Association of Heart Inflammation after Covid 19 Vaccination: The Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- 1. Maryam and Isa Clinic, Malang City, Indonesia
Abstract
Introduction: The COVID-19 contamination which developed in December 2019 is caused by the infection SARS-CoV-2. Contamination with this infection can lead to serious respiratory sickness; in any case, myocarditis has too been detailed. The reason of this ponder is to distinguish the clinical highlights of myocarditis in immunized COVID-19 patients.
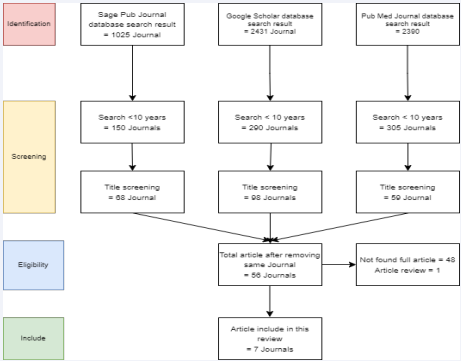
Method: This study using systematic review that search using keyword heart inflammation, myocarditis and Covid-19 Vaccination in Google Scholar, PubMed, and CrossRef. After final screening the author analysize 7 articles.
Result: COVID-19 myocarditis influenced patients over the age of 50 and rates among both sexes were similarly detailed. Patients displayed with dyspnea, hack, fever with hypotension and chest torment. Research facility tests uncovered leukocytosis with expanded C-reactive protein, whereas blood vessel blood gas investigation illustrated respiratory acidosis. All cardiac markers were raised. Radiographic imaging of the chest appeared respective ground glass opacities or reciprocal invades, whereas cardiac attractive reverberation imaging created late gadolinium upgrades. Electrocardiography illustrated ST-segment height or altered T waves, whereas echocardiography uncovered decreased cleared out ventricular launch division with cardiomegaly or expanded divider thickness. Administration with corticosteroids was favored in most cases, taken after by antiviral medicine. The lion’s share of thinks about detailed either recuperation or no encourages clinical disintegration.
Conclusion: Be that as it may, current prove illustrates myocardial aggravation with or without coordinate cardiomyocyte harm, proposing distinctive pathophysiology components mindful of COVID-mediated myocarditis. Built up clinical approaches ought to be sought after until future prove bolster distinctive activities. Huge multicentre registries are prudent to illustrate assist.
Keywords
Heart Inflammation; Covid-19 Vaccination; Myocarditis
Citation
Utami AT (2022) Association of Heart Inflammation after Covid 19 Vaccination: The Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Vasc Med Res 9(1): 1181.
INTRODUCTION
Myocarditis is the dynamic aggravation of the center layer of the heart taken after by a myocardial damage without ischemic occasions [1,2]. The irresistible and non-infectious causes of myocarditis decide its prognostic results. The (focal/diffuse) degrees of myocardial aggravation decide the seriousness of side effects in patients with myocarditis [1]. The age/genderappropriate burden of myocarditis was recorded as 6.1/100,000 for men and 4.4/100,000 for ladies (inside the age extend of 35- 39 a long time) in 2019 [3]; be that as it may, myocarditis-related mortality affected 0.2/100,000 men and 0.1/100,000 ladies within the same year. The clinical thinks about uncover the most noticeably awful results with ineffectively caught on obsessive pathways in 20-30% of hospitalized COVID-19 (coronavirus malady) patients with myocardial harm [4].
Myocarditis, an fiery condition influencing the myocardium,comes aboutfrom a widerangeof bothirresistibleand non-infectious causes. Numerous diverse infections have been embroiled, counting the Center East RespiratoryDisorder (MERS) coronavirus [5], whichcloselytakes afterSARS-CoV-2. Myocarditis is suspected on the premise oflifted troponinswithin the patient’s blood, cardiacarrythmias or diffuse STheighton electrocardiogram (ECG) and cleared out ventricular divider movement variations from the norm (territorial or worldwide hypokinesis) on echocardiogram. The clinical introductions of myocarditis incorporate subclinical, subacute, intense and fulminant shapes, and abrupt-onset myocarditis is known to be related with critical seriousness [6].
METHODS
This study using systematic review that search using keyword heart inflammation, myocarditis and covid-19 vaccination in Google Scholar, PubMed, and CrossRef. After final screening the author analysize 5 articles. As in methods, the author summarize 3 articles that mention in Table 1.
