A Proposed Clinical Grading System to Define Impaired Organ Function and Quality Of Life in Patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Disease in Japan
- 17. Department Ophthalmology, Saitama Medical University International Medical Center, Japan
- 16. Department of Life Science, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Kinki University, Japan
- 15. Laboratory for Malignancy Control Research, Medical Innovation Center, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 14. Department of Pediatrics, Keio University School of Medicine, Japan
- 13. Department of Ophthalmology, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 12. Department of Medicine and Bioreguratory Science, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Japan
- 11. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Tokyo Hospital, Japan
- 10. Department of Neurosurgery, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 9. Department of Neurosurgery, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 8. Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Kumamoto University, Japan.
- 7. Departments of Neuro-Oncology/Neurosurgery, Saitama Medical University International Medical Center, Japan
- 6. Departments of Renal and Genitourinary Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 5. Department of Urology and Molecular Genetics, Yokohama City University School of Medicine, Japan
- 4. Department of Neurosurgery, Yokohama City University School of Medicine, Japan
- 3. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kochi Medical School, Japan
- 2. Department of Ophthalmology, Kochi Medical School, Japan
- 1. Department of Urology, Kochi Medical School, Japan
Abstract
Patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease develop tumors and cysts in the central nervous system (CNS), retina, adrenal gland, kidney and pancreas. These tumors or cysts always require surgical treatment and cause different degrees of impairment in the affected organs. We developed a clinical grading system to evaluate impaired organ function and the quality of life (QOL) of VHL patients. Based on a previous grading system of intractable disease, impaired organ function is divided into five grades (grades 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 for five affected organs) with QOL taken into consideration. The patient’s worst grade was regarded as their final clinical grade. The clinical grading of 46 patients was determined by a questionnaire. Our results showed that proportions of patients with grades 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 were 0% (0), 9% (2), 28% (15), 24% (12), 37% (17), respectively. If patients with two grade 3-affected organs are regarded as finally grade 4, then 46% of patients had grade 4. These results suggest that the organ function of approximately 50% of VHL patients is severely affected. Our study showed that our clinical grading system of VHL disease is relatively easy to use, and reflects the severity and QOL of VHL patients. The use of this system aids the provision of medical care and financial support from the Japanese health care system to VHL patients with severe impairment.
Keywords
• VHL
• Organ function
• QOL
• Clinical grading system
Citation
Shuin T, Yamasaki I, Fukushima A, Nishimori I, Kanno H, et al. (2014) A Proposed Clinical Grading System to Define Impaired Organ Function and Quality Of Life in Patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Disease in Japan. J Transl Med Epidemiol 2(1): 1018.
ABBREVIATIONS
VHL: von Hippel-Lindau disease.
INTRODUCTION
von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant inherited condition. Patients with VHL develop central nervous system (CNS) and retinal hemangioblastomas, pheochromocytomas, renal cell carcinomas or cysts, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors or cysts, which may occur from childhood to advanced age. These tumors or cysts result in various clinical problems in the affected organs and may require multiple surgeries, causing organ impairment. Thus, VHL is a serious disease that disturbs the quality of life (QOL) of patients. Our epidemiological survey showed that there are more than 400 affected patients in Japan [1]. The Japanese Health and Welfare Ministry proposed Japanese VHL study group to develop a clinical grading system for evaluating disease severity. Several clinical grading systems for Parkinson’s disease exist that assess the severity of motor function impairment and QOL [2]. We therefore developed a new clinical grading system for VHL to assess the impairment of affected organs based on another clinical grading system. We then applied this system in the assessment of Japanese VHL patients. Our results showed that 46% of patients had the worst grade. This grading system may be a good tool to assess impaired organ function and QOL of VHL patients in Japan to support their care by the Japanese health care system.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
The clinical grading system was designed by members of the Japanese VHL study group. The VHL study group consists of three urologists, six neurosurgeons, three ophthalmologists, three gastroenterologists, one pediatric endocrinologist and one geneticist. We asked 46 Japanese VHL patients to answer a questionnaire based on our grading system. The ethics committee of Kochi Medical School approved the present study, which involved clinical questions and a checklist to inquire about the clinical grade.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We designed a clinical grading system that evaluates the function of each affected organ, including the CNS, retina, adrenal gland, kidney and pancreas. Grades were defined as follows: grade 0, no apparent tumor or cyst; grade 1, no clinical symptoms and presence of a small tumor or cyst; grade 2, minimal clinical symptoms and presence of a small to medium size tumor or cyst; grade 3, minor clinical symptoms and slightly disturbed QOL with the presence of a moderate size tumor or cyst; grade 4, seriously impaired function in the affected organ and significant disturbance of QOL with the presence of a tumor or cyst (or after surgical treatment). The following six tables show the clinical grading system of the CNS, retina, adrenal gland, kidney, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, and pancreatic cyst (Table 1-6).
