Case Report, Multiple Giant Spiroadenocylindromas in a Geriatric Patient
- 1. Dermatology Resident, Universidad Tecnológica Equinoccial Quito, Ecuador
- 2. Attending Dermatologist, Hospital de Calderón, Quito, Ecuado
- 3. Medical Doctor, Universidad Técnica de Manabí, Quito, Ecuado
Summary
Brooke-Spiegler Syndrome (BSS) is a rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis with variable penetrance, which is characterized by maintaining a progressive association of generally benign cutaneous adnexal neoformations among themselves. cylindromas, spiroadenomas and trichoepitheliomas. Other less frequently involved are trichoblastomas, follicular cysts, and organoid nevi. There are multiple phenotypic variants of SBS, which share the same genotypic origin; due to the overlap of the different lesions between them at a clinical, pathological, and genetic level, of which the present clinical case maintains a variant form that is rare in an association of multiple giant spiroadenocylindromas in a geriatric patient [1-11].
Keywords
• Brooke-spiegler syndrome
• Cylindroma
• Spiroadenoma
CITATION
Basantes A, Suárez E, Ramírez L, Vaca L, Vergara E, et al. (2024) Case Report, Multiple Giant Spiroadenocylindromas in a Geriatric Patient. J Dermatolog Clin Res 12(2): 1164.
INTRODUCTION
The classic phenotype of SBS is the “turban tumor”, formed by cylindromas that are benign pinkish adnexal tumors of the skin, which are millimeters in diameter and length, well circumscribed, smooth, often with visible arboriform vessels [1-6,8-11]. They can be solitary or multiple and are mainly located on the scalp and neck [2,3]. There may also be spiroadenomas, usually blue or skin-colored, painful, usually bleeding, which can reach up to 10 cm in diameter and length, and are also slowly progressive [2]. The finding of the combination of both in histopathology is rare and infrequent [8]. The third cell line is trichoepitheliomas that are observed as small, round, smooth, shiny, slightly translucent, firm, circumscribed papules or nodules and are generally symmetrical [3].
The present case report mentions a rare phenotypic case of SBS in an elderly patient who presented with giant neoformations located on the scalp and in the region of the face and neck, the importance of which lies in the clinical decision of the treatment during and after the SARS-COV2 pandemic over a period of 2 years of follow-up and the aesthetic result that family members demand to improve their living conditions. The legal representative of the patient in this report presented gave her informed consent for the publication of her medical history and photographs, maintaining confidentiality.
PRESENTATION OF THE CLINICAL CASE
Female patient, 80 years old, with difficult verbal communication, who comes with a family member (daughter), low economic resources, with a significant pathological history of high blood pressure for many years, whose daughter reports that for approximately 5 years she has observed multiple nodulations on the scalp and apparently for a year they have been growing in number and size, causing itching, pain and bleeding when scratching.
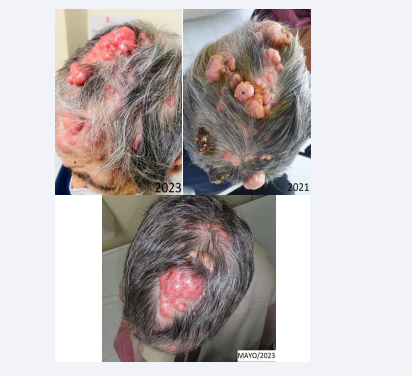
On physical examination, multiple exophytic, mamelonated, giant multilobed neoformations were observed, ranging from 0.5 to 8 cm in diameter, globular in appearance, pink in color, with certain myeliceric and crusted regions, smooth, with superficial telangiectasias, some well delimited, others convergent. In several places, the majority located on the scalp and those of smaller diameter on the face and neck.
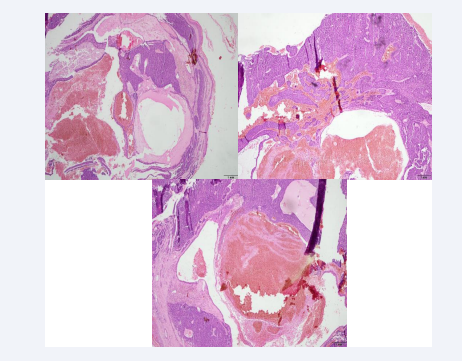
In the first instance, in June 2021, a biopsy is requested which determines (Figures 1-3) that there are neoformations consisting of two histological patterns and finally it is concluded that they are treated as ´´Multiple Spiroadenocylindromas´´ type lesions.
