Robotic AI-Driven Communication Modules for Enhanced Piezo- Metamaterial Sensing and Structural Health Monitoring
- 1. Energy Research Institute, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
ABSTRACT
This study investigates the role of active communication modules in advanced piezo-metamaterial sensing, emphasizing data optimization through miniaturized sensor kits and AI-driven robots. We compare a portable piezo-Arduino sensor kit with three signal display options to a piezo-wireless sensing network kit using robot-based communication modules. Various Arduino C programs were developed for different communication modules using IDE and mBlock scratch (m-BS) interfaces. Additionally, we explore a dual electromagnetic wave-based sensing approach that generates localized surface plasmon (LSP) and surface plasmon polariton (SPP) waves at sensor interfaces.
KEYWORDS
- Arduino
- Piezoelectric
- Metamaterial
- Structural health monitoring
- Sensor
- AI
- Robotics
- Data optimization.
CITATION
Madhav AVG (2024) Robotic AI-Driven Communication Modules for Enhanced Piezo-Metamaterial Sensing and Structural Health Monitoring. J Materials Applied Sci 5(1): 1010.
INTRODUCTION
A study by Strogatz et al. [1], on London’s Millennium Bridge highlights the need for sophisticated communication modules to display live structural health signals, preventing failures due to wobble, sway, and vibrations. Smart materials like piezo materials and metamaterials are effective for sensing and structural health monitoring (SHM). However, neither piezo materials nor metamaterials can address all complexities alone, although they have proven effective in SHM via automation and communication modules [2,3], Researchers like Annamdas and Soh [4,5], have been investigating the feasibility of fusing these materials for civil engineering, providing opportunities for technological advancements. This editorial article draws readers attention towards piezoelectric sensors and LSP-based metamaterial patches and their complementary abilities. Various communication modules conveying information to and from computers and SHM devices are discussed.
RESEARCH FOCUS
The use of Piezo diaphragm sensors (Piezo-D patches) in electromechanical impedance (EMI) sensing is increasing. This editorial summarizes automation via AI-driven robots and electronic devices for rapid data acquisition and intelligent communication between on-site sensors, remote sensing devices, and engineers for SHM. Novel sensing kits and automation via communication modules are presented for real-time monitoring and AI-enhanced decision-making for SHM.
Development of Piezo Material and Metamaterial- Based Sensing Devices
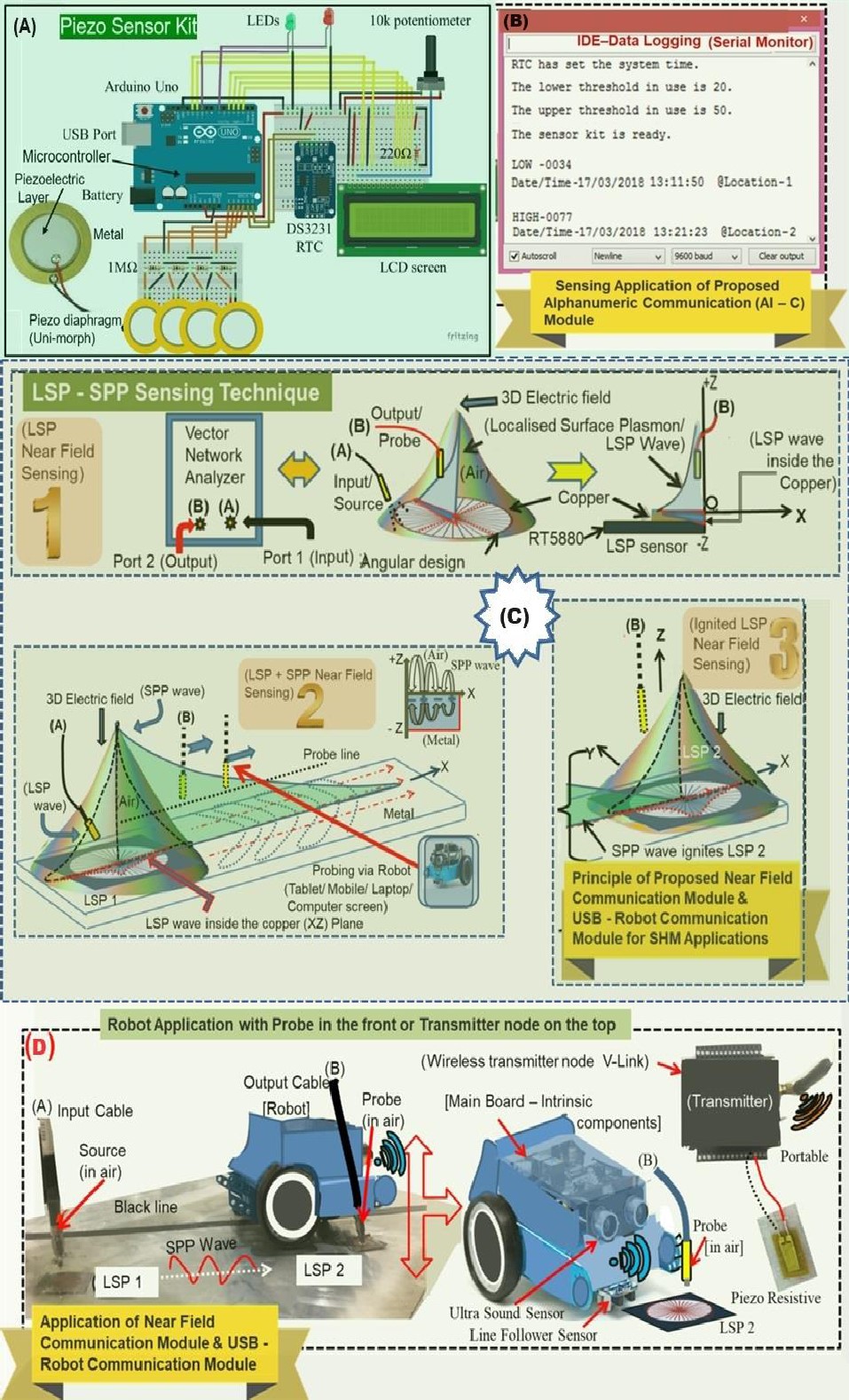
