Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction by an Accessory Renal Artery: An Underrecognized but Reversible Cause of Renovascular Hypertension
- 1. Department of Medicine, University of California San Francisco, USA
- 2. Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, University of California Irvine Medical Center, USA
- 3. Renal Division, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, USA
Abstract
An unusual case of a 41-year-old woman with renovascular hypertension associated with unilateral hydronephrosis and ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) due to an accessory renal artery crossing the ureter were reported. Following surgical correction of the UPJO by dismembered pyeloplasty, the patient’s hydronephrosis resolved, and her requirement for antihypertensive therapy substantially decreased. Our case demonstrates that acquired UPJO due to an accessory renal artery was an important but under recognized cause of renovascular hypertension. In cases of UPJO presenting with hypertension, renal impairment, recurrent urinary tract infection, recurrent stones, or debilitating pain, surgical intervention may be considered. Clinicians should consider UPJO in the differential diagnosis for secondary hypertension, particularly among patients in whom physical exam, laboratory findings, and renal ultrasound with Doppler are unrevealing.
Keywords
• Renovascular
• Hypertension
• Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Citation
Lee BJ, Rhee CM, Hsiao LL (2015) Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction by an Accessory Renal Artery: An Under-recognized but Reversible Cause of Renovascular Hypertension. Ann Clin Exp Hypertension 3(2): 1028.
INTRODUCTION
Renovascular hypertension is a form of secondary hypertension typically caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia [1,2]. Ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO), with a reported incidence of 5/100,000 person-years, is an unusual cause of renovascular hypertension that may be acquired or congenital in etiology [2]. Congenital cases may be caused by functional or anatomic anomalies, the latter of which may rarely be due to extrinsic compression of the ureteropelvic junction by an accessory renal artery [3].
An unusual case of a 41-year-old woman with renovascular hypertension associated with unilateral hydronephrosis and UPJO due to an accessory renal artery crossing the ureter were reported to attract attention to an under-recognized but reversible cause of renovascular hypertension. This report illustrates an unusual case of secondary hypertension due to unilateral extrinsic compression of the ureteropelvic junction by an accessory renal artery.
CASE REPORT
A 41-year-old woman with a history of depression presented to the nephrology clinic with hypertension, left-sided flank pain, unilateral left-sided hydronephrosis, and a subacute decline in renal function. One-and-a-half years prior to presentation, she had been diagnosed with new-onset hypertensive urgency with a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 210 mm Hg. At that time, she denied headaches, diaphoresis, and symptoms suggestive of obstructive sleep apnea. She was not taking oral contraceptives or steroids. Family history was notable for hypertension. Concurrent with the onset of hypertension, she had developed left-sided, dull flank pain. She did not have associated fevers, dysuria, gross hematuria, nausea, or vomiting. She took ibuprofen and naproxen daily to ameliorate the pain.
She was initially started on hydrochlorothiazide but was subsequently switched to atenolol due to lack of improvement in blood pressure (BP). Five months prior to her initial nephrology clinic consultation, she was transitioned from atenolol to lisinopril due to exacerbation of depression; her SBP remained sub-optimally controlled (120 to 160 mmHg).
Physical examination at the time of presentation to the nephrology clinic showed: BP 125/76, body mass index 29 kg/ m2 . Cardiovascular and pulmonary exams were unremarkable; she did not have renal artery bruits. Jugular venous distension and peripheral edema were not observed. She did not have cushingoid facies, enlarged dorsocervical or supraclavicular fat pads, abdominal striae, or proximal muscle weakness; nor did she have flank, spinal, or paraspinal tenderness with palpation.
The patient’s labs (Table 1) demonstrated a subacute rise in her serum creatinine, from 0.87 mg/dL fourteen months prior to presentation to 1.36 mg/dL five months later (subsequent measurements ranging 1.14-1.38 mg/dL). Serum aldosterone was 6.6 ng/dL (reference range: <21 ng/dL), and plasma renin activity level was undetectable (reference range: <0.6 ng/mL/h). Urine metanephrine and normetanephrine levels were normal.
