Evaluation of the Parameters Increasing Intraoperative Difficulty Scores of Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- 1. General Surgery Clinic, Bagc?lar Training and Research Hospital, Turkey
Abstract
Background/Aims: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (LC) is a gold standard technique for Cholecystectomy and one of the most common laparoscopic operation being performed all over the world. To evaluate the factors that affects the difficulty of the elective laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.
Methods: In this prospective observational study 207 consecutive patients were included. Age, gender, body mass index, history of cholecystitis, pancreatitis, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) duration of the operation, scoring of the difficulty of the operation by using a visual analog scale (VAS) score in 5 different phases (entry to abdomen, degree of adhesions, dissection of Calot’s triangle, separation of gallbladder from liver, extraction of gallbladder from abdomen) and discharge time from hospital were recorded.
Results: We found that elders, male patients, patients with the history of cholecystitis and history of ERCP have significantly higher scores compared to others (p<0.005). Interestingly obese patients had lower difficulty scores in dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.03) and separation of gallbladder from the liver (p=0.022).
Conclusions: There are many factors affecting the difficulty of the laparoscopic cholecystectomy. LC after ERCP and cholecystitis are often a technical challenge. History of pancreatitis, obesity and number of stones did not affect the difficulty of the operation.
Keywords
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy; Cholelithiasis; Difficult cholecystectomy; Predictive factors.
CITATION
Solmaz A, Gülçiçek OB, Biricik A, Erçetin C, Yi?itba? H, et al. (2016) Evaluation of the Parameters Increasing Intraoperative Difficulty Scores of Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. J Liver Clin Res 3(1): 1023.
ABBREVIATIONS
LC: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy; ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography; VAS:Visual Analog Scale; BMI: Body Mass Index; DM: Diabetes Mellitus; CAD: Coronary Artery Disease; COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease; CRF: Chronic Renal Failure
INTRODUCTION
Prevalence of gallstones, symptomatic or not, varies from 5 to 22% [1]. Patients with symptomatic gallstones need to be treated with cholecystectomy [2]. Open cholecystectomy had been the gold standard treatment for the gallbladder stones until the application of laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) in France in 1987 [3]. LC is the most commonly performed laparoscopic operation in the world. Laparoscopic surgery has some
advantages like less pain, ileum, allowing earlier oral intake, less hospitalization, better cosmetic results and early return to work [4]. Although LC is safe, effective and commonly performed operation, it has some difficulties in the different stages of the operation. Difficult pneumoperitoneum, relaxation of adhesions, determination of anatomy, dissection of Calot’s triangle and separation of the gall bladder from liver and extraction of gallbladder from abdominal cavity [5,6]. We cannot predict the difficulty of the operation each time before the surgery. Although there are some preoperative scoring systems which have been reported in the literature, there is no intra operative classification of findings at laparoscopic surgery. Kama et al., [7] described some parameters like male gender, upper abdominal tenderness at the time of surgery, having previous upper abdominal surgery, age >60 years and diagnosis of acute cholecystitis[8].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the difficulty of LC operation by using intra operative scoring system and compare the results with some predictive factors of these patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
Two-hundred-nineteen consecutive patents who had elective laparoscopic Cholecystectomy at the Ba?c?lar Training and Research Hospital General Surgery Clinic between April 2015 and January 2016 were included in this study. Inclusion criteria were having laparoscopic Cholecystectomy and willingness to participate of the study. Exclusion criteria were not willing to participate in the study, conversion of operation to open surgery, emergent Cholecystectomy. All the operations were scored by one surgeon who was not attending the operation actively. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The prospective study protocol was approved by Istanbul Training and Research Hospital local ethical committee. Informed consent form was obtained from all participants included in the study. Demographic data (age, gender), body mass index (BMI), liver function tests, comorbid diseases (diabetes mellitus (DM), coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic renal failure (CRF), cirrhosis, number and size of stones, previous cholecystitis, pancreatitis, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and upper abdominal surgery were recorded before the operation. One-surgeon who was not attending the operation, was responsible for the scoring of all operations. He scored the difficulty of the operation 5 different stages: 1. Entry to abdomen: Means first trochar access to abdominal cavity. 2. Degree of dissection of adhesions: Degree of adhesions around gallbladder. 3. Dissection of Calot’s triangle: Surgical dissection of cystic duct and cystic artery. 4. Separation of gallbladder from liver: Indicates separation of gallbladder from liver, 5. Extraction of gallbladder from abdomen: Taking out the gallbladder from abdominal cavity. The degree of difficulty was recorded by using a visual analog scale (VAS) score [1]. Duration of the operation, complications and length of stay in hospital were also recorded. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed by using the NCSS (Number Cruncher Statistical System) 2007 Statistical Software (Utah, USA) package program. Besides descriptive statistical methods (mean, standard deviation) One-way analysis of variance was used for intergroup comparisons, Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used for subgroup analysis, independent T-test was used to compare the pairs and Chi-square test was used for comparison of qualitative data. All p values less than 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant.