The proposed piezo material and metamaterial-based sensing devices are shown in Figure 1, The portable piezo-Arduino sensor kit was developed by assembling components and programming communication modules using Arduino IDE and m-BS interfaces [6-8], The piezo-Arduino sensor kit (Figure 1A,B) employs custom code (see codes in references [9]) on Arduino and robot microcontrollers for wireless sensing network (WSN) kits and EMI techniques. Real-time shock/vibration data is displayed alphanumerically. Additionally, a metamaterial dual sensing approach (Figure 1C) can monitor cracks or loads using electric near-field distribution which is basically electro-magnetic fields via a portable robot (Figure 1D), These smart materials are automated for SHM applications [4,5].
Figure 1 Piezo material and metamaterial sensing devices (A) Piezo – Arduino sensor kit with its components (B) serial monitor display for an experiment (C) Principle of surface plasmon sensing technique in three steps viz., 1. single LSP near field sensing, 2. LSP plus SPP near field sensing and 3. Ignited LSP near field sensing (D) Photo of experimental application of near field communication module and robot communication module along with details of robot and sensors (Viz., 1. Ultra sound sensor, 2. Line follower sensor, 3. LSP 2 sensor and 4. Peizo resistive sensor connected via wireless transmitter node).
Evaluation of Arduino-IDE for Shocks and Vibrations
Software Development: An independent communication (In-C) module was first developed, comprising Arduino C integrated development environment (IDE) application code T [9]. This initiated communication between (a) On-site Sensors or Sensor Devices (O-Sensor-Sd), (b) Multiple Components of Arduino Sensor Device/kit (M-C-Sd), and (c) output signal display platforms via a computer screen. The code T [9], was uploaded to the microcontroller via the USB Port (see section on ‘Methods’). Three experiments were conducted on a representative timber specimen by surface bonding four identical Piezo-D sensors where the host merely supported the sensors (see Supplementary Movies [10]).
Experimental Evaluation of Sensor Kit: The piezo-Arduino sensor kit was tested with three communication modules: In-C (battery-powered, independent communication Module), Al-C (Alphanumeric communication Module for Serial Monitor data logging), and Gr-C (Graphical communication output). The kit measured shocks, displayed data on an LCD, and indicated shock severity with LEDs. In the absence of a computer, the Al-C and Gr-C modules can become In-C modules, showing different outputs for the same sensor kit.
Principle of Proposed Metamaterial LSP Sensor Design
The LSP sensor generates and propagates surface plasmon (SP) waves, creating a sensing electric field measured by an output dipole. The LSP design, sensitive to mechanical stress, was found to be ten times more sensitive than Piezo-D sensors, suitable for SHM applications [4,5].
Design of Automated and Remote-Controlled Robot
Robot Automation: Semi-autonomous robots, controlled using Arduino C-IDE and m-BS interfaces, were used for real-time SHM. The robots facilitated communication between sensors, transmitters, receivers, and computers, displaying impact data graphically. Experiments demonstrated the robot’s ability to detect and display shocks and vibrations in real-time, enhancing SHM efficiency.
