Computer Aided Surgery: Application to Aortic Dissection
- 1. LaMCoS, INSA de Lyon, UMR5259, University of Lyon, 69100 Villeurbanne, France
- 2. Univ Lyon, INSA de Lyon, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, UCBL1, CNRS, LMFA, UMR 5509, F-69621, Villeurbanne, France
- 3. CISTEN, 66 Bd. Niels Bohr, 69603 Villeurbanne, France
- 4. Hôpital Louis Pradel HCL 59 Boulevard Pinel, 69500 Bron
Abstract
In cardiovascular disease, aortic dissection is relatively unknown and difficult to treat. Endovascular treatment seeks to obliterate the entrances to the false lumen with a stent. The currently available surgical tools for endovascular procedures are selected only from information based on medical imaging techniques. The images are carried out before the intervention and therefore do not consider the deformation of the vascular structure by the implementation of the prosthesis. While many biomechanical studies have been done on the endovascular treatment of aneurysms of the abdominal aorta, there are, however, very few such studies on aortic dissections. This paper aims to present a numerical tool, from the open-source software FOAM-Extend®, allowing for Multiphysics numerical simulations performing the fluid-structure coupling between the hemodynamics and the arterial deformation to assist in the planning process. And, in addition using Abaqus software we realize the placement of the surgical tools in a ‘biomecano-faithful’ model.
Keywords
Cardiovascular diseases; Aortic dissection; Hemodynamics; Fluid/Structure Interaction
Citation
Pan W, Kulisa P, Escriva X, Bou-Saïd B, Menut M, et al. (2020) Computer Aided Surgery: Application to Aortic Dissection. Ann Vasc Med Res 7(5): 1120
ABBREVIATIONS
CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamic; FSI: Fluid Structure Interaction; WSS: Wall Shear Stress
INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality in the industrialized world [1]. Among these diseases, aortic dissection is relatively unknown and difficult to treat, with a survival rate for most severe cases not exceeding 10%. This pathology occurs when an injury leads to a localized tear of the innermost layer of the aorta, called the entry port. It allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart and creating a false lumen. The dissection of these layers may extend over a long portion of the thoracic and abdominal aorta. There are several types of dissection classified according to the Stanford Classification (Daily PO 1970).While type A dissection is a clinical emergency and associated with high mortality, type B dissection differs in that the surgeons must choose the method of intervention. Type B is more conducive to endovascular treatment, which seeks to obliterate the false lumen entrance with a stent. Poor redistribution of flow can be harmful to the patient’s health, and the implementation of a stent in the aortic cross-region has significant technical difficulties due to the angulation and the extent of the diseased area. Surgical planning for this procedure is based on medical imaging carried out before the intervention [2]. Therefore, it does not consider the deformation of the vascular structure during the operation, which can lead to a bad sizing and poor positioning of the stent. Looking at the literature, we found that Karmonik et al. [3], have treated this problem, but they use nonrealistic boundary conditions, and they suppose that the structure is rigid. Benfanti et al. [4], have also considered a Newtonian flow when Menut et al. [5], show that this hypothesis is rough. Chen et al. [6], work concerns a non bio-faithful model. Qiao et al. [7], consider the hemodynamic as two phase flow and neglect the shear thinning effect and viscoelastic properties of blood as well. Alimohammadi et al. [8], present interesting work but using non-personalized data. Our aim is to develop a patient-specific numerical analysis, which considers the wall distortion and Newtonian behavior of the blood with realistic boundary condition and patient-specific framework.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fluid-structure interaction without prosthesis
Based on the results of studies already carried out and MRI scans of an affected patient, a numerical FSI model was developed. FSI modeling is often used in the study of cardiovascular medicine [9]. Two different methodologies are usually used to solve the system, which are Monolithic and Partitioned methods (Michler et al. 2004). For this study, from the numerical point of view, we used the partitioned approach. Computational Fluid Dynamic simulations of blood flow in a type B aortic dissection were performed. Navier-Stokes equations for an incompressible fluid were solved using the OpenFOAM® solver. Rigid wall and laminar flow were considered in a first step. In a second step, the inverse method was used to identify the mechanical properties of the artery and thanks to a Mooney Rivlin model we consider the deformability of the structure [8]. A simplification is made for these preliminary calculations by considering isotropic and elastic media [8,9]. The three-element Windkessel model was applied to account for flow resistance encountered by the blood and a Poiseuille velocity profile at the inlet was based on a clinical data of the patient pulsatile flow rate [9]. It has been established [9] that the systolic part can be simplified by considering a Newtonian fluid and a laminar regime hypothesis. The structure was fixed at the entrance and outlet. In the numerical simulation, several calculations were performed using OpenFOAM® software during several cardiac cycles to guarantee the convergence. In FOAM-Extend®, the solver to realize the FSI simulation uses strong coupling with the partitioned approach.