DISCUSSION
Viral myocarditis continuously break down the center layer of the heart through myocardial damage activated by incendiary forms [2]. The viral etiology of myocarditis is predominantly detailed within the Joined together States and othercreatedcountriesof the world [1]. Viral myocarditisadvances with virus-mediated cardiomyocyte harm driven by improper enactment of natural and versatile resistant frameworks. The intense, subacute, and incessant stages of viral myocarditis respond with the degree of cardiomyocyte disintegration and versatile safe reactions
The intense stage of myocarditis advances with the intrusion of infection particles into the cardiomyocytes, taken after by their cleavage, repackaging, and connection to MHC (major histocompatibility complex)-1 receptors on the cell film. This occasion is taken after by the official of CD8+ (cytotoxic) T-cells to the class-I MHC particles on virusinfected cardiomyocytes, subsequently actuating apoptosis and ensuing discharge of cardiac and viral antigens (Figure 1) [6]. The authoritative of viral antigen to toll-like receptors (TLRs) on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) actuates NFkBtranslation figure that potentiates the qualities includedwithin the biosynthesis and discharge of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-12), subsequently activating the adaptive safe reactions within the subacute stage. The virusmediated cytotoxicity eventually actuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and early myonecrosis within the tainted quiet [7].
The versatile safe reactions overwhelm the virusmediated cardiomyocyte harm through cellular penetration of lymphocytes amid the subacute stage. The early stages of the subacute stage advance with the dynamic repackaging of viral antigens within the antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and their interaction with MCH-II receptors. The intense stage shows with the connection of antigen-bound MHC II receptors (on APCs) with the CD4+ Aide T cells that triggers numerous versatile safe reactions intercededby proinflammatory cytokines [7].
The hoisted cytokines (IFN-γ and IL-12) initiate Th1 separation and advance assist enactment of macrophages and cytotoxic T cell-mediated harm [8]; in any case, IL12 height potentiates the movement of common executioner (NK) cells. The actuated Th cells tie to the antigen-oriented MHC II receptors on B-cells to advance the arrangement of virus-specific antibodies and autoreactive antibodies against the cardiac antigens and myosin [9]. The late subacute stage shows with the sequestration of viral antigen-oriented actuated dendritic cells by lymph hubs and preparing of naïve T-cells against SARSCoV-2taintedcells [10]. Theunremitting stageof viral myocarditis advances with myocardial fibrosis, heart disappointment, and widened cardiomyopathy (Table 1).
| Author | Origin | Method | Period | Result | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siripanthong B., Nazarian S., Muser D., Deo R., Santangeli P., Khanji M.Y., Cooper L.T., Jr., Chahal C.A.A | William Harvey Research Institute, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London | These perceptions show that c-Met- and CCR4-expressing T cells are enhanced in heart tissue both in steady-state and provocative conditions, recommending that expression of these receptors is instrumental for physiological T cell distribution to the heart and related lymphoid tissue | 2020 | Effector-T-cell-mediated resistance depends on the productive localization of antigen-primed lymphocytes to antigen-rich non-lymphoid tissue, which is encouraged by the expression of a one of a kind set of "homing" receptors procured by memory T cells. c-Met activating was aduate to bolster cardiotropic T cell distribution, where as CCR4 and CXCR3 supported enrollment amid heart aggravation | Temporal pharmacological bar of c-Met amid T cell preparing driven to upgraded survival of heart, but not skin, allografts related with impeded localization of alloreactive T cells to heart unites. These discoveries propose c-Met as a target for improvement of organ-selective immunosuppressive treatments. |
| Teresa Castiello, Georgios Georgiopoulos, Gherardo Finocchiaro,Monaco Claudia, Andrea Gianatti, Dimitrios Delialis, Alberto Aimo, and Sanjay Pras | Department of Cardiology, Croydon Health Service, London, UK | Efficient audit of MEDLINE and Cochrane Library and looked clinicaltrials.gov for unpublished considers testing treatments with potential suggestion for COVID19-mediated cardiovascular complication. | 2022 | Qualified considers had research facility affirmed COVID-19 and a clinical and/ or histological conclusion of myocarditis by ESC or WHO/ISFC criteria. Reports of 38 cases were included (26 male patients, 24 matured < 50 a long time). The primary histologically demonstrated case was a virus-negative lymphocytic myocarditis; be that as it may, biopsy prove of myocarditis auxiliary to SARS-CoV-2 cardiotropism has been as of late illustrated. Histological information was found in 12 cases (8 EMB and 4 autopsies) and CMR was the most imaging methodology to affirm a conclusion of myocarditis (25 patients). There was a considerable changeability in biventricular systolic work amid the intense scene and in restorative regimen utilized. Five patients passed on in clinic. Cause-effect relationship between SARS-CoV-2 contamination and myocarditis is troublesome to illustrate | the scarcity of distributedinformation and the inhomogeneity of the cases, conclusive statement on guess cannot be made. Immunosuppressants are beneath think about and have a method of reasoning in systemic hyperinflammation disorderincluding the heart, but information are constrained. Recuperation trial disheartens the utilize of dexamethasone in quiet not requiring oxygen; be that as it may, devoted sub-studies on myocarditis have not been made. Colchicine in presently beneath examination, but once more, particular impact on myocarditis is as it were a supposition |