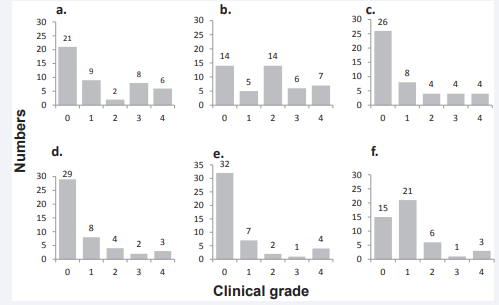
We analyzed the clinical grade of Japanese VHL patients after asking their clinical history symptom and QOL. The answers of the questionnaires were analyzed and the results are described below. If the clinical grade was regarded as the worst grade of the affected organs, the proportion (number) of patients with grades 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 were 0% (0), 9% (4), 28% (13), 24% (11), 37% (17), respectively. If we regard patients with grades 3 and 4 as those with significant disturbance of organ function, the proportions of patients with either grade 3 or 4 of the retina (Figure 1a), CNS (Figure 1b), kidney (Figure 1c), pheochromocytoma (Figure 1d), pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (Figure 1e), and pancreatic cyst (Figure 1f) were 30% (14), 28% (13), 18% (8), 11% (5), 11% (5), and 8% (4), respectively.
Figure 1: Clinical grade of affected organs in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. Clinical grades of the affected organs were determined according to our grading system. A) Retinal henagioblastoma. B) CNS hemangioblastoma. C) Renal cell carcinoma. D) Adrenal pheochromocytoma. E) Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. F) Pancreatic cyst.
We regarded the patients’ highest grades as the final grade. The proportions of patients with grade 4 of one organ, two organs, and three organs were 21% (10), 9% (4), and 7% (3). If patients with two or more grade 3-affected organ functions are regarded as grade 4, then 46% (21) of patients had grade 4 disease.
At present, 56 diseases are regarded as intractable diseases in Japan, and patients suffering from these diseases are fully supported by the Japanese medical insurance system. However, there are many intractable diseases affecting a considerable number of patients. Expansion of the number of diseases with an intractable disease status is being considered to increase financial and medical support to affected patients. The Japanese Welfare Ministry considered expansion of the number of intractable diseases to 300. If the group of intractable diseases is expanded, it would be difficult to provide financial support to all patients with intractable diseases because of financial constraints. A possible solution would be to provide more clinical support to patients with severe disturbance of their QOL, while those with mild disturbance of their QOL would be supported by standard medical insurance. Therefore, we developed this clinical grading system for VHL. The proportion of patients with significant disturbance of QOL was 46% (21 patients). As the QOL of patients is affected for several months after surgical or radiological treatment, the grade should be determined just after these treatments.
Our clinical grading system is still a first step to evaluate QOL of the VHL patients. This grading system especially for renal cell carcinoma and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor may be still very primitive. It requires improvement with more discussion by our research study group. We would like to improve it with applying it for VHL patients.
Table 1: Grading system for CNS.
| N0: | Hemangioblastomas have not been detected by radiological examinations. |
| N1: | Hemangioblastomas have been diagnosed by radiological examinations but neurological disability is not observed. |
| N2: | Hemangioblastomas have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Neurological disability is very minor. QOL is not disturbed. |
| N3: | Hemangioblastomas have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Moderate neurological disability. QOL is moderately disturbed. |
| N4: | Hemangioblastomas have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Severe neurological disability. QOL is severely disturbed. |
Grade N4 is assigned to severely disabled patients who need help with activities of daily living.
Grade N3 is assigned to moderately disabled patients who require regular, but not daily, assistance with activities.
