Association between Anti Topoisomerase I and Esophageal Dysmotility in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis
- 1. University of Calgary, Canada
- 2. University of Alberta, Canada
- 3. Peak Medical Speciality Center, Canada
Abstract
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation and fibrosis of visceral organs with significant morbidity and mortality. In SSc, the association between anti-topoisomerase/Scl70 (ATA) antibodies and esophageal dysmotility remains controversial given conflicting evidence from prior works. Our retrospective study of 32 patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) aims to contribute to the body of work clarifying this relationship. Patients underwent high resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) and serum autoantibody testing (ATA, RNA polymerase III (RP11/RP155), Ro52/TRIM21) within 3 months of HRM, with motility classified as per the Chicago Classification v3. Patients were characterized into “unmeasurable motility” (absent contractility) and “measurable motility” (normal or ineffective esophageal motility. Our results demonstrated 15 (47%) patients with unmeasurable and 17 (53%) with measurable motility respectively. Those with unmeasurable motility had higher ATA levels (p=0.046), with the only two patients with normal motility having undetectable ATA levels. No significant motility differences were seen with anti-RP11, RP155 or Ro52. Unlike previous works, our work included only patients with dsSSc reducing the effect of disease subtype on results and excluded structural dysphagia through concurrent esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Our work was limited by small sample sizes and semi-qualitative assays, however adds to the growing literature suggesting an association between higher ATA level and esophageal dysmotility.
Keywords
• Autoantibodies
• Systemic Sclerosis
Citation
Levin D, Choi M, Woo M, Durand C, Li D, et al. (2025) Association between Anti-Topoisomerase I and Esophageal Dysmotility in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. J Autoimmun Res 6(1): 1032.
BRIEF REPORT
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multi-system autoimmune disorder characterized by vasculopathy, inflammation and fibrosis of visceral organs resulting in significant morbidity and mortality [1]. While the exact pathogenesis of SSc is unknown, auto-antibodies have been postulated to play a role. Antibodies against topoisomerase I (ATA, Scl70), detected in 9-71% SSc patients and fewer than 1% non-SSc patients [2], are associated with the diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc). The link between ATA and esophageal dysmotility is controversial; with some studies showing increased esophageal retention on manometry [3], and lower esophageal sphincter pressures [4], while others have not found differences in either manometry [5], or scintigraphy [6]. Instead, disease subtype (dcSSC in particular) was postulated to play a greater role in dysphagia. Our work contributes to solving this uncertainty by demonstrating an association between ATA and severe esophageal dysmotility. This was a retrospective, single center (Calgary, AB, Canada) study of patients who underwent high resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) and had serum tested for autoantibody levels (concentrations) within 3 months of HRM. Sera were tested for SSc-related autoantibodies including ATA, -RNA polymerase III (RP11 and RP155) and -Ro52/TRIM21 by Euroline SSc profile line immunoassay (LIA) (Euroimmun GmbH, Luebeck, Germany) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Only ATA, RP11, RP155 and Ro52 were included due to other antibodies tested being positive in less than 3 patients. High resolution esophageal manometry was performed in the upright position, and was performed within 3 months of autoantibody analysis. Manometric data were analyzed using Manoview Analysis Software version 3.0 (Medtronic). Esophageal contractile vigor was evaluated by the distal contractile integral (DCI). As per Chicago Classification version 3.0 [7], an effective swallow was defined as DCI between 450 and 8000 mmHg. cm.sec, a weak swallow as 100 to 450 mmHg.cm.sec, and a failed swallow as 50% effective swallows. Patients with absent contractility are considered to have “unmeasurable motility” whereas patients with IEM or normal motility had “measurable motility”. Mann-Whitney rank-sum test was used to compare autoantibody levels between the patients with unmeasurable vs measurable motility. A two-tailed p value of <0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism (California, USA). The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was approved by the University of Calgary Conjoint Research Ethics Board (REB16-2461). All patients provided written consent. The research was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964.
Patient characteristics are given in Table 1. Of the 32.
