How Gartner’s Duct Cyst Affects Women’s Sexuality: A Case Report
- 1. Department of Gynecology-Obstetrics and Endocrinology, University Hospital Center IBN SINA, Morocco
- 2. Department of Gynecology-Obstetrics and Endoscopy, University Hospital Center IBN SINA, Morocco
Abstract
Background: Gartner’s duct cyst is a relatively common benign cystic lesion, not exceeding 2 cm in diameter and frequently located in the vaginal wall. It arises from the incomplete involution of the mesonephric remnants of Wolff’s ducts. They are usually asymptomatic and often noticed incidentally on routine gynecologic examination or on imaging tests; however, larger cysts are a rare situation that can cause mass effects on adjacent pelvic structures and may produce symptoms such as dysuria, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, protrusion from the vagina masquerading as uterovaginal prolapse. Standard treatment protocol remains undetermined; options ranging from conservative approach (needle aspiration, expectant care) to radical management (surgical excision, marsupialization).
Case Presentation: We hereby report an uncommon case of a 32-year-old patient who presented in our outpatient department with complaint of pelvic organ prolapse and dyspareunia. Examination revealed a non-reducible cyst-like mass of approximately 6 cm at the expense of the posterior vaginal wall. Transvaginal excision was done and confirmed as Gartner’s cyst in histopathological examination.
Conclusions: Large Gartner’s cysts are a relatively rare entity that can significantly affect patient’s quality of life. The protocol for diagnosis and management of these lesions is still unclear; however, symptomatic cysts may require surgical treatment, usually with excellent outcome. Dyspareunia is a warning sign which must be taken seriously by all practitioners and which requires gynecological and often psychological management.
Keywords
Gartner duct cyst; Vaginal cyst; Dyspareunia
ABBREVIATIONS
GDC: Gartner’s Duct Cysts; MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Citation
SLAOUI A, LOUZALI FZ, ZERAIDI N, LAKHDAR A, BAYDADA A, et al. (2022) How Gartner’s Duct Cyst Affects Women’s Sexuality: A Case Report. JSM Sexual Med 6(1): 1081.
BACKGROUND
Discovered in 1822 by Hermann Treschow Gärtner [1], a Danish surgeon and anatomist, Gartner’s duct cyst is a relatively common benign tumor of the vagina arising from a persistent embryological remnant of Wolff’s duct. In the male embryo, Wolff’s ducts are destined to become the paired epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, and seminal vesicles. In the female embryo, its normal evolution is to disappear completely. However, in some cases, it may persist as small, asymptomatic cysts running along the old course of the duct in the vaginal wall [2,3]. These cysts are located with predilection at the level of the anterolateral wall of the vagina [4]. They present as a small (< 3 cm), fluctuating, painless and non-reducible cyst-like mass and are diagnosed by physical examination [5].
Our goal is to explore the clinical features, diagnosis, and management of Gartner’s gland cyst. For this purpose, we report the case of a 32-year-old woman who presented a large cystic mass arising from the posterior vaginal wall which was mimicking a pelvic organ prolapse, but appropriate clinical evaluation supported with investigations clinched the diagnosis of Gartner’s gland cyst that was successfully treated by surgical excision.
CASE REPORT
We hereby report the case of a 32-year-old nulliparous woman, with no history of either vaginal trauma or surgery and no significant past gynecologic or urologic history, who was referred to the gynecological outpatient department at our institution for pelvic organ prolapse and dyspareunia. She reported no fever, abnormal vaginal discharge or urinary tract symptoms. The patient was always afraid to explore her sexuality with her partner and this disease was a real obstacle to her personal development.
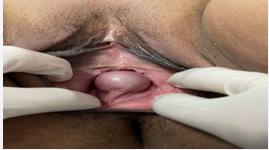
Figure 1: Photography of a large Gartner’s duct Cyst.
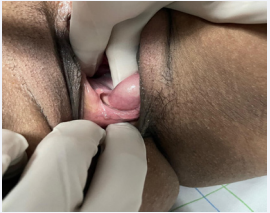
General, physical, and systemic examinations were unremarkable. Per vaginal examination revealed a smooth, nontender, mobile cystic-appearing mass, painless to manipulation, of 6 cm in the longest diameter, pedunculated in the midline of the posterior wall of the vagina (Figures 1,2). There was no evidence of pelvic-organ prolapse. On per rectal examination, uterus felt normal sized, non-tender, mobile with both fornices free. The rest of the genitourinary system was without notable abnormalities. Her laboratory routine investigations were within normal limits and urinalysis and pregnancy tests were negative. Transvaginal and pelvic ultrasonography showed a large, welldefined, anechoic fluid filled cyst of 6x5x4 cm that was distinct from the uterus, without intra-cystic solid component and devoid of its own vasculature, originating from the distal one third of the posterior vaginal wall along the midline and extending to the introitus. The diagnosis of a large Gartner’s cyst was retained. Ultrasound of the urinary tract in search of associated abnormalities was normal.
Figure 1: Photography of the same Gartner’s duct Cyst showing his posterior implantation.
Considering the size of the lesion and its symptomatic nature, surgical excision was recommended via a vaginal approach, under spinal anesthesia. A transverse incision was made around the cyst carefully avoiding rupture; the cyst was then dissected sharply and bluntly apart from the posterior vaginal wall. Base of the cyst was clamped, cut and ligated. Excess vaginal tissue was trimmed and vaginal mucosa was sutured using 2-0 Vicryl with multiple interrupted stitches. The microscopic evaluation of the drained fluid was normal and no bacterium was detected on culture. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of Gartner’s duct cyst with cuboidal epithelial lining.