Table 2: Grading system for retinal hemangioma.
| R0: | Retinal hemangiomas have not been detected. |
| R1: | Retinal hemangiomas have been detected but treatment is not necessary. QOL is not disturbed: retinal exudative changes are not observed and visual acuity is not disturbed. |
| R2: | Retinal hemangiomas have been detected and treatments are effective. QOL is not disturbed: retinal exudative changes are well controlled by treatments and visual acuity is not disturbed. |
| R3: | Retinal hemangiomas have been detected and treatments are ineffective. QOL is moderately disturbed: retinal exudative changes are not controlled by treatments and visual acuity is disturbed. |
| R4: | Retinal hemangiomas have been detected and treatments have minimal effect. QOL is severely disturbed: treatments for retinal exudative changes are not indicated and visual acuity is severely disturbed. |
Grade R4 is assigned to visually disabled patients who need help with activities of daily living.
Grade R3 is assigned to moderately disabled patients who require regular, but not daily, assistance with activities.
Table 3: Grading system for pheochromocytoma.
| Ph0: | Pheochromocytomas have not been detected by endocrinological examinations and radiological examinations |
| Ph1: | Pheochromocytomas have been diagnosed by endocrinological examinations. Symptoms of overproduction of catecholamines are absent. QOL is not disturbed |
| Ph2: | Pheochromocytomas have been diagnosed by endocrinological examinations or radiological examinations. Symptoms of overproduction of catecholamines are absent after medical treatment. QOL are not disturbed after medical treatment. |
| Ph3: | Pheochromocytomas have been diagnosed by endocrinological examinations and radiological examinations. Symptoms of overproduction catecholamines are not controlled by medical treatments. Symptoms due to shortage of catecholamines or other adrenal hormones after removal of both adrenal glands are also included in this category. QOL is moderately disturbed (Karnofsky Performance Status is between 70 and 90). |
| Ph4: | (1) Pheochromocytomas have been diagnosed by endocrinological examinations and radiological examinations. Symptoms of overproduction of catecholamines are present even after medical and surgical treatments. Symptoms due to the shortage of catecholamine or other adrenal hormones after the removal of both adrenal glands are also included in this category. QOL is severely disturbed (Karnofsky Performance Status is less than 60.) (2) Malignant pheochromocytomas with distant metastasis are included in this grade. |
Table 4: Grading system for renal cell carcinoma.
| R0: | Renal cell carcinomas (RCC) have not been detected by radiological examinations. |
| R1: | RCC have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Tumors did not require immediate treatment. Renal function (e.g. eGFR) is not impaired. QOL is not disturbed. |
| R2: | RCC have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Tumors required immediate medical treatments. Renal function is not impaired even after treatment. QOL is not disturbed. |
| R3: | RCC have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Tumors required immediate medical treatment. Renal function is moderately impaired after treatment. QOL is moderately disturbed. |
| R4: | RCC have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Tumors required immediate medical treatment. Renal function is severely disturbed after treatments. QOL is severely disturbed. |
Table 5: Grading system for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
| PNET0: | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have not been detected by radiological and endocrinological examinations. |
| PNET1: | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have been diagnosed by radiological or endocrinological examinations. Tumors do not require immediate medical treatments. QOL is not disturbed. |
| PNET2: | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have been diagnosed by radiological or endocrinological examinations. Tumors required immediate medical treatments. QOL is minimally disturbed. |
| PNET3: | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and distant metastases have been diagnosed by radiological or endocrinological examinations. Tumors required immediate treatments. QOL is moderately disturbed. |
| PNET4: | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and distant metastases have been diagnosed by radiological or endocrinological examinations. Tumors required immediate treatments. QOL is severely disturbed. |
Table 6: Grading system for pancreatic cyst.
| PC0: | Pancreatic cysts have not been detected by radiological examinations. |
| PC1: | Pancreatic cysts have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Symptoms are absent. QOL is not disturbed. |
| PC2: | Pancreatic cysts have been diagnosed by radiological examinations but does not requires immediate treatment. QOL is minimally disturbed. |
| PC3: | Pancreatic cysts have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Abdominal pain or symptoms due to decreased pancreatic function are present. Immediate medical treatment was required. QOL is moderately disturbed. |
| PC4: | Pancreatic cysts have been diagnosed by radiological examinations. Abdominal pain or symptoms due to decreased pancreatic function are present. Immediate treatment was required. QOL is severely disturbed. |
CONCLUSION
We developed a clinical grading system to evaluate impaired organ function and QOL of VHL patients. Our results showed that the clinical grading system for VHL disease was relatively easy to use. It reflected the severity and QOL of VHL patients. The use of this system aids the provision of medical care and financial support from the Japanese health care system to severely impaired VHL patients.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the Japanese VHL patients who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Japanese Scientific Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.