, MD 20701 USA) was used to test the three antibiotics at the five different concentrations. Sterile disks were dipped into the different antibiotics concentrations and placed on the infected BHI or Brucella agar plates. Each concentration was tested nine times. All BHI plates were incubated aerobically at 37ºC. Brucella plates were placed at 37ºC in anaerobic bags with indicators to ensure an anaerobic environment was achieved. Eight plates, four BHI and four Brucella, were kept as controls. These were infected with the caries bacteria and no antibiotic disks were placed on them. All plates were checked for a zone of inhibition after 48 hours. Statistical analysis: chi square test was used and the significance level was set at P<0.5.
List of commercial products used in the study.
Product Source
Brain Heart Infusion broth AS872 Anaerobe
Systems, Morgan Hill, CA
Thioglycolate broth AS801 Anaerobe
Systems, Morgan Hill, CA
Brain Heart Infusion agar plates AS6424, Anaerobe
Systems, Morgan Hill, CA
Brucella agar plates AS111, Anaerobe
Systems, Morgan Hill, CA
Sterile Disks Anaerobe Systems,
Morgan Hill, CA
McFarland standard 97298 MG Scientific,
Pleasant Prairie, WI
Anaerobic bio-bags type A BD Scientific, USA
Ciprofloxacin Fluka, Sigma-Aldrich,
Switzerland
Metronidazole Fluka, Sigma-Aldrich,
Switzerland
Minocycline Sigma-Aldrich, USA
RESULTS
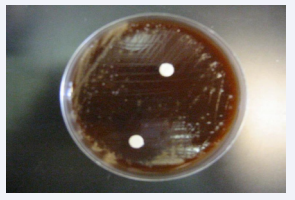
All control groups showed growth of bacteria. Ciprofloxacin showed zones of inhibition (Figure 1)
Figure 1 Ciprofloxacin 2µg/ml on brain heart infusion agar, clear zones of inhibition.
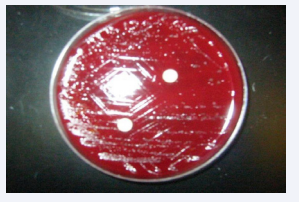
at all concentrations in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. Metronidazole (Figure 2)
Figure 2 Metronidazole 8µg/ml on brucella agar, no zone of inhibition seen.
and Minocycline did not show any zones of inhibition at any concentration in either aerobic or anaerobic environments. The differences in inhibition zones were found to be statistically significant P= 0.007.
DISCUSSION
The flora from deep carious lesions is poly-microbial and anaerobic bacteria dominate the flora [7-9]. Therefore it was considered relevant to expose the three antibiotics to the whole caries flora both aerobically and anaerobically. The disk test of antibiotics sensitivity was used as it is a standard test for evaluating antibacterial activity [20]. The finding of no zones of inhibition around the test disks with Metronidazole or Minocycline does not mean that these antibiotics had no effect. A poly-microbial culture, contrary to a single species culture, is affected in multiple ways depending on the different species involved. Some of the microorganisms may have been killed or inhibited, whereas other species were unaffected and could therefore grow close to the test disk. Minocycline is a semi synthetic derivative of tetracycline having a broad spectrum of activity against gram positive and negative bacteria [21,22]. In addition to being an antibiotic Minocycline has other properties [23] including a wide use as an anti-inflammatory agent [24]. It has also been found that Minocycline inhibits angiogenesis [25] which would make it a less desirable drug when the goal is to achieve pulp regeneration. Metronidazole - 5-nitroimidazole - is an antibiotic that is active against most Gram-negative and Grampositive anaerobic bacteria [26-28]. As deep caries contains mainly anaerobic microorganisms [9] Metronidazole would be expected to be effective against many caries bacteria. Earlier studies have found that metronidazole alone is efficient against caries bacteria both in vitro and in vivo [18,19]. The finding of this study that metronidazole did not eradicate all caries bacteria is likely to be caused by differences in testing techniques. Hoshino [19] enclosed Metronidazole in carious cavities which could add to the antibacterial effect of the antibiotic, whereas the present study used a disk diffusion method which does not have additional effects. Ciprofloxacin – fluoroquinolone - is a broad spectrum antibacterial agent. Most Gram-negative bacteria are highly susceptible to Ciprofloxacin, gram-positive bacteria are generally susceptible or moderately susceptible [29-31]. Ciprofloxacin showed clear zones of inhibition in both aerobic and anaerobic tests demonstrating that under the present conditions this antibiotic was capable of killing or suppressing the growth of all bacteria.
CONCLUSION
The results of the present study suggest that Ciprofloxacin alone can be the antibiotics of choice for eradication of bacteria from deep carious lesions.
REFERENCES
6. Law AS. Considerations for regeneration procedures. Pediatr Dent. 2013; 35: 141-152.
7. Edwardsson S. Bacteriological studies on deep areas of carious dentine. Odont Revy. 25: 32. 1974.
8. Hoshino E. Predominant obligate anaerobes in human carious dentin. J Dent Res. 1985; 64: 1195-1198.
9. Siqueira JF. Pulpal infections, including caries. Chapter 10 in Seltzer and Bender’s Dental Pulp 2nd ed. Eds Hargreaves KM, Goodis HE, Tay, FR. Quintessence 2012. 205-239.
12. Ding RY, Cheung GS, Chen J, Yin XZ, Wang QQ, Zhang CF. Pulp revascularization of immature teeth with apical periodontitis: a clinical study. J Endod. 2009; 35: 745-749.
26. Templeton R. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of metronidazole. A review. In: Metronidazole. ed 2. Proceedings of the International Metronidazole Conference, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam. 1977: 28-49.
27. Müller M. Mode of action metronidazole on anaerobic microorganisms. In: Metronidazole. ed 2. Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Anaerobic Infections. 1979, Royal Society of Medicine. Grune & Stratton, Inc, New York. 1979: 223-228.
28. Goldman P. Metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1980; 303: 1212-1218.