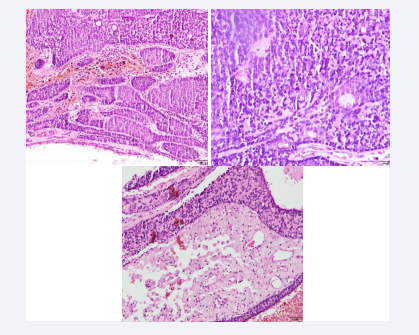
Figure 1: The sections show atrophic skin with loss of the ridge network that surrounds a neoformation consisting of two different histological patterns. The first and predominant one is composed of a multinodular proliferation composed of small cells with round and hyperchromatic nuclei and larger cells with clear cytoplasm, vesicular nucleus and prominent eosinophilic nucleolus, which are arranged in a trabecular pattern, with foci of ductal differentiation. presence of hyaline droplets and predominantly lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate. Courtesy: Dr. Mónica Salazar- Dermatopathologist
Figure 2: A second pattern is composed of islands of basaloid cells that have a puzzle-shaped arrangement and are surrounded by a thickened eosinophilic basement membrane. In addition, prominent cystic changes are observed that compromise the spiradenomatous part of the lesion and are associated with intratumoral hemorrhage. Courtesy: Dr. Mónica Salazar- Dermatopathologist
Figure 3: During the year 2021, multiple giant spiroadenocylindromas are observed, the largest diameter being located in the parieto-occipital region, causing aesthetic deformation of the skull. During the year 2023, the excision of several tumors has been achieved in 5 stages of minor surgery, allowing the skin to expand and recover.
where, due to the complexity and advanced age of the patient, the clinical decision is made to refer to the plastic surgery service of the health home where she was treated; However, during the years of pandemic that followed due to SARS-COV2 and due to excessive demand for care, she could not be cared for or receive timely treatment. Finally, by consensus of the Dermatology service of the patient’s hospital, it was decided to administer intralesional corticosteroids as the first treatment measure to make attempts to reduce the size of the lesions and subsequently schedule excision of the multiple lesions at various times, which until At the moment in the month of May/2023, five interventions have been successfully carried out for total excision of the neoformations and excision of two more times is proposed this year.
DISCUSSION
SBS initially described in 1892 and 1899 by the authors of the same name, and with more than 200 cases reported until 2020, is caused by transcription errors in the tumor suppressor gene ´´CYLD´´ located on chromosome 16q12. q13 for cylindromas and 9p21 for trichoepitheliomas [10]. It is believed that the gene acts as an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, which is an essential transcription factor in the correct proliferation of skin annexes, any alteration at the level of the CYLD gene It would facilitate the formation of cellular neoformations of the sebaceous, apocrine and eccrine sweat glands, and the hair follicle [8]. Sometimes, the same tumor has different associated cell groups, as in spiroadenocylindroma [7]. Other pathologies such as multiple familial trichoepithelioma and familial cylindromatosis are considered variants of this syndrome, although they were initially described as different pathologies [2,8]. The exact incidence is unknown [12]. It is predominantly common in females and usually occurs in the second or third stage of life [9,10,12]. Clinically, the lesions appear as multiple globular, hemispheric, smooth, well-defined tumors, firm in consistency, generally asymptomatic and of variable size and which can ultimately become deforming tumors located in 91% of the head and neck [2-4,6-12].
Malignancy of spiradenomas and cylindromas, including metastases to lymph nodes, thyroid, liver, lungs and bones, has been described in people with SBS, but is rare [1-4]. In addition, there are records of association with basal cell carcinoma, adenoma, and salivary gland adenocarcinoma6. The diagnosis of this syndrome does not require the presence of the three main types of tumors, only the presence of two of them is necessary [7].
The treatment is not really standardized; however, it is expected to be aimed at improving the quality of life of patients; especially in cases where there is the possibility of performing curative therapy when it has been detected in time. In addition, consideration must be given to whether it is an isolated or palliative lesion or whether the deformation is evident or multiple. The most commonly used therapies are surgical interventions, such as electrosurgery, cryosurgery, laser surgery and radiosurgery. Other options are ablative therapies, dermabrasion, CO2 or erbium-YAG lasers, cryotherapy, among others. [2-8,11,12]. In addition to the surgical approach to treatment, NF-κβ inhibitor medications including aspirin, prostaglandin A1, adalimumab, topical imiquimod, and vismodegib have been successfully tested [2-8,11,12].
CONCLUSION
This patient was treated for the first time in 2021, however, due to the SARS-COV2 pandemic, she did not have continuous follow-up, and treatment began 2 years after the biopsy diagnosis. It is significant to have this pathology among the differential diagnoses, since despite having a poorly known incidence and limited case reports being found in the literature, early diagnosis and timely treatment and follow-up are important.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
2. Ramallo C. Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: Clinical case presentation. Med Cutan Iber Lat Am. 2021; 49.
6. Letona-García N. Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: A rare disease to take into account in dermatological practice. Revis Bionatura. 2022; 7: 7.
9. Llancapi P. Multiple Cutaneous Cylindromas. Rev. Chilena Dermatol. 2013; 29: 389 – 396.
11. Escanilla Figueroa C. Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, a rare entity: Report of 2 cases. Piel (Barc). 2016.