Hydatid Liver Disease: Single Center Experience
- 1. Department of general and thoracic surgery, Ramallah hospital, Palestine
Abstract
Background: Hydatid cyst is a parasitic infection which is mostly caused by Echinococcus granulosus. This continues to be an essential cause of morbidity and mortality in many parts of the world including Palestine, where it is an important public health problem with increasing Incidence due to globalization. The study was conducted to find out the incidence, presentation and the outcome of management of patients presented with liver hydatid disease in one tertiary center in Palestine.
Methods: A single-center retrospective analysis of collected database of all patients who underwent treatment for liver hydatid disease from the period of January 2014 till January 2016
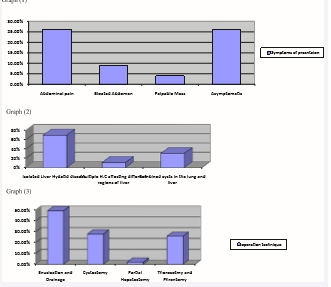
Results: 46 patients with liver hydatid disease were included in the study. 27 patients (58.7%) were males and the rest were females (41.3%). The most common presentation was abdominal pain (26.1%), bloated abdomen (9%) and a palpable mass in the right upper quadrant in 2 patients (4%). The majority of the patients (70%) were diagnosed to have isolated liver hydatid disease. Various procedures were performed; enucleation and drainage in 22 patients (49.5%), cystectomy in 13 patients (28%), partial hepatectomy was done in 1 patient (2 %), thorocotmy and phrentomy as one stage were used in 12 patients (26%) who have combined cyst in the right lung and liver. Postoperative complications were seen in 10 patients (21%) in which the recurrence rate was the highest complication (17%).
Conclusion: Results suggest the safety and efficacy of radical procedures in the surgical management of liver hydatid disease and selecting the suitable method is individualized depending on many factors which has an important role in lowering morbidity, mortality, and the recurrence rate.
Keywords
Hydatid ; Liver disease ; Liver cysts ; Echinococcosis.
CITATION
Nairat MM (2017) Hydatid Liver Disease: Single Center Experience. J Liver Clin Res 4(1): 1032.
INTRODUCTION
Hydatid disease is a parasitic infection caused by a tapeworm of the Genus Echinococcus. It affects humans as well as other mammals like; sheep, dogs, rodents and horses. Human hydatid disease or echinococcosis has a worldwide distribution, and it is an endemic in many countries in the Mediterranean region, the middle and south east and south America [1]. Two species appear to be of a pathological and surgical importance which are; E.granulosus and E.multilocularis [2]. Hydatid cyst is one of the known causes of liver mass. Investigations and appropriate management improving the quality of life and substantially decrease the mortality ratio [3]. The adult E.granulosus is a worm that resides in the jejunum of dogs and other canines, it produces eggs that passed in the stool, eggs then ingested by an intermediate host like humans and sheep in which liberates an embryo in the duodenum, then the embryo passes through the intestinal mucosa to enter the portal circulation [4]. Most of these embryos are trapped in the liver, the rest passes through the liver and scattered to other organs, once they settle, they develop into cysts. The haydatid cyst of liver has 2 layers; the ectocyte which results from the host reaction and the inner endocyte, which is a parasite derivative and has an outer laminated and inner germinal layer [5]. The diagnosis of liver haydatid disease is based on the patient’s history, clinical findings, haematological, serum biochemical profiles and serological testing in which can be negative in 10-20% of the cases [6]. Early diagnosis is important, as if the diagnosis is late; cysts then complicate making the treatment difficult and long lasting. The radical surgical removal of the cystic lesion remains the mainstay of treatment with a high success rate [7]. Chemotherapy, with benzimidazole compounds has also been used with some success to sterilize the cyst, decrease the chance of anaphylaxis, and reduce the complications and recurrence rate post-operatively. In recent years, a third treatment option was introduced (PAIR, puncture, aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration) and is indicated for patients who cannot undergo surgery [8]. But still the surgical treatment technique for liver hydatic cyst (LHC) cannot be standardized, and the surgical technique should be tailored according to the extent of the cyst and any adjunct complications of hydatid disease [9]. In this study, we present the experience of Ramallah hospital in the treatment of hydatid liver disease patients by a retrospective analysis of collected database of all patients undergoing treatment for liver hydatid disease from a period of 2014 till 2016.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In Ramallah hospital, 46 patients with hydatid liver disease were treated between January 2014 and December 2015, 36 of the patients were treated surgically, and the rest were treated with albendazole without surgical intervention. Each patient’s medical record was reviewed retrospectively for the results of the physical examination, serum biochemistry, abdominal ultrasound (US), and spiral abdominal computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. The Gharbi classification system was used to stage the hydatid disease. Surgical treatment was used for all cysts that were larger than 7 cm, those that were complicated and those that were not suitable for other interventions. All patients were treated with albendazole (10 mg/kg) 2 weeks before surgery, and this medication was continued for 2 months postoperatively. Postoperative monitoring by regular physical examination, abdominal CT scan, and liver enzymes tests were done. Data Analysis was done by SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Among 46 patients who had hydatid liver disease, 27 patients (58.7%) were males and 19 patients (41.3%) were female (Table 1).
|
Table 1: Sex. |
||
|
Male |
Female |
Total |
|
27 |
19 |
46 |
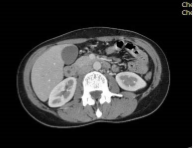
The patients were between 3 and 73 years of age. The most common presentation was abdominal pain (26.1%), bloated abdomen (9%) and palpable mass in the right upper quadrent in 2 patients (4%). 12 patients (26%) were asymptomatic and discovered incidentally, graph (1). The majority of patients (70%) were diagnosed to have isolated liver hydatid cyst. Most of the liver cysts were located in the right lobe in 39 patients (85%), whereas 2 patients (4 %) found to have the cysts in the left lobe of the liver (Figure 1, Table 2).