| Bhurint Siripanthong, Saman Nazarian, Daniele Muser, Rajat Deo, Pasquale Santangeli, Mohammed Y Khanji, Leslie T Cooper Jr, C Anwar A Chahal | School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom. | Case report | 2020 | Human coronavirus-associated myocarditis is known, and a number of coronavirus infection 19 (COVID-19)–related myocarditis cases have been detailed. The pathophysiology of COVID-19–related myocarditis is thought to be a combination of coordinate viral harm and cardiac harm due to the host’s resistant reaction. COVID-19 myocarditis conclusion ought to be guided by bits of knowledge from past coronavirus and other myocarditis encounter. The clinical discoveries incorporate changes in electrocardiogram and cardiac biomarkers, and impeded cardiac work. When cardiac attractive reverberation imaging isn't attainable, cardiac computed tomographic angiography with postponed myocardial imaging may serve to prohibit noteworthy coronary supply route illness and recognize myocardial fiery design. Since numerous COVID-19 patients have cardiovascular comorbidities, myocardial localized necrosis ought to be considered. | A few cases of coronavirus-related myocarditis have been detailed. Its pathophysiology likely could be a combination of the coordinate viral offended to cardiomyocytes and the human’s safe reaction to virally contaminated myocardium. Straightforward bedside tests such as serial ECG and cardiac biomarkers can raise doubt of acute-onset cardiac indications. Specific consideration ought to be given to biomarkers changes or patterns and not fair readings gotten in separation. Cardiac imaging strategies such as ECG and CMR can be utilized to help determination; be that as it may, recognizing between differential analyze of stress-induced cardiomyopathy, sepsis-related cardiomyopathy, and intense coronary disorder can be troublesome. An intrusive coronary angiogram will regularly be justified, particularly in more seasoned patients. The conclusive determination of myocarditis is gotten through EMB, and in case an intrusive catheterization is to be performed, concomitant EMB would include small time and no assist chance of disease spread vs catheterization |
| Anders Husby | Denmark | Population based cohort study | 2021 | Inoculation with mRNA-1273 was related with a altogether expanded hazard of myocarditis or myopericarditis within the Danish populace, basically driven by an expanded hazard among people matured 12-39 a long time, whereas BNT162b2 inoculation was as it were related with a altogether expanded chance among ladies. Be that as it may, the outright rate of myocarditis or myopericarditis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA immunization was moo, indeed in more youthful age bunches. | The benefits of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination should be taken into consideration when translating these discoveries. Bigger multinational ponders are re- quired to assist explore the dangers of myocarditis or myo-pericarditis after inoculation inside littler subgroups. |
| Elisabeth Albert | Department of Radiology University of Massachusetts Medical School, UMass Memorial Medical Center, | Case Report | 2021 | The coronavirus infection 2019 (COVID-19) immunization regularly leads to minor side-effects, that will be more strongly after the moment dosage, but more genuine side impacts have been detailed. We report a case of a 24-yearold man who displayed to the healing center with intense substernal chest torment, 4 days after his moment COVID-19 Moderna immunization. Research facility ponders uncovered lifted troponins and negative viral serologies. Cardiac attractive reverberation imaging (cMRI) illustrated edema and deferred gadolinium upgrade of the cleared out ventricle in a midmyocardial and epicardial dissemination. The quiet was analyzed with myocarditis taking after Moderna inoculation. Our case report raises concern that myocarditis could be a uncommon side impact of COVID-19 immunization | In spite of our report, it shows up that there's a altogether higher chance of cardiac inclusion from COVID-19 contamination compared to COVID-19 inoculation. |
| Enrico Ammirati | De Gasperis” Cardio Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, Italy | Case Report | 2021 | An something else solid 56-year-old man displayed to the crisis division complaining of intense onset of chest torment 3 days after the moment dosage of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 immunization. | In conclusion, the case report proposes that pharmacovigilance on cardiac damage may well be considered, particularly with suspected or confirmed previous history of COVID-19 pointed to effectively rummage around for intense myocarditis when chest torment or distress is detailed. |