RESULTS
The study was enrolled a total of 219 subjects. Conversion to open cholecystectomy was necessary in 12 patients (5.4%), who were excluded from the study due to the aim of the study. Thus 207 patients left in the study. The reason for conversion was adhesions in 10 patients and anatomic uncertainty in 2 patients. Majority of patients were female (n=152) (73.4%) and mean age was 46.74 (range 17-78). Patients were divided into 3 groups; young (18-25 years) (n=17, 8.2%), young-adults (2664 years) (n=163, 78.7%) and elders (≥65 years) (n=27, 13%) according to their age (Table 1).
|
Table 2: Analysis of effect of cholecystitis on intraoperative scores. |
|||
|
|
Cholecystitis (-) (n:140) |
Cholecystitis (+) (n:67) |
p |
|
Entry to abdomen |
2.28 ± 1.61 |
2.61 ± 1.72 |
0.174 |
|
Dissection of adhesions |
2.83 ± 1.85 |
4.12 ± 2.73 |
0.0001 |
|
Dissection of Calot’s triangle |
3.18 ± 1.74 |
5.22 ± 2.62 |
0.0001 |
|
Separation of gallbladder from liver |
3.24 ± 1.68 |
5.3 ± 2.62 |
0.0001 |
|
Extraction of gallbladder |
2.84 ± 1.9 |
3.84 ± 2.48 |
0.002 |
|
Hospital stay (hour) |
27.85 ± 12.08 |
33.9 ± 17.33 |
0.004 |
|
Duration of operation (minutes) |
35.41 ± 12.84 |
47.84 ± 21.17 |
0.0001 |
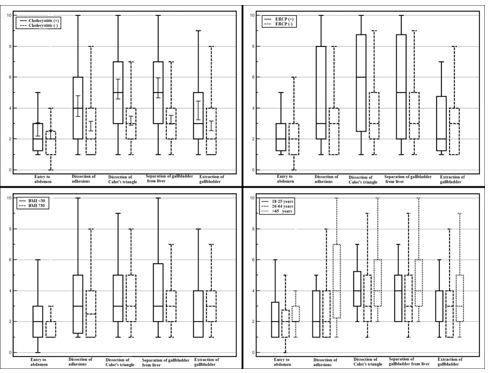
Mean operation time was 39.43 minutes (range 25-105 minutes). The operation mortality rate was 0%. Patients with the history of cholecystitis (n=140) (67.6 %) had significantly higher scores in dissection of adhesion (p=0.0001), dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.0001), separation of gallbladder from liver (p=0.0001), extraction of gallbladder (p=0.002), but entry to abdomen score was not significantly different (p=0,174). Duration of operation (p=0.0001) and length of stay in the hospital (p=0.004) were also significantly higher in patients with the history of cholecystitis (Table 2).
|
Table 2: Analysis of effect of cholecystitis on intraoperative scores. |
|||
|
|
Cholecystitis (-) (n:140) |
Cholecystitis (+) (n:67) |
p |
|
Entry to abdomen |
2.28 ± 1.61 |
2.61 ± 1.72 |
0.174 |
|
Dissection of adhesions |
2.83 ± 1.85 |
4.12 ± 2.73 |
0.0001 |
|
Dissection of Calot’s triangle |
3.18 ± 1.74 |
5.22 ± 2.62 |
0.0001 |
|
Separation of gallbladder from liver |
3.24 ± 1.68 |
5.3 ± 2.62 |
0.0001 |
|
Extraction of gallbladder |
2.84 ± 1.9 |
3.84 ± 2.48 |
0.002 |
|
Hospital stay (hour) |
27.85 ± 12.08 |
33.9 ± 17.33 |
0.004 |
|
Duration of operation (minutes) |
35.41 ± 12.84 |
47.84 ± 21.17 |
0.0001 |
Number of gall bladder stone didn’t affect any score of the patients. History of acute pancreatitis didn’t increase the scores significantly. However, history of ERCP increased some of the scores significantly (dissection of adhesion (p=0.008), dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.004), separation of gallbladder from liver (p=0,038), but other scores, entry to abdomen (p=0.373) and extraction of gallbladder (p=0,978)) were not significantly different). Duration of operation (p=0.001) and length of stay in the hospital (p=0.001) were also significantly higher in patients with the history of ERCP (Table 3).
