Children and COVID-19: Clinical Insights, Immune Landscape, and Future Directions
- 1. Consultant Cardiologist, Lilavati hospital and Research Centre, India
- 2. Consultant Intensivist, Lilavati hospital and Research Centre, India
- 3. Consultant Pediatrician, Lilavati Hospital and Research Centre, India
- 4. Consultant Infectious disease specialist, Lilavati Hospital and Research Centre, India
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, is among the most defining public health crises of our time. While it wreaked havoc across adult populations globally, children presented a unique paradox—often exhibiting milder disease or remaining asymptomatic, yet not untouched by the broader implications. As the virus evolved, so did our understanding of its diverse effects on Pediatric health, ranging from clinical manifestations to developmental and psychological consequences.
Keywords
• COVID-19 pandemic
• SARS-CoV-2
• Children
• Clinical Insights
Citation
Bang V, Ramananthan S, Ugra D, Nagvekar V (2025) Children and COVID-19: Clinical Insights, Immune Landscape, and Future Directions. Pediatr Child Health 13(4): 1360.
INTRODUCTION
The Pediatric Paradox of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, is among the most defining public health crises of our time. While it wreaked havoc across adult populations globally, children presented a unique paradox-often exhibiting milder disease or remaining asymptomatic, yet not untouched by the broader implications. As the virus evolved, so did our understanding of its diverse effects on Pediatric health, ranging from clinical manifestations to developmental and psychological consequences. This chapter aims to comprehensively analyze the course of COVID-19 in children, from immunological peculiarities and clinical presentations to emerging concerns such as MIS-C, Long COVID, and the pandemic’s psychosocial toll.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
How COVID-19 Behaved in the Pediatric Population
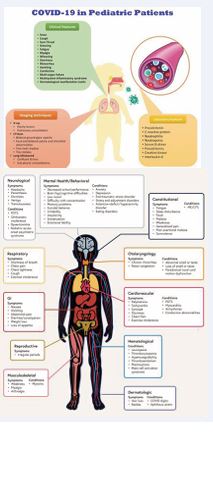
In the early stages of the pandemic [1], Pediatric cases constituted less than 5% of confirmed infections. However, with expanded testing, school reopening, and the emergence of new variants, this number rose significantly. Most infections in children were traced to household contacts, and the burden varied geographically with waves of transmission.The Omicron variant marked a turning point [2], Pediatric cases. Nonetheless, hospitalizations and mortality in children remained markedly lower than adults. Infants, particularly those under one year, and children with underlying conditions such as asthma, obesity, or immunodeficiency, were observed to be at higher risk for severe disease. Understanding these epidemiological trends has been critical in shaping public health responses and prioritizing vaccination drives for children., with increased transmissibility resulting in larger numbers (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Covid-19 in Pediatric Patients.
Ann Pediatr Child Health 13(4): 1360 (2025).
IMMUNOLOGY
The Unique Pediatric Immune Response
Children’s relative resilience to severe COVID-19 has fascinated immunologists. Several hypotheses have been posited:
Lower ACE2 expression in Pediatric respiratory epithelium, limiting viral entry.
Pre-existing cross-reactive immunity due to frequent exposure to common cold coronaviruses.
Trained innate immunity, wherein prior vaccinations or infections prime a robust early immune response.
A less aggressive cytokine release profile, reducing the risk of hyperinflammatory responses seen in adults.
Additionally, the Pediatric thymus is more active, contributing to a more responsive T-cell repertoire. This immunological advantage, however, does not fully protect against all consequences, as evidenced by MIS-C and Long COVID, which may stem from immune dysregulation rather than active infection [3].
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Most children with SARS-CoV-2 infection present with mild, self-limiting symptoms such as fever, cough, rhinorrhea, fatigue, gastrointestinal disturbances, or sore throat. Anosmia and ageusia, hallmark adult symptoms, were also noted but less frequently reported in younger children.In neonates and infants, nonspecific symptoms such as lethargy, poor feeding, and irritability pose diagnostic challenges. Diagnosis relies on RT-PCR or rapid antigen testing. Serological assays have been useful in post- infectious syndromes such as MIS-C. Radiographic abnormalities, when present, are typically less extensive than in adults.Despite the overall benign course, clinicians must maintain vigilance for red flag signs indicating progression to severe disease, including respiratory distress, altered mental status, or dehydration.
MULTISYSTEM INFLAMMATORY SYNDROME IN CHILDREN (MIS-C)
MIS-C emerged as a novel and serious post-infectious complication [4], typically occurring 2–6 weeks following SARS-CoV-2 exposure. It is characterized by persistent fever, multiorgan dysfunction, elevated inflammatory markers, and often cardiovascular involvement.
Key features include:
Mucocutaneous signs (conjunctivitis, rash) Gastrointestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting,
diarrhea)
Hypotension or shock
Elevated CRP, D-dimer, ferritin, troponin
The pathogenesis likely involves immune dysregulation and autoantibody formation. Treatment protocols involve intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), corticosteroids, and, in refractory cases, biologics like anakinra or tocilizumab. With timely recognition and intervention, most children recover well, although long-term cardiac surveillance is recommended.
THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES AND VACCINATION
The cornerstone of Pediatric COVID-19 treatment has been supportive care. In mild cases, home isolation, hydration, and symptom management suffice. Hospitalized children may require oxygen therapy, anticoagulation, or anti-inflammatory agents depending on severity.
Monoclonal antibodies saw restricted use due to agelimitations and variant-specific efficacy.
Vaccination remains the most effective preventive strategy. mRNA vaccines, initially tested in adults, were eventually approved for use in children over 5 years and later expanded to younger age groups. Safety data has been reassuring, with rare adverse events like myocarditis being mild and self-limiting.
Despite this, vaccine hesitancy among caregivers— driven by misinformation and perceived low risk— continues to challenge immunization efforts. Clear communication and Pediatrician-led advocacy are essential to address this gap.
LONG COVID IN CHILDREN: MYTH OR EMERGING REALITY?
Long COVID, characterized by persistent symptoms [5], lasting beyond four weeks after infection, is a recognized phenomenon in adults. In children, the picture is less clear due to overlapping symptoms with other post-viral syndromes and the psychological impact of the pandemic itself.
Commonly reported symptoms include: Chronic fatigue
Headache
Sleep disturbances
Difficulty concentrating (“brain fog”)
Palpitations or dizziness
Current studies estimate prevalence between 2% to 10% among infected children. Although most cases resolve over time, the need for a multidisciplinary approach, including psychological support and rehabilitation, cannot be overstated.
PSYCHOSOCIAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL IMPACT
The indirect effects of the pandemic on children may outlast the virus itself. School closures, lack of peer interaction [6], disruption of routines, and increased screen time have taken a toll on mental health and development.Surveys have reported rising trends in anxiety,depression, sleep disturbances, and behavioral issues among children and adolescents. Children with neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism or ADHD, experienced exacerbation of symptoms due to loss of structure and therapies.In addition to mental health services, interventions must prioritize re-engagement with school, social skills retraining, and parental support to mitigate long-term damage.
HEALTH SYSTEM RESPONSE: LEARNINGS AND GAPS
The pandemic tested Pediatric healthcare systems worldwide. While many children avoided hospitalization, those who required intensive care often did so for severe respiratory or inflammatory complications.Telemedicine emerged as a vital tool for continuing care, yet digital inequity hindered access for underprivileged populations. Routine immunization programs suffered setbacks in many countries, raising concerns of future outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.These experiences underscore the need for resilient, inclusive Pediatric healthcare infrastructure, capable of responding to both infectious crises and ongoing developmental needs.
ETHICAL AND POLICY REFLECTIONS
The pandemic raised complex ethical questions involving children-from inclusion in vaccine trials to the contentious issue of school closures. Balancing public health priorities with child rights required nuanced decision-making.Children, often voiceless in policy discourse, bore disproportionate educational and emotional burdens. Future responses must integrate child-centered ethical frameworks that prioritize both safety and holistic well- being.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS AND RESEARCH PRIORITIES
As COVID-19 transitions to an endemic phase, several questions remain:
What is the duration of immunity in children post infection or vaccination?
Can we develop pan-coronavirus vaccines that obviatevariant-specific concerns?
What genetic or immunological factors protect children from severe disease?
How can we better define and manage Long COVID in Pediatrics?
What role do social determinants play in infection patterns and outcomes?
Investment in Pediatric-specific research and global collaboration will be pivotal in preparing for future pandemics and improving child health outcomes.
CONCLUSION
COVID-19 in children is a story of resilience interspersed with moments of vulnerability. While most children sailed through the infection with minimal physical morbidity, the hidden scars-emotional, developmental, and societal— may take longer to heal. This pandemic offers a unique opportunity to reimagine Pediatric care: integrating biological insight with psychological support, and clinical acumen with compassionate policy. The child must now stand at the center of every future public health blueprint.
REFERENCES
- Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, et al. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics. 2020; 145: e20200702.
- Götzinger F, Santiago-García B, Noguera-Julián A, Lanaspa M, Lancella L, Carducci FIC, et al. COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: a multinational, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020; 4: 653-661.
- Viner RM, Mytton OT, Bonell C, Melendez-Torres GJ, Ward J, Hudson L, et al. Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: a systematic review and meta- analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2021; 175: 143-156.
- Feldstein LR, Rose EB, Horwitz SM, Collins JP, Newhams MM, Son MBF, et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383: 334-346.
- Molteni E, Sudre CH, Canas LS, Bhopal SS, Hughes RC, Chen L, et al. Illness duration and symptom profile in symptomatic UK school-aged children tested for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021; 5: 708-718.
- Loades ME, Chatburn E, Higson-Sweeney N, Reynolds S, Shafran R, Brigden A, et al. Rapid systematic review: The impact of social isolation and loneliness on the mental health of children and adolescents in the context of COVID-19. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020; 59: 1218-1239.