A New Surgical Technique for Treatment of Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Ferromagnetic Glossal Prosthesis (FGP)
- 1. Dr.Suat Seren Chest Diseases and Chest Surgery Training and Research Hospital,Turkey
Citation
Afrashi A (2015) A New Surgical Technique for Treatment of Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Ferromagnetic Glossal Prosthesis (FGP). J Sleep Med Disord 2(1): 1011.
DEAR EDITOR,
Obstruct?ve Sleep Apnea is a disease consist of episodes of partial or complete closure of the upper airway that occur during sleep and lead to breathing cessation defined as a period of apnea more than 10 seconds. Symptom include restlessnes, snoring, reccurent awakening, morning headache and excessive daytime sleepiness. Diagnosis of OSA is based on sleep history and Polysomnography [1,2]. Positional obstructive sleep apnea mostly occures in supine position [3]. Today the major surgical treatment methods for positional obstructive sleep apnea are Hyoid suspension, resection of base of the tongue, Genioglossus advancement, Coblation of base of the tongue [4,5].
In all of these surgical procuders surgeons aim to prevent a wider retroglossal space during sleep. In this designed new technique Ferromagnetic Glossal Prosthesis (FGP) could solve this problem with a new and easy surgical way during sleep.
Ferromagnetic Glossal Prosthesis (FGP): It contains two parts for using in base of the tongue and chin.
1- Internal part of prosthesis: It contains an fragmantated thin parts like lace of a ferromagnetic material such as Iron (Fe), coated with biocompatible Silicone or another biocompatible material (Figure1a).
Figure 1: a) Internal part of prosthesis.
2- External part of prosthesis: It contains a natural magnet with power between 8000-12000 Gauss. This part will use only during sleep over the skin of the chin (Figure1b).
Figure 1: B) External part of prosthesis.
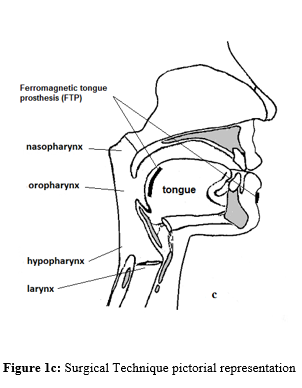
Surgical Technique: Patient should be in supine position and under general anesthesia during surgery. After inserting Davis-Boyle mouth gag, surgeon should make an 3 cm long incision horizontaly in base of the tongue. Then surgeon should make blunt dissection under mucosal and submucosal layers 4 cm long downward. After that he/she should insert the internal part of prosthesis and at the end close the incision (Figure 1c).
Figure 1c: Surgical Technique pictorial representation
A few days after surgery patient should use the external part of the prosthesis in external part of chin during sleep (Figure 1c). The magnetic power of external part of prosthesis could pull the internal part of prosthesis and base of the tongue together and this will prevent the collapse of glossopharyngeal region and obstructive attacks. The advantage of this method is that years after performing operation, in possible decrease of tonus of tongue’s muscles we could use more powerful external part of prosthesis to pull more the base of tongue.
Regards,
Arman Afrashi
Dr. Suat Seren Chest Diseases and Chest Surgery Training and Research Hospital
Turkey