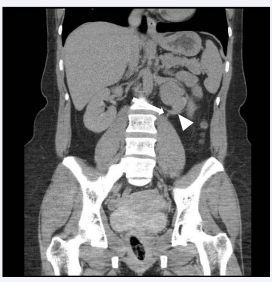
Two-and-half years prior to presentation, the patient had undergone a renal ultrasound demonstrating normal renal anatomy. However, a repeat study obtained by her primary care provider prior to the nephrology consultation showed moderate left-sided hydronephrosis in the context of symmetric, normalsized kidneys; doppler ultrasound demonstrated mildly elevated resistive indices bilaterally but was negative for renal artery stenosis. She then underwent contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) urogram (benefit deemed greater than risk of contrast-induced nephropathy), which demonstrated left-sided ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO), with an accessory left renal artery crossing the ureter (Figure 1). The ureter distal to this crossing renal artery was of normal caliber.
Figure 1 Coronal view of a contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) urogram showing an accessory left renal artery (arrowhead) crossing the ureter (arrow).
Based on these findings, the patient was advised to refrain from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and her creatinine subsequently decreased to 1.07 mg/dl. She was referred to a urologist who performed a left dismembered pyeloplasty, which entailed amputation of the renal pelvis lower pole (including the ureteropelvic junction) and reconnection of the ureter to the renal pelvis. Two months later, follow-up renal ultrasound showed significant improvement in her left-sided hydronephrosis, and her creatinine remained stable. While the patient continued to require anti-hypertensive medications one month post-surgery, her BP trajectory improved with reduction in her anti-hypertensive dosage requirements.
DISCUSSION
In the general population, clinical clues suggestive of secondary hypertension include: 1) onset of hypertension before 30 years of age, 2) acute rise in BP in a patient with previously controlled hypertension, 3) malignant hypertension, and 4) persistent hypertension despite concurrent use of three or more antihypertensive medications (including a diuretic). Additional findings specifically suggestive of renovascular hypertension include 1) onset of stage II hypertension (BP ≥160/100) after age 55, 2) worsening renal function after initiation of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensinII-receptor blocker (suggestive of bilateral renovascular disease), 3) unilateral renal atrophy, and 4) unexplained sudden-onset pulmonary edema [1].
Renovascular hypertension is typically caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. UPJO, with a reported incidence of 5/100,000 person-years [2], may be acquired (e.g., nephrolithiasis, postoperative or inflammatory strictures, urothelial neoplasms) or, more commonly, congenital [3]. Congenital cases may be due to functional disturbances or anatomical lesions, the latter of which may be subdivided into intrinsic (e.g., stenosis from an adynamic ureteral segment) and extrinsic causes, including external compression of the ureteropelvic junction by an accessory renal artery.
There are several mechanisms by which unilateral UPJO due to an obstructing renal artery may result in secondary hypertension. Reduction in renal arterial blood flow due to compression of the renal artery may cause increased renin secretion from the juxtaglomerular apparatus, causing increased conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, with subsequent increase in angiotensin II and aldosterone production. Excess aldosterone, in turn, results in sodium retention, blood volume expansion, and elevated BP. Previously reported cases of UPJO associated with aberrant renal vasculature demonstrated elevated renin levels in the ipsilateral renal vein or peripheral veins; in several instances, surgical correction of the obstruction resulted in normalization of renin levels and resolution of hypertension [4-6].
In contrast, there have also been several reported cases of unilateral hydronephrosis and hypertension in the absence of hyper-reninemia [7-11], as in our case. One postulated mechanism for this finding is that loss of nephron function due to hydronephrosis, combined with an inability of the contralateral kidney to compensate for the resulting sodium retention, leads to increased extracellular fluid volume and hypertension [7,13]. Another proposed mechanism is that UPJO may result in reduced release of Medullipin I, a hormone produced by renomedullary interstitial cells that serves as the biologic reciprocal of the reninangiotensin system [12]. Hepatic cytochrome P-450 enzymes convert Medullipin I to Medullipin II, which has vasodilatatory and diuretic functions [2,12].