METHODS
Hardware Design of Sensor Kit
The circuit diagram of the hardware kit is given in ref. [11]. The sensor kit comprises an Arduino UNO Rev 3 board, a 9V battery, breadboards, RTC Module, LEDs, and LCD screens. The components are connected to the core unit, housed in an insulating material casing with openings for sensors, USB ports, and LEDs.
Working Principle
The sensors generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress, recorded as a voltage by the ADC of the core unit. The analog voltage is converted to a digital value using the analogRead function in the programming codes.
WSN Kit and Robots
The WSN kit includes a portable transmitter and receiver with inbuilt antennas, facilitating wireless communication between sensors and computers. The study used a jeep-shaped robot and a remote-controlled car. The robot is equipped with an mCore main board, ultrasonic sensor, and line follower sensor, enabling automated SHM tasks (Table 1). Operated using USB- Robot communication modules 1 and 2 based on the code (W and L, [9,12]).
Table 1: Experimental Details and Communication Modules.
|
Item No. |
Program (Code) & Display |
|
Experiment 1: Sensor kit (Figure 1a) and Supplementary Movie 1 [10,11]. In-C Module is adopted. |
Code T & LCR screen, (Power: 9V Battery). LED indicator (green: red indicate low: high proportional to digital 0-1023 (random threshold, <20 for low and >50 for high). |
|
Experiment 2. Sensor kit (Figure 1b) and Supplementary Movie 2 [10,11]. Al-C Module is adopted. |
Code T & LCR screen, real time numerical display on Serial Monitor Screen, (Laptop USB or 9V Battery) |
|
Experiment 3. Sensor kit and Supplementary Movie 3 [10,11], [Gr- C Module is adopted. |
Code G & LCR screen, real time graphical display on bridge control panel |
|
4: WSN kit (Sensor – Connect Communication Module), [Figure 2] |
Sensor – Connect program & real time graphical computer display |
|
5: Robot with WSN transmitter node on the top (USB – Robot Communication Module -1). Robot with EM Probe in the front (USB – Robot Communication Module -2), See [Figures] 1(D) & 2 |
Code W and Code L (no display: automatic function) |
Abbreviations: In-C, Al-C, Gr-C Modules represent Independent, Alphanumeric, Graphical communication Modules
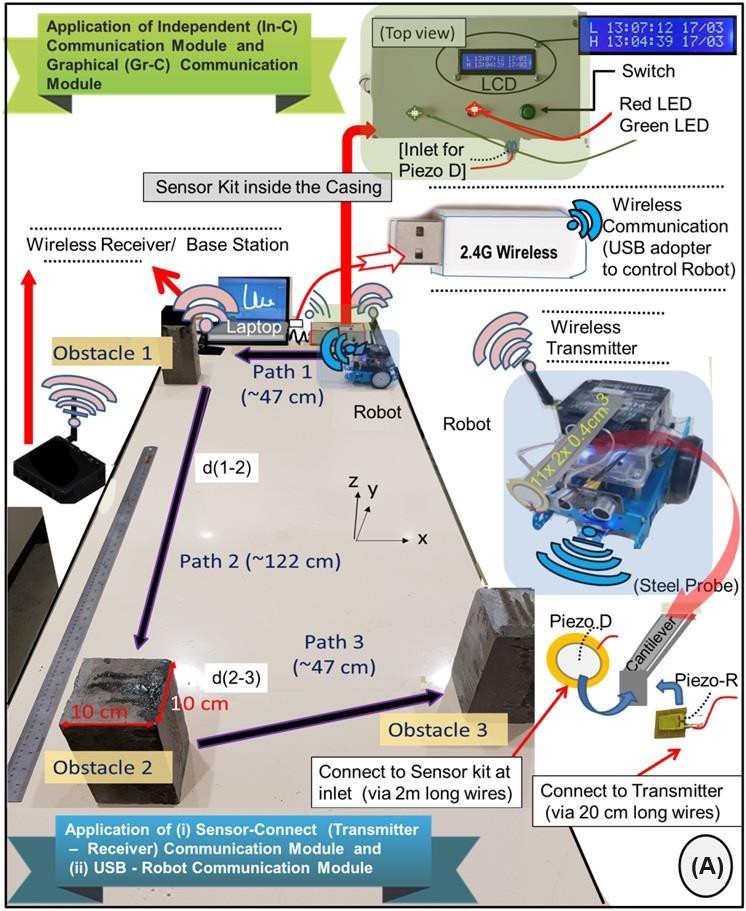
Robot Automation: Robot automation offers advantages in environments with limited human access or where labor reduction is desired. While fully autonomous robots reliant on AI are promising, semi-autonomous systems provide greater flexibility and effectiveness for real-time SHM under direct human control [13-16]. This study employed two robots: a jeep- shaped model programmed in Arduino C and controlled via m-BS and USB interfaces, and a remote-controlled car. A piezo-Arduino sensor kit and a robot-mounted piezo-WSN kit were used (Figure 2) see Video in [12]). The WSN kit, comprising a transmitter and receiver, communicated via a Sensor-Connect module. The jeep- shaped robot carried a transmitter, a projected metallic beam equipped with Piezo-D and Piezo-R sensors, and an ultrasonic sensor (Figure 1D). Data from these sensors was transmitted to a nearby receiver and sensor kit. An experiment was conducted to assess sensor performance under impact conditions. The robot was programmed to collide with three concrete blocks, triggering data acquisition from both sensor kits. The ultrasonic sensor guided the robot’s path and enabled obstacle avoidance. Graphical outputs displayed impact data in real-time, with clear peaks indicating collisions (Figure 2B). Semi-autonomous robots are preferred for real-time SHM. Piezo-D and Piezo-R sensors measured impact data. Ultrasonic sensor guided robot navigation. Real-time data visualization captured impact events [12].
