Neoplastic Transformation of Odontogenic Cyst
- 1. Department of Dentistry, Sagrado Coração University, Brazil
Abstract
A 16-year old boy received the diagnosis of plexiform solid ameloblastoma after a second biopsy of a radiolucent lesion located around the crown of tooth 38, previously treated as an odontogenic cyst. Due to the degree of invasiveness of the odontogenic tumor, the treatment of choice was partial resection of the mandible. Twenty months after the surgery, the patient is under orthodontics treatment for a further oral rehabilitation with autogenous bone grafts and dental implants. This report reinforces the necessity of criteriously observation and conduction of non-erupted teeth, exhaustively being emphasized in literature
Keywords
• Ameloblastoma
• Odontogenic cysts
• Odontogenic tumors
Citation
Ribeiro Junior PD, da Silva WS, Abiati RP, Kawakami RY, da Silva AA, et al. (2016) Neoplastic Transformation of Odontogenic Cyst. Clin Res Infect Dis 3(1): 1022.
INTRODUCTION
Odontogenic cysts are known to originate from odontogenic epithelium, which presents particular behavior being able to participate, along with the neural crest derived mesenchyme (ectomesenchyme) of enamel, dentin and root development. During early tooth formation, oral epithelium proliferates and invades the ectomesenchyme to originate tooth germ, and also tooth’s root by Hertwig’s epithelial sheath. In this process, some epithelial cells suffer apoptosis and some of them remain throughout the bone, giving rise to the gubernaculum dens, and periodontal ligament, known as epithelial rests of Malassez [1]. In addition, inner epithelium of enamel organ differentiates into ameloblasts for enamel secretion and maturation, undergoing morphological changes, from tall secretor to cubic and quiescent cells, lining the dental follicle and protecting enamel until tooth eruption. Some changes can happen until tooth crown erupts, leading to cystic transformation of this epithelium. Inflammation can induce cystic transformation of the dental follicle leading to the development of the inflammatory paradental cyst, usually associated to semi-erupted third molars. However, non-defined etiology cysts are considered of developmental origin, such as the dentigerous cyst.
Literature points out the potential of the development of some odontogenic neoplasms from the epithelial lining of the dentigerous cyst, including adenomatoid odontogenic tumor [2,3] and, more often, ameloblastomas [4,5], first described by Cahn [6], in 1933. In this way, especial attention should be taken to those individuals presenting non-erupted teeth in order to avoid major consequences from the evolution of these lesions. However, some controversies exist about the possibility of such ameloblastomatous transformation, especially because of the lack of microscopic criteria and radiographic similarities with other lesions [7].
Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma (PIOSCC) is a rarely reported neoplasm arising in the mandible or maxilla from residual odontogenic epithelium, initially without contact with the oral mucosa. Diagnosis of PIOSCC might be made only when primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the oral mucosa is excluded as well as SCC of the paranasal sinuses or skin and metastatic tumours from malignant neoplasms localized in distant sites. There are three subtypes of PIOSCC: 1 – solid SCC, 2 – SCC arising from the lining of a dentigerous cyst, and 3 – SCC from a keratocysticodontogenictumour (KCOT) or other benign epithelial odontogenic tumours [8].
The aim of this study is to present a case of a solid ameloblastoma arising from the wall of a cystic lesion in the mandible, based on evidences from the literature.
CASE PRESENTATION
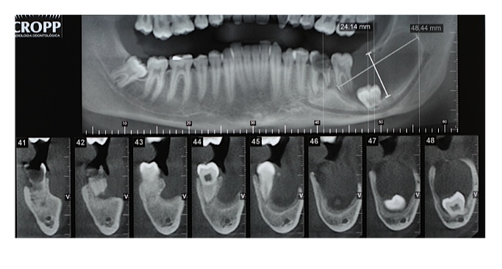
A 16-year old boy was referred to the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery clinic of Sagrado Coração University, Bauru, Brazil, searching for treatment of a lesion located in the left side of his mandible. He reported a previous biopsy two years back with the diagnosis of odontogenic cyst, which was decompressed in two different moments, without success. He presented a slight face asymmetry because of an edema of the left side of the mandible. Intra-oral examination also revealed swelling of left retro-molar area, absence of tooth 38 and an active fistula in the alveolar mucosa draining purulent secretion. Tooth 36 presented a large carious lesion non-responsive to thermal pulp test. Panoramic radiography taken before the first decompression procedure revealed a large unilocular radiolucency involving the crown of tooth 38, which was pushed down to the base of the mandible, involving the apical area of tooth 36 presenting root resorption, towards the ramus of the mandible. A cone beam tomography was requested and revealed bone formation involving the apices of tooth 36 and part of the ascending mandibular ramus resulting in a 4.9 x 2.5 cm lesion, which excluded the hypothesis of periapical inflammatory lesions caused by pulp necrosis (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Radiolucent area involving the apices of tooth 37 and the crown of 38, extending to mandibular ramus
Antibiotic therapy was provided in order that infectious inflammation did not interfere in tissue morphology and a new incisional biopsy was performed, with the diagnosis of plexiform solid ameloblastoma. The patient and his parents were informed about the treatment modalities and the related prognosis, and partial resection of the mandible was chosen.