| David Hana | Department of Medicine, West Virginia University School of Medicine, | Survey through PubMed and other detailing frameworks like VAERS for the detailed cardiovascular antagonistic occasions postCOVID-19 inoculation | 2021 | we decided that the rate of all the detailed cardiovascular occasions is exceptionally uncommon. Also, the immunization was at first given to the elderly and high-risk populaces in which cardiovascular occasions such as myocardial localized necrosis and arrhythmias are as of now more predominant, whereas other cardiovascular occasions such as myocarditis or vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia were more common in more youthful populaces. | Additionally, a coordinate causal relationship, in case any, between inoculation and antagonistic occasions is however to be completely illustrated. In this way, at this time point, the benefits of immunization distant exceed the chance. |
The actuated spike (S) proteins of SARS-CoV-2 particles associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) on the target cells to intervene their section into the have framework. The ACE2 receptor expression happens in cardiomyocytes after the interruption of SARS-CoV-2 into the epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract and sortII pneumocytes [12]. The cardiomyocyte harm by SARS-CoV-2 may take after abnormal safe reactions that create in other sorts of viral myocarditis. Future clinical considers still require depicting the pathophysiological forms administering myocardial harm and myocarditis in patients with COVID-19.
The coordinate cell damage and T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity increased by IL-6 intervened cytokine storm (CS) administer the pathophysiology of viral myocarditis [7]. The checked rise within the proinflammatory cytokines counting, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in seriously sick SARS-CoV-2 patients recommends that CS improvement may play an vital part within the clinical movement of COVID-19 [13,14]. The movement of monoclonal-antibody (like tocilizumab) against the IL-6 receptors in COVID-19 pneumonia patients includes to their therapeutic administration within the current situation [15,16].
The clinical thinks about too emphasize the part of the HGF-c-MET (transmembrane tyrosine kinase) pivot within the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 initiated myocardial harm [17]. The localized irritation inside the heart advances with cardiomyocyte discharge of hepatocyte development figure (HGF) and its interaction with the c-MET receptors on naïve T cells in lymph hubs [17,18]. The natural myocardial forms and immune-mediated hyperinflammatory reactions taking after viral presentation moreover decide the patho physiological components of SARS-CoV-2 myocarditis [19].
Figure 1: Screening Flow Chart for Systematic Review.
Administration of Myocarditis due to COVID-19 Contamination or Immunization
The symptomatology of COVID-19 infection-induced or post-vaccine-related myocarditis incorporates shortness of breath, weariness, and chest torment. Patients with tall seriousness myocarditis regularly report the signs of right-sided heart disappointment, counting lifted jugular venous weight, right upper quadrant torment, and fringe edema [20]. Few patients with COVID-19 moreover create extreme diffuse cardiac aggravation driving to fulminant myocarditis, ventricular arrhythmias, and cardiogenic stun. Fulminant myocarditis as a rule creates inside 2-3 weeks of contracting the infection and presents with ventricular brokenness and intense onset of heart disappointment [18]. CDC advocates myocarditis screening for patients who create shortness of breath, chest torment, or palpitations inside 7 days of getting the mRNA COVID-19 immunization [21]. The more youthful patients with COVID-19 indications moreover require myocarditis screening to run the show out their coronary attribution.
Administration of COVID-19 contamination or antibody related myocarditis
The current treatment methodologies supposedly don’t demonstrate advantageous for patients with COVID-19 infection or vaccine-related myocarditis. The current therapeutic administration of COVID-19-related myocarditis depends on corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) to challenge the movement of diffuse non-specific resistant framework enactment [18-27]. The adequacy and security of corticosteroids in COVID-19 scenarios, in any case, warrant encourage examination. The evidence-based myocarditis administration rules by AHA and ESC confine the utilize of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) based on their attribution for renal impedance and sodium maintenance which will worsen intense ventricular/LV systolic brokenness in COVID-19 related myocarditis patients [1,18,23]. The COVID-19 patients may assist require heart disappointment treatment based on their hemodynamic soundness and cardiac yield [19].