The postoperative course was uneventful. After the surgical resection, the clinical problems resolved. She was feeling much better about herself and we found out that she was expecting her first child. No recurrence was observed within 1 year follow-up.
DISCUSSION
The reproductive duct systems remain sexually indifferent until 7 weeks of gestation [6]. Two pairs of genital ducts are present at this time: the mesonephric (Wolffian) duct and paramesonephric (Mullerian) duct [6,7]. The absence of antiMullerian hormone (AMH) and SRY gene in females conditions the regression of Wolff ducts and further differentiation of Mullerian ducts [6-8]. If the Wolffian ducts persist in vestigial form, they can lead to Gartner’s cysts [6-8]. Remnants of the Gartner duct may be detected in up to one fourth of adult women, whilst Gartner’s cysts arise only in approximately 1%–2% of the population [8].
Most often discovered incidentally during a routine gynecological examination or iconographic exploration (ultrasound or MRI), their size generally does not exceed 2cm. However, as these cysts are closed structures, they may increase in size due to mucus production and thus be responsible for functional signs such as dyspareunia, dysuria, pelvic heaviness, vaginal discharge, a mass effect on the adjacent anatomical structures and recurrent episodes of urinary retention [7,9]. These lesions are classically located in the antero-lateral wall of the proximal one-third of the vagina, although they have exceptionally been described in a posterior location [4, 9]. Gartner duct cysts are most often isolated findings, but can also be associated with the metanephric urinary system abnormalities such as ectopic ureter and ipsilateral kidney hypoplasia [10]. In the case reported here, other concomitant genitourinary malformations were investigated and ruled out.
The differential diagnosis could include Bartholin’s gland cyst (vestibular gland), urogenital prolapse (cystocele, rectocele, elytrocele), urethral diverticulum, epidermoid inclusion vaginal cysts (which are post-traumatic: operative, sequelae of episiotomy), endometriosis and malignant growth among others [10-12]. Imaging by ultrasound or MRI is essential to characterize the cyst, identify its exact location and to clarify the anatomical relationship with the neighboring organs [13,14]. In our case, we carried out a transvaginal and abdominal ultrasound that identified a well-defined, avascular, single cystic mass, sonolucent fluid filled, of approximately 6 cm, independent from bowel or bladder (cystocele or enterocele excluded).
Confirmation is by histopathological examination, revealing cellular remnants composed of non-mucin secreting low columnar and cuboidal epithelium [15]. Most GDC are benign. However, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out a malignant degeneration, especially if the mass appears to be solid. Only in exceptionally rare and isolated cases has there been a malignant transformation identified [13].
Very little information is available in the literature regarding management of Gartner’s gland cysts. Different therapeutic options are possible [13-16]. Their management is a controversial topic because of their benign nature and the chance of spontaneous regression. However, surgical intervention is indicated mainly in symptomatic cases [3-5]. Conservative management may include a simple needle aspiration or waiting for a spontaneous rupture. This approach is advisable in asymptomatic cases only [15]. Surgical management involves surgical excision and ablation, incision and drainage or marsupialization [15]. The few rare cases reported in the literature suggest that surgical treatment is the preferred method for symptomatic cysts [13,15]. In a study involving 15 patients by Abd-Rabbo et al. [16], aspiration and injection sclerotherapy with 5% Tetracycline has been reported as being an ideal, safe and effective simple office procedure for management of symptomatic Gartner cysts with good results and no side effects. Given the size of the lesion presented in our case and its symptomatic nature, expectant management was not appropriate and surgical excision was considered to be the adequate treatment. The postoperative course was uneventful and no complication was observed. Moreover, histopathological findings were consisted with the presumptive clinical and surgical diagnosis with typical benign cells appearances.
We have not found any articles in the literature that link Gartner’s cyst to a deterioration of the patient’s sexuality. Often responsible for dyspareunia, women who suffer from it do not feel that this symptom is important enough to consult a specialist. This diagnostic delay is consistent with the literature [17]. Particularly in our context, patients do not come to the clinic until there is a greater impact on their quality of life. As for our patient who consulted two years after the onset of dyspareunia. It was only when she thought she had pelvic organ prolapse that she consulted a doctor. Dyspareunia is unfortunately often ranked below the other symptoms and patients do not feel the urgency to be treated [17]. However, all practitioners should be reminded that it is a symptom that affects quality of life, self-image and often personal fulfilment. Case reports such as this one help to highlight that this is not a symptom to be taken lightly, on the contrary.
CONCLUSIONS
Large Gartner’s cysts are a relatively rare entity that can significantly affect patient’s quality of life. The protocol for diagnosis and management of these lesions is still unclear; however, symptomatic cysts may require surgical treatment, usually with excellent outcome. Dyspareunia is a warning sign which must be taken seriously by all practitioners and which requires gynecological and often psychological management.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editorin-Chief of this journal.
REFERENCES
8. Rios SS, Pereira LC, Santos CB, Chen AC, de Fatima B, Vogt M. Conservative treatment and follow-up of vaginal Gartner’s duct cysts: a case series. J Med Case Rep. 2016; 10: 147.
10.Hoogendam JP, Smink M). “Le kyste du conduit de Gartner”. Le Journal de médecine de la Nouvelle-Angleterre. 2017; 376: e27.
11.Tiwari C, Shah H, Desale J, Waghmare M. Kyste néonatal de conduit de Gartner: Deux rapports de cas et revue de littérature”. Médecine de la période de développement. 2017; 21: 35-37.
13.Baggish MS. Atlas of pelvic anatomy and gynecologic surgery. Fourth ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016.
17. Lee NMW, Jakes AD, Lloyd J, Frodsham LCG. Dyspareunia. BMJ. 2018.