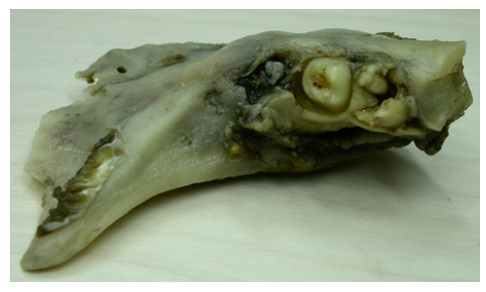
Tridimensional reconstruction image was obtained from the tomography, along with the confection of a prototype of the mandible to offer more details of the extensions and dimensions of the pathology, permitting a more reliable surgical planning, and also to facilitate previous plate conformation and its adaptation. Surgical procedure was performed under general anesthesia, and no intercurrence was registered (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Occlusal view of the resected mandible showing the invasiveness of the ameloblastoma
Post-operatory panoramic and PA of the mandible radiographs revealed a satisfactory reconstruction plate adaptation.
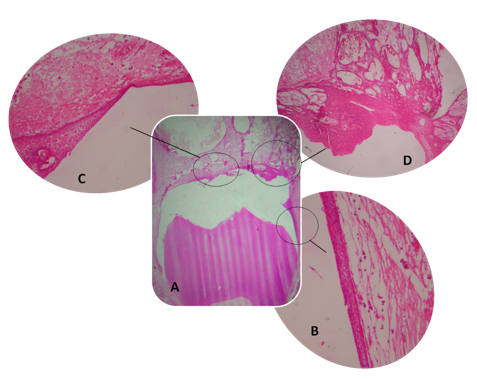
Histopathology revealed the crown of tooth 38 surrounded by a cystic lesion lined by a thin stratified epithelium in the most cervical region, sustained by a loose connective tissue presenting eventual mononuclear leukocytes. As long as the epithelial lining directed toward the occlusal region, it became thicker, and cells’ cytoplasm became vacuolated, until a proliferative invasive neoplasm was seen, arranged in islands or network of columnar hyperchromatic cells, among a tissue resembling stellate reticulum, characterizing both follicular and plexiform pattern [8] (Figure 3).
Figure 3: A) Cystic space surrounding the crown of tooth 38 lined by a transforming epithelium; B) regular squamous stratified epithelium, sustained by a connective tissue presenting eventual mononuclear leukocytes; C) hyperplasic epithelium, presenting some vacuolated cells; D) neoplastic proliferation of the odontogenic epithelium
The margins of the resected mandible were free of the disease.
At the moment, the patient is under a 30-month post-operatory observation, under orthodontics therapy for further oral rehabilitation with autogenous bone graft and endosseous implants.
DISCUSSION
Neoplastic transformation of the dentigerous cyst into unicystic or solid ameloblastoma is somewhat controversial, although this occurrence has been eventually reported [4,5]. The incidence of PIOSCC derived from odontogenic lesions is complicated to determine. If the disease is not in its early stages, it is difficult to demonstrate the actual site of malignant transformation. At later stages, the carcinoma may destroy the structures of the original lesion [8,9].
Radiographic and histological aspects are pointed out as the main causes of misdiagnosis. According to Shear and Speight [7] (2011), such transformation is not possible, and the fact of a lesion is observed involving the crown of a non-erupted tooth, or an incisional biopsy taken from an area of thin lining epithelium of a unicysticameloblastoma, should be the main reasons for these mistakes. Along with these considerations, distinction among cystic lesions of the jaws is challenging due to the similarities that can be found in the epithelial lining [10,11]. However, in order to clarify and orientate histological diagnosis, McMillan and Smillie [12] (1981) reviewed five cases of solid ameloblastoma arising from the wall of dentigerous cysts, identifying common microscopic characteristics amongst them, including stratified squamous epithelium cystic lining sustained by a connective tissue with a moderate mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate. Similar features were described by Dunsche et al. [13] (2003) in a histological analysis of 101 cystic lesions removed from the mandibular third molar region diagnosed as dentigerous cysts, discarding the possibility of misdiagnosis with unicysticameloblastomas when two sections are examined. In their review, 68.3% of all cystic lesions presented inflammatory infiltrate. Immunohistochemistry evidences suggest that inflammation alters proliferative potential of odontogenic cysts epithelial lining by the release of growth factors and cytokines [14,15].
Although in the present case the patient had previously undergone two decompression procedures, and the fact that the lesion had been infected, a clear morphology of the dentigerous cyst lining epithelium could be seen from the most cervical region of crown of the involved tooth, similar to those presented by McMillan and Smillie [12] (1981). No ameloblastomatous cells were observed in the cervical lining, or proliferative nodules projecting into the cyst lumen in a plexiform fashion [16]. Cell vacuolization was noted as the lining was seen toward the occlusal region, but no columnar, pre-ameloblasts-like cells were detected. However, some compression of the cystic lining may occur, as previously cited by Shear and Speight [7] (2011), altering tissue morphology. Nimonkar et al. [5] (2012) also presented three cases of ameloblastomas arising from dentigerous cyst, and although no description of the cysts were given, the corresponding figures presented the same characteristics as ours.
Despite all the discussion found in literature on the origin of the ameloblastomas, the fact is that odontogenic cystic lesions, specially the follicular ones, represent a “source” for the development of epithelial odontogenic tumors. The present case is in accordance with what have been presented in literature, and reinforces the necessity of careful examination and follow up of individuals presenting non-erupted teeth, recommending their extraction as soon as possible, along with the histological analysis of the pericoronary tissue for the investigation of occult pathologies.