Simulation of tools insertion
Modeling the tools’ insertion is a non-linear numerical problem, mainly due to numerous contacts between deformable, tortuous, heterogeneous bodies, and large deformations of complex materials such as arterial tissue. For this study, the Abaqus© software with an explicit diagram is used for the numerical calculations. According to [10], an implicit analysis leads to several months’ calculation times, linked mainly to the evaluation and costly inversion of the stiffness matrix. Compared to an implicit method, an explicit temporal integration scheme leads to more reasonable calculation times and guarantees more robustness in terms of numerical stability (better contact management). With Abaqus© we treat the complex contact between the aorta and the surgical tools. Next, we show the results of numerical simulations performed only in structural calculations, without considering the hemodynamic effects on the wall.
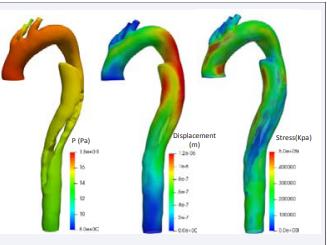
As for the simulation of fluid-structure interaction, it is necessary in the case of tools insertion to firstly create a numerical bio-faithful model. Next, we hypothesize an elastic behavior with Young’s modulus of 4.66Mpa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.45 for the dissection. The rest of the aorta is modeled with an elastic behavior with Young’s modulus of 3Mpa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.45 [8]. In addition, we used from previous work [11] the mechanical properties of the tools. The modeling of the environment surrounding aorta tissue is rarely studied in the literature. But, in the context of the study of Menut [10-13], which has chosen to model the areas of attachment of the aorta at the level of the spine by springs whose stiffness allows them to get as close as possible to intraoperative aortic deformation (Figure 2).
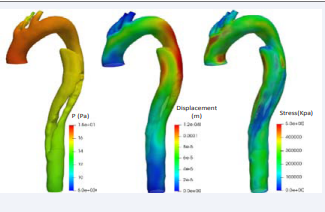
Figure 2: FSI simulation at systolic pressure with a Young modulus of the structure at 300MPa (Left: fluid pressure; Center: solid displacement; Right: WSS.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We did a whole completely cardiac cycle for two simulations with different Young modulus values of the structure. Figure 1
Figure 1: FSI simulation at systolic pressure with a Young modulus of the structure at 30 GPa (Left: fluid pressure; Center: solid displacement; Right: WSS.
shows the results of FSI simulation at systolic pressure with a Young modulus of the structure at 30 GPa, which can represent a highly calcified wall. The obtained result in terms of pressure is higher than those obtained in the literature [8] because of different factors: patient-specific data and realistic boundary conditions.
Simulation of tools insertion
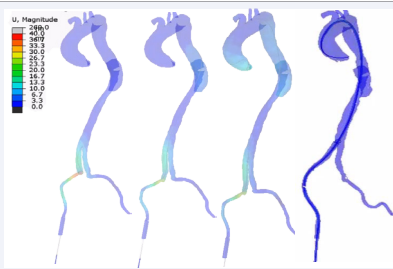
Figure 3
Figure 3: Movements observed on the aorta according to the simulation of tool insertion.
shows that firstly the rigid guide inserts in the aorta to lead the rest of the surgical tools inserted in the aorta. Numerical simulations of catheter rise begin after insertion of the rigid guide.