Table 1: Patient Characteristics.
|
|
All patients (n=32) |
Patients with Unmeasurable Motility (n=15) |
Patients with Measurable Motility (n=17) |
P-Value*** |
|
Age at HCT in years, median (range) |
53 (28 – 64) |
46 (28 – 63) |
54 (33 – 64) |
0.634 |
|
Female, n (%) |
21 (66%) |
9 (60%) |
12 (71%) |
0.529 |
|
SSc Duration in months (from first non-Raynaud’s symptom), median (range) |
22 (5 – 50) |
23 (11 – 42) |
21 (5 – 50) |
0.621 |
|
Main SSc Manifestations* |
|
|
|
|
|
Skin tightness, n (%) |
32 (100%) |
15 (100%) |
17 (100%) |
N/A |
|
Interstitial lung dis., n (%) |
22 (69%) |
12 (80%) |
10 (59%) |
0.265 |
|
Neuropathy, n (%) |
8 (25%) |
2 (13%) |
6 (35%) |
0.229 |
|
Myositis, n (%) |
3 (9%) |
2 (13%) |
1 (6%) |
0.589 |
|
Modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS), median (range) |
28 (11 – 47) |
25 (13 – 42) |
30 (11 – 47) |
0.316 |
|
FVC (% predicted), median (range) |
80 (56 – 124) |
76 (56 – 109) |
84 (57 – 124) |
0.496 |
|
DLCO (mL/min/mmHg), median (range) |
20.0 (9.8 – 30.9) |
17.6 (10.7 – 30.9) |
21.2 (9.9 – 27.5) |
0.493 |
|
Reflux Esophagitis per EGD, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
None |
22 (69%) |
9 (60%) |
13 (76%) |
0.450 |
|
Mild (LA grade A or B) |
2 (6%) |
0 (0%) |
2 (12%) |
0.486 |
|
Severe (LA grade C or D) |
8 (25%) |
6 (40%) |
2 (12%) |
0.106 |
|
Medications**, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Corticosteroids |
14 (44%) |
5 (33%) |
9 (53%) |
0.143 |
|
Mycophenolate Mofetil |
21 (66%) |
11 (73%) |
10 (59%) |
0.472 |
|
Methotrexate |
23 (72%) |
12 (80%) |
11 (65%) |
0.444 |
|
Hydroxychloroquine |
9 (28%) |
1 (7%) |
8 (47%) |
0.018**** |
|
Proton Pump Inhibitor |
30 (94%) |
14 (93%) |
16 (94%) |
>0.999 |
|
Domperidone |
3 (9%) |
1 (7%) |
2 (12%) |
>0.999 |
|
H2 Blocker |
1 (3%) |
1 (7%) |
0 (0%) |
0.469 |
* Aside from esophageal involvement.
** At the time of manometry for proton pump inhibitor, domperidone, and H2 blocker. At any time between SSc diagnosis and the manometry for corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine.
*** Statistical significance was determined via Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables. Chi-square test was used if the number of patients in every subgroup was 5 or greater, otherwise Fisher exact test was used.
**** To our knowledge, no association between increased HCQ use in SSc and esophageal dysmotility has been reported in the literature. Also, there is no strong evidence for its use in treating esophageal dysmotility (McMahan ZH et al. Systemic sclerosis gastrointestinal dysmotility: risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2023, Mar;19:166).
Abbreviations: HCT = hematopoietic cell transplantation, SSc = systemic sclerosis, ILD = interstitial lung disease, FVC = forced vital capacity, LA grade = Los Angeles grade, PDE5 = Phosphodiesterase-5, H2 = histamine receptor 2.
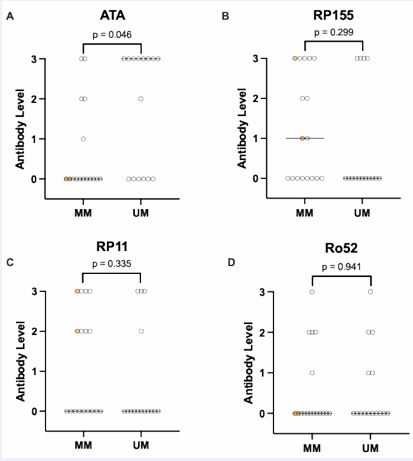
patients evaluated, 15 (47%) had “unmeasurable motility” and 17 (53%) had “measurable motility”. The latter group consisted of 15 patients with IEM and 2 patients with normal motility. The patients with unmeasurable motility had higher ATA levels compared to patients with measurable motility (high positive vs. undetectable, p = 0.046, Figure 1). The two patients with normal motility had undetectable ATA. The levels of RP11, RP155, and Ro52 did not significantly differ between the patients with unmeasurable and measurable motility (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Comparison of serum levels of scleroderma panel antibodies between patients with measurable motility (MM) and unmeasurable motility (UM). A semiquantitative scale was used for the antibody levels, i.e., 0 (negative), 1 (weak positive), 2 (medium positive), and 3 (high positive). Median antibody level is denoted by a horizonal line. The circles highlighted in yellow denote patients with normal motility.