|
Table 3: Analysis of effect of ERCP on intraoperative scores. |
|||
|
|
ERCP (-) n:196 |
ERCP (+) n:11 |
p |
|
Entry to abdomen |
2.36 ± 1.6 |
2.82 ± 2.36 |
0.373 |
|
Dissection of adhesions |
3.15 ± 2.14 |
5 ± 3.46 |
0.008 |
|
Dissection of Calot’s triangle |
3.73 ± 2.16 |
5.73 ± 3.41 |
0.004 |
|
Separation of gallbladder from liver |
3.83 ± 2.14 |
5.27 ± 3.47 |
0.038 |
|
Extraction of gallbladder |
3.16 ± 2.15 |
3.18 ± 2.27 |
0.978 |
|
Hospital stay (hour) |
29.02 ± 13.2 |
43.91 ± 23.4 |
0.001 |
|
Duration of operation (minutes) |
38.48 ± 15.47 |
56.36 ± 30.75 |
0.001 |
|
Abbreviations: ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. |
|||
In our study most of the scores were significantly higher, dissection of adhesion (p=0.028), dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.0001), separation of gallbladder from liver (p=0.0001), extraction of gallbladder (p=0.023) in male than female patients. Just entry to abdomen score was similar between male and female patients (p=0.306). Duration of operation (p=0.001) and length of stay in the hospital (p=0.001) were also significantly higher in male patients (Table 4).
|
Table 4: Effect of gender on intraoperative scores. |
|||
|
|
Male (n:55) |
Female (n:152) |
p |
|
Entry to abdomen |
2.58 ± 1.56 |
2.32 ± 1.68 |
0.306 |
|
Dissection of adhesions |
3.82 ± 2.37 |
3.04 ± 2.18 |
0.028 |
|
Dissection of Calot’s triangle |
5.05 ± 2.38 |
3.4 ± 2.07 |
0.0001 |
|
Separation of gallbladder from liver |
4.8 ± 2.36 |
3.59 ± 2.11 |
0.0001 |
|
Extraction of gallbladder |
3.73 ± 2.39 |
2.96 ± 2.03 |
0.023 |
|
Hospital stay (hour) |
37.4 ± 23.01 |
27.06 ± 7.66 |
0.0001 |
|
Duration of operation (minutes) |
46.13 ± 21.64 |
37.01 ± 14.29 |
0.001 |
In our LC series non-obese patients had significantly higher scores in dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.03) and separation of gallbladder from liver (p=0.022), other scores and duration of operation and hospital stay were not significantly different compared to obese patients (Table 5).
|
Table 5: Effect of BMI on intraoperative scores. |
|||
|
|
BMI<30 (n:143) |
BMI ≥30 (n:64) |
p |
|
Entry to abdomen |
2.38 ± 1.48 |
2.39 ± 1.98 |
0.981 |
|
Dissection of adhesions |
3.37 ± 2.33 |
2.97 ± 2.06 |
0.236 |
|
Dissection of Calot’s triangle |
4.07 ± 2.43 |
3.33 ± 1.8 |
0.03 |
|
Separation of gallbladder from liver |
4.15 ± 2.37 |
3.38 ± 1.82 |
0.022 |
|
Extraction of gallbladder |
3.18 ± 2.25 |
3.13 ± 1.92 |
0.861 |
|
Hospital stay (hour) |
30.99 ± 16.38 |
27.17 ± 6.93 |
0.075 |
|
Duration of operation (minutes) |
41.28 ± 18.34 |
35.31 ± 12.7 |
0.019 |
|
Abbreviations: BMI: Body Mass Index Note to Editor: This paper has been accepted as a poster presentation in 24th International Congress of the E.A.E.S (The European Association of Endoscopic Surgery), Amsterdam The Netherlands. |
|||
Tukey’s multiple comparison test was demonstrated that elders had significantly higher score of dissection of adhesion than young (p=0,002) and young-adults (p=0.0001). Other scoring parameters were not significantly different between age groups. The duration of operation (p=0,029) and the hospital stay (p=0,021) were longer in elderly patients, compared to youngadults. The duration of operation (p=0,431) and hospital stay (p=0,301) were not significantly different in elderly patients, compared to young patients. All the results of the predictive factors affecting the intra operative scores of the LC can be seen in Figure 1 together.
