A Bubbly Nephron–Emphysematous Pyelonephritis A Case Report and Literature Review
- 1. Internal Medicine Resident, University of Connecticut, USA
- 2. Department of Nephrology, University of Connecticut, USA
Abstract
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a rare gas producing necrotizing infection of renal parenchyma, which overlooked can lead to a mortality rate as high as 80%. A 54-year-old female with a history of diabetes presented to the emergency department with dull left sided flank pain. She computed tomographic (CT) scan showed air in the renal collecting system in addition to an obstructing stone, confirming the diagnosis of EPN. She was admitted, received intravenous (IV) antibiotics, and underwent a procedure to place aureteralstent to help relieve the obstructing stone. She improved clinically and was able to be discharged home. EPN is most common in the diabetic and female populations. Most notably, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella and Proteus speciesare the most common bacteria found in blood and urinary cultures in these cases. Management depends on radiological staging of EPN by CT scan. Class 1 can be managed with antibiotics alone; classes 2 and 3 need percutaneous drainage in addition to antibiotics. High risk class 3 is indicated by the presence of thrombocytopenia, renal failure, altered mental status or shock on presentation in which case a nephrectomy could be required. Regardless of class, all patients with EPN and an obstructing stone should surgical intervention. Additionally, if the initial intervention fails, nephrectomy should be pursued given the high mortality of this disease. Diagnosis of EPN requires a high degree of suspicion. After diagnosis, patients should be monitored closely and managed with IV antibiotics as well as an individualized surgical approach, depending on radiological staging and risk factors.
Keywords
• Emphysematous pyelonephritis
• Acute pyelonephritis
• Surgical intervention
Citation
Gomes LK, Little E, Attique H, Trivedi R (2017) A Bubbly Nephron – Emphysematous Pyelonephritis, A Case Report and Literature Review. JSM Renal Med 2(1): 1011.
ABBREVIATIONS
EPN: Emphysematous Pyelonephritis; E. Coli: Escherechia Coli; BUN: Blood Urea Nitrogen; CT: Computed Tomography; PCD: Percutaneous Catheter Drainage
INTRODUCTION
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a rare gas producing necrotizing infection of renal parenchyma [1,2], which overlooked can lead to a mortality rate as high as 80% [3]. Early diagnosis and intervention can decrease mortality down to 19-43% [2]. As patients can present with vague and unspecific symptoms [3,4], a high degree of suspicion by the clinician is needed to lead to an early diagnosis and improved patient outcomes. Here, we present a case of emphysematous pyelonephritis followed by a comprehensive literature review of the topic.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 54-year-old female with a past medical history of diabetes mellitus type 2 and nephrolithiasis presented to the emergency department with a chief complaint of acute onset of dull left flank pain. It was associated with nausea, vomiting and severe malaise. During assessment, she denied any fevers, discharge or change in urine color but noted increased urinary frequency and sense of urinary urgency.
On initial assessment, the patient was afebrile and hypertensive at 163/91 mm Hg with a heart rate of 122 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 24 breaths per minute and saturating 100% on room air. On physical exam, it was noted that the patient appeared to be in mild distress with left costo-vertebral angle tenderness elicited on percussion. The remainder of physical exam was unremarkable.
Lab results were significant for a creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL (0.8 mg/dL at baseline) and BUN of 31 mg/dL. The remainder of the basic metabolic panel was within the normal range. Her white blood cell (WBC) count was elevated at 17.5 k/uL. A urine analysis was completed, which showed the presence of a large amount of blood, as well as being positive for nitrates and leukocyte esterase. In addition, the urine sample had more than 20 WBCs. Urinary pH was 5.5 with a specific gravity of 1.025. Urine and blood samples were sent for culture to complete an appropriate workup.
Due to her symptoms and previous medical history, a computed tomography (CT) scan of her abdomen and pelvis was obtained. A 5.6 x 3.3 mm stone was seen in her left ureter with associated hydronephrosis (Figure 1).
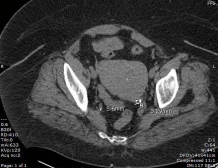
Figure 1 Stone present in the left ureter measuring 5.6 x 3.2mm.
Importantly, presence of air was described in the patient’s collecting system (Figures 2 and 3).
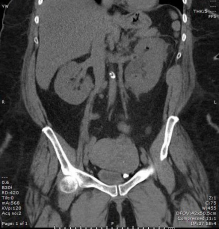
Figure 2 Air in the collecting system of the left kidney in the upper pole. Presence of hydronephrosis also seen.
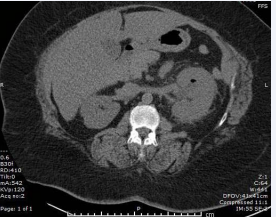
Figure 3 Presence of air in the upper pole of the left kidney by a coronal image
The patient was subsequently diagnosed with EPN related to an obstructing ureteral stone.
Urology was consulted and the patient was taken to the operating room for an emergent ureteral stent placement. As per recommendations given by the Infectious Disease department, the patient was started on Aztreonam 1g every 12 hours due to her history of an allergic reaction to penicillin. Pansenstitive E. Coli grew in the patient’s urinary culture, however her blood cultures remained sterile. During her hospitalization, the patient’s creatinine was monitored and it showed a marked improvement towards her baseline level prior to her discharge. The patient’s clinical picture improved with 3 days of IV antibiotic. Given her clinical improvement, the patient was discharged home to further complete an 11-day course of oral double-strength Bactrim twice a day.