Figure 2 Evaluation of piezo-sensor kit (A) Test setup with three obstacles and, close-up views of the robot and projected cantilever beam (B) graphical display of sensor kit showing collisions.
CONCLUSIONS
The crowd synchrony on London’s Millennium Bridge highlighted the importance of using smart materials with automated communication modules for structural monitoring. Piezoelectric materials and metamaterials are effective for SHM, suitable for both non-destructive and destructive testing. This research explores data transmission through wires and antennas and communication via wired or wireless robots, in both frequency and real-time domains. The presented communication modules help engineers customize SHM techniques for specific structural complexities and promote the miniaturization of portable equipment. The WSN kit, typically a stationary strain measuring device, was adapted to measure shocks and vibrations via a movable robot carrying a transmitter node. This adaptation was enabled by activating two communication modules using Sensor-Connect software and Program code-W. Automations for the sensor kit and robot mobility for the WSN kit and metamaterial dual LSP sensing technique were developed through various communication modules. This study facilitated rapid data acquisition and communication between piezo sensors, sensing devices, remote transmitters and receivers, and output signals in real-time on computers or LCD screens. This includes communication between multiple components of the same sensing devices, particularly for the sensor kit, WSN kit, and robot.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
To my Teacher: Prof. Soh Chee Kiong, Retired Professor of Nanyang Technological University Singapore. To my Family: Shantanu Vasudev Krishna (my Son) and Radhika Madhav Annamdas (my Wife) of Birla Open Minds International School, India
REFERENCES
- Strogatz S, Abrams D, McRobie A, Eckhardt B, Edward O, Edward O, et al. Crowd synchrony on the Millennium bridge. Nature. 2005; 483: 43-44.
- Ali A, Hu B, Ramahi O. Intelligent Detection of Cracks in Metallic Surfaces Using a Waveguide Sensor Loaded with Metamaterial Elements. Sensors. 2015; 15: 11402-11416.
- Kedare AK, Mundada K. Miniaturized Device for SHM Using Electromechanical Impedance Technique. InveCompTec. Springer. 2020; 98.
- Annamdas VGM, Soh CK. A perspective of non-fiber-optical metamaterial and piezoelectric material sensing in automated structural health monitoring. Sensors. 2019; 19: 1490.
- Annamdas VGM, Soh CK. Evaluation of peak-free electromechanical piezo-impedance and electromagnetic contact sensing using metamaterial surface plasmons for load monitoring. Sma Mate Stru. 2017; 26: 015003.
- Arduino. Arduino-an open-source computer hardware and software company. 2024.AnalogRead. 2024.
- Makeblock. Robot devices. 2024.
- Annamdas V. Editorial_Article_ProgramCodes, Mendeley Data. 2024.
- Artificial Intelligence (Vasudev). Supplementary Movies 1, 2, 3 (Editorial Article), YouTube, 2024.
- Annamdas V. Circuit Diagram used in Sensor Kit”, Mendeley Data. 2024.
- Artificial Intelligence (Vasudev). Supplementary Movie 4 Sensor Kit Evaluation (Editorial Article), YouTube, 2024.
- Huston D. Essera B. Gaidaa G. Arms S. Townsend C. Chese SB, et al. Wireless inspection of structures aided by robot. SPIE Health Monitoring and Management of Civil Infrastructure Syst. 2001; 4337: 147-154.
- Huston DR, Miller J, Esser B. Adaptive, robotic, and mobile sensor systems for structural assessment. Smart Structures and Materials: Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems. 2004.
- Zhu D. Yi X. Yang W. Lee KM. Guo AJ. Mobile sensing system for structural health monitoring: design and validation. SMS. 2020; 19: 055011.
- Lattanzi D. Miller G. Review of Robotic Infrastructure Inspection Systems. J of Infra Syst. 2017; 23.