Figure 1: The distribution of predictive factors affecting difficulty scores of laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
DISCUSSION
Cholecystectomy is one of the most common laparoscopic operations done all over the world. It has been the gold standard treatment modality for the diseases of gallbladder since 1987. Conversion rate of laparoscopic cholecystectomy to open surgery is about 7-35 % in the literature [9]. The main cause of conversion is generally adhesions of gallbladder due to the cholecystitis of the patient in the past or inability to delineate the anatomy [10,11].Scoring and grading surgical conditions provide us a uniform tool for reporting the severity of the disease. There is not an accepted objective scoring system of difficulty of laparoscopic cholecystectomy yet. In this prospective study we aimed to determine the preoperative risk factors of the patients affecting the difficulty of the LC, by scoring the operation in 5 stages. We included just elective laparoscopic cholecystectomies which were completed laparoscopically. History of cholecystitis, pancreatitis or ERCP, old age, male gender and multiple stones were included as risk factors in this study. Repeated attacks of acute cholecystitis and hospitalization increase the difficulty of laparoscopic cholecystectomy due to adhesions in pericholecystic region [12,13]. Similar results have been found in this study. All scores of the difficulty were significantly higher in patients with the history of cholecystitis than others, except score of entry to the abdomen (0.174) which was not affected from history of cholecystitis. History of acute pancreatitis has not been included as a difficulty factor in most of the studies about the LC. Nachnani et al., [14] claimed that pancreatitis is predictive factor for the LC in 2005. Although, all scores of patients with the history of pancreatitis were higher than others, the difference was not statistically significant (p>0, 05). ERCP is minimal invasive endoscopic method for the diagnosis and treatment of biliary tree pathologies. Today it is mostly performed for the extraction of common bile duct stones.In our study group indications for ERCP are choledocholithiasis for 7 patients and suspicion of common bile duct stone. Timing of operation after ERCP is still controversial in the literature [15,16]. We operate these patients after 4-6 weeks after ERCP. Pre-operative ERCP has been considered to be predictive factor for difficulty of LC by publishes [5,17,18]. In our study patients with the history of ERCP (n=11) had significantly higher scores of dissection of adhesion (p=0.008), dissection of Calot’s triangle (p=0.004) and separation of gallbladder from liver (p=0,038).
There are some literatures suggesting that male gender is as a risk factor of difficult cholecystectomy [19-21]. It may be due to more pericholecystic fibrosis attributed by macrophages, mast cell and eosinophils in males more than females. There is more collagen formation in both in the sub mucosal area of gall bladder wall and in pericholecystic tissue of men [22]. In this regard we have found similar results with the literature.
Male patients had significantly higher scores than females, except entry to abdomen which was not significantly different (p=0.306). Duration of the operation was also significantly higher in our study like the literature. Rosen et al., [23] had claimed the obesity for the risk factor of difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy. However, some other studies suggest no difference between obese and nonobese patients [24]. It is still controversial in the literature. In our study we found some opposite data. Entry to abdomen, degree of dissection of adhesions, extraction of gallbladder from abdomen scores was not significantly different. However, scores of dissection of Calot’s triangle, separation of gallbladder from liver were significantly higher in obese group. That may be due to more fatty tissue of pericholecystic area makes dissection easier. However, duration of operation was significantly higher in obese group (p=0,019).
Increased age has been accepted as a predictive factor for increasing the difficulty of LC [14,25]. We divided patients in 3 groups according to age. Elders had significantly higher scores of dissection of adhesion than young (p=0,002) and young-adults (p=0.0001). Other scores were not significant. It may be due to the adhesions and fibrosis formation of elder patients.
Karadeniz et al., [3] reported a relationship between number of gallbladder stones and difficulty of operation and switching to open surgery in 50 patient studies. We did not find any significant different scores between patients with one or multiple stones.
CONCLUSION
In this prospectively designed observational study we conclude that age, male gender, history of cholecystitis and history of ERCP are predictive difficulty factors for LC. However, obesity, history of pancreatitis and number of stones does not affect the difficulty of LC. We suggest large, multi centric studies to prove the efficacy of scoring systems.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
This paper has been accepted as a poster presentation in 24th International Congress of the E.A.E.S (The European Association of Endoscopic Surgery), Amsterdam, The Netherlands.