CONCLUSION
The characterization of blood behavior with the deformability of the arterial wall is a first step into the surgical procedure simulation. Numerical predictions will allow the surgical team to choose surgical tools and stent and identify its most suitable positioning for each patient. With these calculations, it was possible to obtain the information concerning the flow around aortic dissection and compare different cases to find an effective method on the stent position in the aorta. This research project aims to develop a numerical tool to predict the consequences of these changes in flow, hence assisting in the surgical planning process. In the next future, we will perform the numerical simulation for the stent deployment to compare with the clinical images to validate our simulations, which we will present in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the China Scholarship Council.
REFERENCES
- OMS. 2016. Rapport sur la situation mondiale des maladies non transmissibles. 2015.
- Daily PO, Trueblood HW, Stinson EB, Wuerflein RD, Shumway NE. Management of acute aortic dissections. Ann Thorac Surg. 1970; 10: 237-247.
- Anne Amblard, Hélène Walter-Le Berre, Benyebka Bou-Saïd, Michel Brunet. Analysis of type I endoleaks in a stented abdominal aortic aneurysm. Med Eng Phy. 2009; 31: 27-33.
- C Karmonik, J Bismuth, D J Shah, M G Davies, D Purdy, A B Lumsden. Computational Study of Haemodynamic Effects of Entry- and Exit-Tear Coverage in a DeBakey Type III Aortic Dissection: Technical Report. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; 42: 172-177.
- Mirko Bonfanti, Stavroula Balabani, John P Greenwood, Sapna Puppala, Shervanthi Homer-Vanniasinkam, Vanessa Díaz-Zuccarini, et al. Computational tools for clinical support: a multi-scale compliant model for haemodynamic simulations in an aortic dissection based on multi-modal imaging data. J R Soc Interface. 2017; 14: 20170632.
- M Chen. Chirurgie endovasculaire virtuelle pour patient-spécique: application au traitement de l'anévrisme de l'aorte thoracique. Thesis. INSA Lyon. 2016.
- H Y Chen, S V Peelukhana, Z C Berwick, J Kratzberg, J F Krieger, B Roeder, et al. Editor's choice–fluid–structure interaction simulations of aortic dissection with bench validation. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016; 52: 589-595.
- Qiao Y, Zeng Y, Ding Y, Fan J, Luo K, Zhu T. Numerical simulation of two-phase non-Newtonian blood flow with fluid-structure interaction in aortic dissection. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019; 22: 620-630.
- Mona Alimohammadi, Joseph M Sherwood, Morad Karimpour, Obiekezie Agu, Stavroula Balabani, Vanessa Díaz-Zuccarini. Aortic dissection simulation models for clinical support: fluid–structure interaction vs. rigid wall models. Biomed Eng Online. 2015; 14: 34.
- M Hirschhorn, V Tchantchaleishvili, R Stevens, J Rossanoe, A Throckmorton. Fluid-structure interaction modelingin cardiovascular medicine–A systematic review 2017–2019. Med Eng Phy. 2020.
- C Michler, S Hulsho, E Van Brummelen, R.de Borst. A monolithic approach to fluid-structure interaction. Computers & Fluids. 2004; 33: 839-848.
- Amblard A, B Bou-Saïd. Modelling the blood flow in an aorta; the MPTT and Modified MPTT models. Tribol Interf Eng Series. 2005; 48: 381-387.
- Marine Menut, Benyebka Bou-Said, Helene Walter-Le Berre, Philippe Vézin, Leila Ben Boubaker. Characterization of the Mechanical Properties of the Human Aortic Arch Using an Expansion Method. J Vasc Med Surg. 2015; 3: 4.