The demonstrative examination ought to run the show out fulminant myocarditis in COVID-19 patients with sepsis some time recently regulating intravenous liquid revival to play down the hazard of lethal complications. Besides, cardiogenic stun in fulminant myocarditis regularly goes with ventricular tachyarrhythmias and bradyarrhythmia overwhelmed by a heart square, syncope, and sudden cardiac passing [20]. The current AHA rules advocate the usage of cardiogenic stun administration treatment convention for patients with fulminant myocarditis. The mechanical circulatory bolster by extracorporeal layer oxygenation (ECMO), a ventricular help gadget (VAD), or an intra-aortic swell pump may help the long-term restorative administration of hemodynamically unsteady COVID-19 patients with myocarditis [18].
COVID-19 immunization actuated myocarditis
The clinical information for most patients with myocarditis did not uncover their showing side effects (barring eight patients with chest torment as their displaying complaint) [28,29,30]. The clinical discoveries encourage affirmed myalgia in two patients and fever in one case [28,29]. The information advance clarified the onset of myocarditis in patients after a fewweeks of getting the COVID-19 antibody [31]. The patients detailed myocarditis side effects inside three days of accepting the first/second measurements; be that as it may, most introductions related with the moment measurements of the COVID-19 antibody. The understanding we examined created myocarditis indications inside two days of accepting the COVID-19 immunization. The therapeutic writing uncovered COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis patients inside the age gather of 20-30 a long time, not at all like our understanding, who had completed her 6th decade of life.
The persistent we examined displayed with T-wave reversals that coordinated the ECG discoveries recorded for three cases within the therapeutic writing. We assist taken note T-wave reversals in two patients [28,31] and ST-segment height in twelve of the detailed seventeen cases. The ECG discoveries assist related with the cardiac biomarker heights and serum troponin peaks at changing levels within the enrolled patients. The discoveries from our quiet at first uncovered a typical troponin level that along these lines trended upwards amid her therapeutic management. The seventeen cases we recovered from the restorative writing displayed with a protected discharge division, barring one persistent who created apical hypokinesia [28].
The persistent we overseen displayed a essentially diminished launch division (10%) and cleared out ventricular dyskinesia. She had a restricted pretest likelihood for ACS within the nonattendance of cardiac hazard variables. The persistent declined cardiac catheterization in spite of the therapeutic suggestion. We advance taken note cardiac catheterization attempted for thirteen out of seventeen patients enlisted within the therapeutic writing. The patients who gotten cardiac catheterization had no history of coronary course illness. The raised cardiac markers and chest pain demonstrated to be the most noteworthy confounders within the symptomatic appraisal of myocarditis. We managed obtrusive mechanical ventilation and vasopressor bolster to our understanding unguided by a cardiac MRI. The seventeen cases detailed in therapeutic writing, in any case, gotten cardiac MRI during their restorative administration. Our discoveries advance uncovered a stamped height within the procalcitonin level (185ng/mL) of the myocarditis persistent.
CONCLUSION
The results of this case situation affirm myocarditis as a plausible complication of COVID-19 antibodies. The differential evaluation of patients with COVID-19 immunization status and side effects of intense cardiac decompensation must run the show out myocarditis to maintain a strategic distance from deadly complications. An early conclusion is key to play down COVID-19 vaccine-related misfortunes and make strides the therapeutic administration of patients suspected of myocarditis. In addition, the author will continue to support halal treatment based on the Qur’an and Sunnah in the intervention against Covid-19 which is much safer and is blessed by Allah SWT and Rasulullah Muhammad.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The author would like to say alhamdulillah, sholawat and hopefully continue to be devoted to the great prophet Muhammad and his family. The author would also like to thank Maryam and Isa Clinic and beloved mom and dad for their support so far
REFERENCES
1. Santoso A, Pranata R, Wibowo A, Al-Farabi MJ, Huang I, Antariksa B. Cardiac injury is associated with mortality and critically ill pneumonia in COVID-19: A meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2021; 44: 352-357.
2. Tian W, Jiang W, Yao J, Nicholson CJ, Li RH, Sigurslid HH, et al. Predictors of mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virology. 2020; 92: 1875-1883.
3. Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S, et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020; 368: l6890.
4. Ogilvie D, Fayter D, Petticrew M, Sowden A, Thomas S, Whitehead M, et al. The harvest plot: a method for synthesising evidence about the differential effects of interventions. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008; 8: 8.
5. Cooper LT Jr, Keren A, Sliwa K, Matsumori A, Mensah GA. The global burden of myocarditis: part 1: a systematic literature review for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors 2010 study. Glob Heart. 2014; 9: 121–129.