DISCUSSION
Regarding its epidemiology, EPN is most commonly seen in diabetic patients [2] and has a female to male ratio of 6:1 [5], with the only exception being males that undergo renal transplantation [6]. Patients with diabetes are more likely to be affected since these patients have impaired immune responses, decreased tissue perfusion and elevated levels of blood glucose. This provides an optimal environment for fermenting bacteria to flourish, the most prevalent being gram negative bacteria – E. Coli, followed by Klebsiella sp and Proteus sp [4,7]. The fermentation of elevated glucose [2] in body tissues by these organisms leads to the gas formation characteristic of EPN. It has been observed that patients which present with EPN without a history of diabetes usually have an underlying urinary obstruction [8]. Women have a higher rate of all urinary tract infections [4] therefore it is not surprising that they have a higher rate of incidence for EPN.
On presentation, the history and physical exam findings can often be unspecific. Most patients will present with findings suggestive of pyelonephritis with fever (92% of cases), flank pain (88.5%) and costo-vertebral angle tenderness (76%). The findings of costo-vertebral angle crepitation upon palpation and pneumaturia are findings with higher specificity for EPN; nonetheless their presence is rare [9]. Consequently, the diagnosis can only be established after imaging has confirmed characteristic findings.
With the clinical presentation often being unspecific, it is quite common for EPN to be diagnosed after incidental findings on imaging. In cases where abdominal radiographs were the initial imaging choice, free air was observed in the renal parenchyma in up to 85% of cases [10]. However, this finding can also be present in other medical conditions including renal enteric or renal-cutaneous fistulas, post nephrostomy tube insertion, psoas abscesses or retroperitoneal perforation of the abdominal viscus. Therefore, further imaging is often needed to establish the diagnosis. CT scans are the preferred imaging study in this setting, as this modality will not only make a distinction between the aforementioned diagnoses, but will also aid in prognostication and determination of treatment.
Therapeutic management for EPN is currently guided by CT findings, which have been shown to correlate with clinical outcomes [2]. A summary of the classification system and recommended management can be viewed in Table 1.
Appropriate antibiotic choice is the cornerstone of treatment for EPN. A third generation cephalosporin is a good initial choice as they cover gram negative and anaerobic bacteria. Vancomycin should be added for coverage if a patient has undergone recent urogenital instrumentation. Carbapenem would be the antibiotic of choice for a patient who presents with EPN and has had either a recent hospitalization with antibiotic use or renal failure that required dialysis [11]. The choice of antibiotic use in our case was a reflection of these recommendations with consideration of the patient’s allergy profile. Urological evaluation should be sought in cases of EPN to confirm the presence of any urological obstructions requiring relief. Possible interventions include percutaneous catheter drainage (PCD) or nephrostomy [2,8].
For classes 1 and 3a/3b described in Table 1, there is uncertainty in the appropriate surgical management, consequently making the process of establishing the patient’s prognosis pivotal. To help determine the appropriate surgical management for class 3 cases, several studies attempted to delineate poor prognostic markers for EPN. Amongst these studies, a couple of markers are mentioned frequently, including thrombocytopenia [11], renal failure, acute kidney injury and need for renal replacement therapy, altered mental status and shock on presentation [12,13]. Our patient had one poor prognostic marker from her acute kidney injury. It is suggested that if the patient has 2 or more of these criteria, a nephrectomy would be part of the appropriate clinical management [2]. Interestingly in class 1 cases, such as our patient, if the choice is between treatment with antibiotics alone versus antibiotics and PCD, presence of hypoalbuminemia has been independently associated with antibiotic failure. Therefore, albumin levels should be checked in these cases and when low, supports the use of a combination of antibiotics with PCD for adequate treatment [12]. Our patient’s albumin levels were within normal limits. Independent of class, if PCD fails, nephrectomy is indicated due to the risk of a fulminant course of EPN characterized by necrosis, microabscess formation and possible intravascular thrombosis. In summary, early nephrectomy should be pursued if the patient has EPN class 3 and poor prognostic markers. In a situation where a patient has failed treatment with PCD, a late nephrostomy is then indicated for salvage therapy.
When PCD is the management of choice, a repeat CT scan in 1 week after the procedure is indicated to ensure resolution of infection and to assess complications such as renal scarring. Imaging should be done sooner if a patient continues to clinically deteriorate despite treatment. No further imaging is required in cases where a patient has been successfully managed [14].
The diagnosis of EPN requires a high degree of suspicion due to the often vague presenting symptoms. In patients, who are diabetic females that present with symptoms suggestive of pyelonephritis, EPN should be included in the clinician’s list of differential diagnosis. After the appropriate imaging has been obtained and a diagnosed of EPN has been established, all patients should be started on IV antibiotics. In cases with urogenital obstruction, further interventions will be needed. The surgical approach should be individualized to each patient taking into consideration their imaging classification and presence of poor prognostic markers. Through early diagnosis and tailored intervention, renal preservation and lower mortality rates can be achieved.








































































































