A total 3 studies have reported on the association between ATA and abnormal esophageal manometry [3,4] or video/fluoroscopy [8]. In all three studies, cohorts included patients with dcSSc and lcSSc, with dsSSc patients representing either a minority [3,4] or not explicitly defined [8]. Given this, findings attributed to the presence of ATA may have been associated with the dsSSc phenotype which has more severe esophageal involvement [6]. The manometry results in both the Stacher and Roman studies were not classified via the Chicago Classification, which is the current reference standard for the classification of esophageal motility disorders [7]. In contrast, our entire cohort was made up of dsSSc patients, used the Chicago Classification v3, and had esophagogastroduodenoscopies completed within 3 months of manometry to further exclude structural dysphagia.
Patients in the Hara study [8], were on average older and coupled with a trend towards younger age in our patients with unmeasurable motility suggests our findings were less likely confounded by age-associated dysmotility. Previous studies demonstrated median disease duration from 5-10 years [3-8] vs. the shorter duration seen in our cohort (22 months). This was not impacted by measurable vs. unmeasurable motility, reducing the impact of progressive fibrotic disease unrelated to the presence of ATA itself. Our cohort also had similar numbers of patients on proton pump inhibitor therapy between those with measurable vs. unmeasurable motility. Interestingly, there were 6 patients with unmeasurable motility in our cohort who had undetectable ATA, suggesting it may not be necessary in the development of severe dysmotility. Alternatively, other ATA-independent mechanisms may promote esophageal dysmotility.Our work has a few limitations. First, despite our large data set of patients with dcSSc (n=32), it is too small for meaningful multivariate analysis taking into consideration patient age, skin tightness severity or other factors. Second, we did not have the ideal control group of dcSSc patients without esophageal dysmotility, as such patients are rare. Nevertheless, it is reassuring that 2 patients without detectable ATA did not have esophageal dysmotility. Finally, the autoantibody assay employed was semi qualitative, potentially obscuring statistical differences. Barring these limitations, our study suggests that ATA is associated with severe esophageal dysmotility specifically in patients with dcSSc.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are grateful to Mei-Feng Zhang and Jean Kawasoe for expert technical assistance.
REFERENCES
- Thoreau B, Chaigne B, Mouthon L. Role of B-Cell in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2022; 13: 933468.
- Spencer-Green G, Alter D, Welch HG. Test Performance in SystemicSclerosis: Anti-Centromere and Anti-Scl-70 Antibodies. Am J Med. 1997; 103: 242-248.
- Roman S, Hot A, Fabien N, Cordier JF, Miossec P, Ninet J, et al. Esophageal dysmotility associated with systemic sclerosis: a high- resolution manometry study. Dis Esophagus. 2011; 24: 299-304.
- Stacher G, Merio R, Budka C, Schneider C, Smolen J, Tappeiner G. Cardiovascular autonomic function, autoantibodies, and esophageal motor activity in patients with systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27: 692-697.
- Karamanolis GP, Denaxas K, Panopoulos S, Bournia KV, Zorbala A, Kamberoglou D, et al. Severe oesophageal disease and itsassociations with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017; 35: 82-85.
- Vischio J, Saeed F, Karimeddini M, Mubashir A, Feinn R, Caldito G, et al. Progression of esophageal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2012; 39: 986-991.
- Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, et al. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015; 27: 160-174.
- Hara M, Ueha R, Sato T, Goto T, Yoshizaki A, Sumida H, et al. Clinical Risk Factors for Dysphagia and Esophageal Dysmotility in Systemic Sclerosis. J Clin Med. 2023; 12: 3448.