Figure 1 Abdominal CT scan, showed hydatid liver cyst in left lobe.
|
Table 2: Affected lobes of the liver |
|
|
Left lobe of liver |
Right lobe of liver |
|
4 % |
85% |
Moreover, 14 patients (30.5%) were found to have combined cysts in the right lung and liver. Multiple hydatid cysts affecting different regions of liver in both lobes were seen in 5 patients (11%). 14 patients had extrahepatic cysts, which were on the surface of the spleen in one patient and within the lung in the other 13 patient, graph (2). The size of the cysts ranged from 3 to 14 cm, most of operated cases were considered to have huge cysts. Mortality rate was 0%. Midline incision was preferred in 30 patients (83.3%), followed by right subcostal incision in 6 patients (16.7%). Of the 46 patients who had liver cysts and were surgically treated; enucleation and drainage was done in 22 patients (49.5%), cystectomy done in 13 patients (28%), partial hepatectomy was done in 1 patient (2%), thorocotmy and phrentomy as one stage were used in 12 patients (26%) who had combined cysts in the right lung and live, graph (3).
Postoperative complication was seen in 10 patients (21%). the recurrence was seen in 8 patients (17%), and Wound infection developed in 4 patients (8.6%). The most common complication was the recurrence, while wound infection was the most common early complication In postoperative period. The mean duration of the hospitalization was 4 days.
DISCUSSION
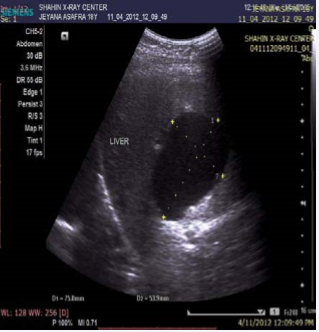
Hepatic hydatid cyst is still an endemic health problem in Palestine (70% of the patients were from the middle and south regions), as in some other areas of the world specially the Mediterranean area. Hydatid cyst of the liver is frequently silent and only diagnosed incidentally during abdominal investigation for other pathology. The clinical signs appear gradually with the increase volume of the cyst. The most common symptom, when it occurs, is right upper quadrant or epigastric pain and the most common findings on examination are an enlarged liver and a palpable mass [10], which was totally defined in our study as (26%) of all patients who were discovered incidentally. So the symptoms of hydatid cysts of the liver depend on many factors as the localization and the size of the cyst. It has been reported that asymptomatic cases constituted to (38%) to (60%) of all patients [11]. The diagnosis is most easily set by ultrasound (which is the most useful noninvasive diagnostic test and is also used to classify the cysts (Figure 2),
Figure 2: US Abdomen, showed huge hydatid cyst in liver.
or other imaging techniques such as CT-scan or MRI [12], which provide better information regarding the location and size of the cyst [13] ) combined with case history. Serological tests such as ELISA or immunoblotting can be used in addition, which is sensitive in (80-100%) of the liver cysts but only (5056%) for other organs [14]. Serological tests usually useful for the differential diagnoses in difficult cases. As for the treatment of liver hydatid disease, it differs depending on different factors such as; the stage, localization, size, complications of the cysts, and the physician himself. Surgery remains the gold standard choice. The aim of surgical intervention is to inactivate the parasite, to evacuate the cyst along with resection of the germinal layer, to prevent peritoneal spillage of scolices, to do management of communication between cyst and adjacent structures and to obliterate the residual cavity, which can be performed successfully in more than 90% of patients [15]. Albendazole, which is an antiparasitic drug, have been used for the treatment of the hydatid disease and in the early 1980s [16], it was recommended as the chemotherapeutic agent of choice for liver hydatid disease. The usual dosage is 10-15 mg/ kg/day, that used especially in inoperable patients and for cases with a high surgical risk, or as a conservative treatment for small non complicated or multiple cysts. Multiple radical surgical procedures can be used to treat liver hydatid disease with low rate of recurrence as; cystectomy, Pericystectomy , lobectomy or total hepatectomy [17]. Cystectomy – The procedure involves removal of hydatid cyst, comprising laminar layer, germinal layer and cyst contents (daughter cysts and brood capsules). It is simple to perform and has a low recurrence rates (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Intact Hydatid liver cyst after surgical complete Resection.
Pericystectomy – this procedure involves a non-anatomical resection of cyst and surrounding compressed liver tissue. This is technically a more difficult procedure than cystectomy and can be associated with considerable blood loss. Hepatic resection is recommended for known cases of recurrence, or sometimes for huge peripherally located cysts because of the low rate of recurrence. But, the arguments against hepatic resection as a primary modality of treatment still present due to morbidity or mortality that may result and because of the distortion of the anatomy which makes surgery harder. However, partial cystectomy with enuceolation and drainage are the most frequently used operations to treat liver hydatid disease [18]. As for the postoperative complications, recurrence was the highest one in our study (17%), regarding to the literature, the recurrence rates of the surgical techniques range between 0% and 25%, but as yet no prospective randomized study had shown superiority of one operative technique over the other [19, 20].
CONCLUSION
Hepatic hydatid cyst is still an endemic health problem in Palestine. Diagnosis of liver hydatid disease is made with Ultrasonography and computed tomography. Surgery combined with medical treatment by albendazole is effective in the eradication of hepatic hydatid disease and in the prevention of local recurrences. Results suggest the safety and efficacy of radical procedures in the surgical management of liver hydatid disease and selecting the suitable method is individualized depending on many factors(the stage, localization, size, complications of the cysts, and even the physician himself) which has an important role in lowering morbidity, mortality, and the recurrence rate.