Clinical Evidences from Ultrasound
- 1. Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Torino, Italy
- 2. Department of Neuroscience, University of Torino, Italy
Abstract
Following preliminary in-vitro evidences for the ability of hyperoxygenated saline in promoting wound healing and in-vivo evidence for the effectiveness in increasing wound oxygenation, we propose a therapeutic approach for Critical Limb Ischemia. Our small sample of patients showed a good compliance for the procedure and their lesions beneficed from the treatment both immediately and at 3 months follow up.
Keywords
• Chronic wounds
• Sonication
• HHMEC-1
• Vascular ulcers
Citation
Varetto G, Trucco A, Prato M, Rispoli, Gibello L, et al. (2017) Clinical Evidences from Ultrasound –Mediated Oxygen Delivery to Lower Extremity Wounds. J Chronic Dis Manag 2(1): 1009.
INTRODUCTION
The age-related and/or specific pathologies related (eg. diabetes, prolonged recumbency, etc.) deterioration of the blood perfusion to the distal parts of the limbs implies a state of reduced oxygenation predisposing the formation of chronic leg ulcer and Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI), which are difficult to be clinically managed especially in the long-term treatment in home care.
As shown by various authors, the healing times are rather long, reaching up to one year in about 50% of all patients [1-3].
S. Covington published in 2012 that sonication of hyperoxygenated saline to patients affected by CLI was able to significantly increase wound oxygen level and could be a valuable therapeutic option for CLI as safer and cheaper alternative to hyperbaric oxygen treatment [4].
Hyperoxigenated saline (OSS) have a good oxygen-storing capacity of 40 mg/l of oxygen either before or after 20-min UV-C sterilization, and proved to be stable over time when stored at 4°C, as confirmed by long-term checking of oxygen content [5,6].
Due to the critical issue of the poor solubility of oxygen in water at atmospheric pressure, and of its tendency to diffuse into air, before and during delivery OSS should be contained within a closed receptacle.
Moreover, in order to avoid any possible adverse effect due to the direct administration of OSS on open wounds, delivery in the proximity of the ulceration would be strongly preferred, but penetration should be enhanced e.g. via Ultrasound (US) sonication [7,8].
Both problems could be addresses by the use of a patch connected to the US probe able to carry OSS for the time of the delivery. Such systems, operating at proper frequency and power for optimizing transdermal penetration are already on the market [9].
We performed some preliminary studies of the OSS effectiveness on an in-vitro wound healing assay of long-term cell line of dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) immortalized by SV 40 large T antigen [10], kindly provided by the Center for Disease Control, Atlanta, GA and cultured as described in a recent paper [11].
HMEC-1 cells were plated in each chamber of Ibidi’s culture inserts with cell growth medium and, after 24 h, culture inserts were detached resulting in two confluent monolayers, divided by a space (scratch) of 500 µm. Thereafter, cells were washed with PBS and incubated in fresh medium for 8 h in the presence or absence of 10% v/v OSS, either in normoxic (20% O2 ) or hypoxic (1% O2 ) conditions.
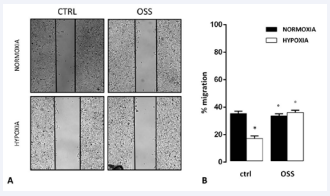
As shown in Figure (1), hypoxic HMEC-1 displayed a lower ability to migrate compared to normoxic cells.
Figure 1: Effects of hypoxia and OSS on migration and wound healing abilities of human microvascular dermal endothelial cells.
However, the migration ability of hypoxic HMEC-1 was significantly increased in the presence of OSS, suggesting a peculiar role for oxygen in promoting HMEC-1 migration and wound healing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In order to assess the clinical advantages of the above therapy, the absence of adverse side effects and its feasibility in home care regime, our team treated a limited group of patients affected by ulcers that were unlikely to heal by delivering sterilized OSS inserted into Wound Shield Patches for instillation therapy and connected with an ultrasound device designed for sonophoretic administration (Wound Shield, Nanovibronix Ltd, Israel). To prevent oxygen diffusion into the air, OSS is contained in a plastic bag enclosed into the patch that is almost impermeable towards the outside but diffusible towards the patient’s skin.
Our endpoints were the following:
- To assess whether the therapy is well tolerated and safe
- To work out a therapeutic protocol
- To define a procedure for evaluating short and long term effectiveness
RESULTS
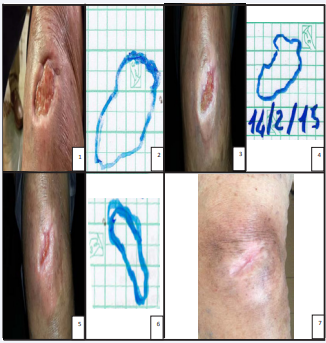
4 patients underwent 6 treatment sessions within 2 weeks. Lesions were evaluated before and after treatment and every month for at least 3 months later treatment according to Push Tool 3.0 [12], and EPUAP scales, cartographic assessment see Figure (2), and patient-reported pain symptoms [13,14].
Figure 2: A: representative images. B: means ± SEM of scratch lengts. Results are from three independent experiments performed in duplicates. Data were also evaluated for significance by ANOVA: *vs normoxic untreated cells: p< 0.001; °vs hypoxic untreated cells: p< 0.001.
Ulcers showed an average improvement of 1.5 points on the scale Push Tools 3.0 after two weeks and 3 points after a month, with a reduction in size of the lesions. Some patients also reported a reduction in pain see Table (1).
|
Table 1: Data about the reduction in surface extent of the lesion and in PUSH and VAS scales. |
|||||||
|
Patient |
Time of Insurgence (months) |
After treatment |
At 3 months |
||||
|
Surface red |
PUSH red |
VAS red |
Surface red |
PUSH red |
VAS red |
||
|
1 |
5 |
- |
- |
-4 |
65% |
- 2 |
- 4 |
|
2 |
4 |
81% |
-2 |
- |
93% |
-4 |
- |
|
3 |
24 |
- |
-1 |
- |
- |
-1 |
- |
|
4 |
4 |
- |
- |
-2 |
- |
- |
-2 |
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
Leading studies have shown in recent years the best outcomes of ulcer healing with combined therapies that promote tissue oxygenation, endothelial function and reduce the adverse consequences resulting by insufficient arterial-venous circulation [15-17].
The decrease of oxygen in the limbs of patients affected by CLI is a severe problem for the survival of the limb and makes necessary timely revascularization procedures [18].
In a significant number of cases, unfortunately, there are more treatment options or interventional care in case of failure or worsening of the disease.
The only use of local dressings finally does not allow a healing progress especially in conditions of infection or significant involvement of the fibrin-necrotic ulcer bed.
The procedure which combines the delivery of OSS and the ultrasound treatment has been well tolerated by patients, who did not report particular disorders or trouble [7,8]. Although the assessment of clinical effectiveness would require a much larger sample, our preliminary results are quite encouraging and complement the important findings of Covington et al. [4].
Such results encourage further advancements in oxygen delivery in CLI. In particular, preliminary in-vitro and in-vivo studies suggest that OSS could be substituted by Oxygen-loaded nanobubbles [5,6], which would be more effective since:
- Sonophoresis would be optimized by the gaseous nature of the oxygen carrier;
- Oxygen delivery would be sustained (up to 4-6 hours) instead of lasting only for the administration time
- Natural biopolymers for the nanobubbles coating could be selected (e.g. chitosan) in order to exert a bacteriostatic and antimicrobic effect.