6. Shi S, Qin M, Shen B, Cai Y, Liu T, Yang F, et al. Association of Cardiac Injury With Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiology. 2020; 5: 802-810.
7. Guo T, Fan Y, Chen M, Wu X, Zhang L, He T, Wang H, Wan J, Wang X, Lu Z (2020) Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020; 5: 811-818.
8. Bonow RO, Fonarow GC, O’Gara PT, Yancy CW. Association of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with myocardial injury and mortality. JAMA Cardiol. 2020; 5: 751-753.
9. Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020; 17: 259–260.
10.Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46: 846–848.
11.Peretto G, Sala S, Caforio ALP. Acute myocardial injury, MINOCA, or myocarditis? Improving characterization of coronavirus-associated myocardial involvement. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41: 2124–2125.
12.Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Jiang C, Liu PP, Poutanen SM, Penninger JM, et al. SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009; 39: 618– 625.
13.Escher F, Pietsch H, Aleshcheva G, Bock T, Baumeier C, Elsaesser A, et al. Detection of viral SARS-CoV-2 genomes and histopathological changes in endomyocardial biopsies. ESC Heart Failure. 2020; 7: 2440–2447.
14.Wan S, Yi Q, Fan S, Lv J, Zhang X, Guo L, Lang C, Xiao Q, Xiao K, Yi Z, Qiang M, Xiang J, Zhang B, Chen Y (2020) Characteristics of lymphocyte subsets and cytokines in peripheral blood of 123 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP).
15.Liu T, Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang L, Ma H, Li Z, Zhang J, Cheng J, Zhang X, Wu G, Yi J. The potential role of IL-6 in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019. 2020.
16.Gong J, Dong H, Xia S, Huang Y, Wang D, Zhao Y, et al. Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19: : a retrospective study. BMC Infect Dis. 2020; 20: 963.
17.Basso C, Aguilera B, Banner J, Cohle S, d’Amati G, de Gouveia RH, et al. Guidelines for autopsy investigation of sudden cardiac death: 2017 update from the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology. Virchows Arch. 2017; 471: 691-705.
18.Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, Basso C, Gimeno-Blanes J, Felix SB, et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. 2013; 34: 2636-2648.
19. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020; 395: 1054–1062.
20.Calabrese LH. Cytokine storm and the prospects for immunotherapy with COVID-19. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020; 87: 389-393.
21.Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020; 395: 1033–1034.
22.Friedrich MG, Sechtem U, Schulz-Menger J, Holmvang G, Alakija P, Cooper LT, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in myocarditis: A JACC White Paper. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 53: 1475–1487.
23.Baughman KL. Diagnosis of myocarditis: death of Dallas criteria. Circulation. 2006; 113: 593–595.
24.Bracamonte-Baran W, ?iháková D. Cardiac autoimmunity: myocarditis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017; 1003: 187–221.
25.Fujioka M, Suzuki K, Iwashita Y, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Ito M, Katayama N, et al. Influenza-associated septic shock accompanied by septic cardiomyopathy that developed in summer and mimicked fulminant myocarditis. Acute Med Surg. 2019; 6: 192–196.
26.Basso C, Leone O, Rizzo S, De Gaspari M, van der Wal AC, Aubry M-C, et al. Pathological features of COVID-19-associated myocardial injury: a multicentre cardiovascular pathology study. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41: 3827–3835.
27.Wenzel P, Kopp S, Göbel S, Jansen T, Geyer M, Hahn F, et al. Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA in endomyocardial biopsies of patients with clinically suspected myocarditis tested negative for COVID-19 in nasopharyngeal swab. Cardiovasc Res. 2020; 116: 1661–1663.
28.Wichmann D, Sperhake JP, Lütgehetmann M, Steurer S, Edler C, Heinemann A, et al. Autopsy findings and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2020; 173: 268–277.
29. Xiong TY, Redwood S, Prendergast B, Chen M. Coronaviruses and the cardiovascular system: acute and long-term implications. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41: 1798–1800.
30.Merken J, Hazebroek M, Van Paassen P, Verdonschot J, Van Empel V, Knackstedt C, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy improves both shortand long-term prognosis in patients with virus-negative nonfulminant Utami AT (2022) Association of Heart Inflammation after Covid 19 Vaccination: The Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Vasc Med Res 9(1): 1181. Cite this article inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2018; 11: e004228.
31.RECOVERY Collaborative Group; Peter Horby, Wei Shen Lim, Jonathan R Emberson, Marion Mafham, Jennifer L Bell, Louise Linsell, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19 — preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384: 693-704.