The optimal management strategy for UPJO is not welldefined. Current indications for surgical correction of UPJO include concurrent hypertension, renal dysfunction, recurrent flank pain, urinary infection, or nephrolithiasis [2]. In the absence of these complications, active surveillance is recommended, given that only 30% of cases develop indications for surgical correction within four years of initial diagnosis [13]. If surgery is pursued, dismembered pyeloplasty is the treatment of choice. Reported success rates for this intervention, defined as absence of obstruction on postoperative follow-up radiologic studies, stabilization of renal function, and resolution of preoperative symptoms, are 90-100% [2].
Given this patient’s severe hypertension, renal impairment, young age, and low perioperative risk, surgical correction of her UPJO was the optimal management strategy. Although her renal dysfunction was most likely due to heavy non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and resolved after cessation of these analgesics, there remained concern that persistent leftsided hydronephrosis and impaired left-sided renal perfusion would eventually lead to left-sided renal atrophy. Dismembered pyeloplasty resulted in resolution of her left-sided hydronephrosis. In contrast to all five reported cases of secondary hypertension associated with UPJO caused by an accessory renal artery treated with surgery [4-6,14], this patient’s BP improved but did not completely normalize independent of anti-hypertensive treatment. Thus, it is possible that the patient’s continued need for anti-hypertensive medications post-operatively, albeit at a lower dose, suggests underlying essential hypertension.
In conclusion, this case demonstrates that acquired UPJO due to an accessory renal artery is a unique and reversible cause of renovascular hypertension. In UPJO cases associated with hypertension, renal impairment, or symptoms such as debilitating pain, recurrent infection, and recurrent stones, surgical management is advised. Clinicians should consider UPJO in the differential diagnosis for secondary hypertension, particularly among those in whom physical exam, lab findings, and renal ultrasound with Doppler are unrevealing.
Table 1: Relevant laboratory results.
| Laboratory Test | Date | Result | Assay Referent Range (units) | |
| Creatinine | Month 1 | 0.87 | 0.50-1.20 (mmol/L) | |
| Month 5 | 1.36 | |||
| Month 5 | 1.21 | |||
| Month 13 | 1.38 | |||
| Month 13 | 1.14 | |||
| Month 13 | 1.31 | |||
| Potassium | Month 1 | 4.4 | 3.5-5.0 (mmol/L) | |
| Month 5 | 3.2 | |||
| Month 5 | 4.5 | |||
| Month 13 | 4.8 | |||
| Month 13 | 4.1 | |||
| Bicarbonate | Month 1 to Month 13 | 24-29 | 22-31 (mmol/L) | |
| Nonfasting serum glucose | Month 1 to Month 13 | 88-106 | 70-100 (mg/dL) | |
| Total calcium | Month 13 | 9.6 | 8.8-10.4 (mg/dL) | |
| Ionized calcium | Month 13 | 1.25 | 1.13-1.32 (mmol/L) | |
| TSH | Month 11 | 1.51 | 0.5-5.7 (mIU/L) | |
| Serum aldosterone | Month 5 | 6.6 | ≤21 (ng/dL) | |
| Plasma renin activity (PRA) | Month 5 | undetectable (<0.6) | ≤0.6-3.0 (ng/mL/hr) | |
| Urine metanephrines | Month 1 | 178 | 30-350 (µg/24 hrs) | |
| Urine normetanephrines | Month 1 | 412 | 50-650 (µg/24 hrs) | |
| Urinalysis | ||||
| Leukocyte esterase | Month 13 | negative | N/A | |
| Nitrites | Month 13 | negative | N/A | |
| Protein | Month 13 | negative | N/A | |
| Blood | Month 13 | negative | N/A | |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Financial Disclosure: LLH receives research support from the SDSC Foundation. None of the other authors declare any relevant conflicts of interest.
Funding/Support: The authors receive support from the SDSC Foundation (LLH).
Role of the Sponsors: The sponsor had no role in the design and conduct of the report, in the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data, or in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.