Intestinal Absorption of Vitamin a and Short Bowel Syndrome
- 1. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Akita University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
- 2. Department of Cell Biology and Morphology, Akita University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan
Abstract
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is required for many physiological activities. Short bowel (SB) syndrome is caused by resection of a large part of the small intestine due to various diseases, and SB patients suffer from insufficient absorption of every kind of nutrient, including proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins.
Among them, vitamin A has a trophic effect on intestinal epithelial cells, facilitating “intestinal adaptation”. In this short review, we introduce studies reported thus far regarding vitamin A absorption using SB model animals. Histological and physiological changes caused by small bowel resection are now understood at the molecular level. More detailed understanding of the effects of major bowel resection on nutrient absorption, especially of vitamin A, will contribute to improved management of SB syndrome in the future.
Keywords
Short bowel syndrome; Vitamin A; Cellular retinol-binding protein II; 14 Lecithin; Retinol acyltransferase.
Citation
Hebiguchi T, Mezaki Y, Morii M, Watanabe R, Yoshino H, et al. (2014) Intestinal Absorption of Vitamin A and Short Bowel Syndrome. JSM Cell Dev Biol 2(2): 1012.
ABBREVIATIONS
REs: Retinyl Esters; SB: Short Bowel; CRBP II: Cellular RetinolBinding Protein II; LRAT: Lecithin: Retinol Acyltransferase; CMs: Chylomicrons; Apo: Apolipoprotein; SB: Short Bowel; PPAR: Peroxisome-Proliferator Activated Receptor; RXR: Retinoid X Receptor; FABP: Fatty Acid Binding Protein; ILBP: Lipid Binding Protein
VITAMIN A ABSORPTION IN THE INTESTINE
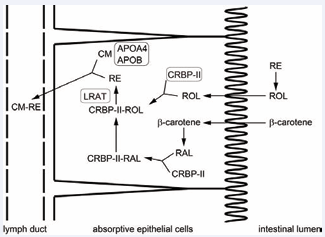
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin needed for many physiological activities. Animals, including humans, cannot synthesize vitamin A within their bodies. Therefore, they obtain vitamin A from food (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Vitamin A absorption and transport in the intestine.
Abbreviations: APOA4: Apolipoprotein A-IV; APOB: Apolipoprotein B; Cms: Chylomicrons; CRBP II: Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein II; LRAT: Lecithin:Retinol Acyltransferase; RAL: Retinal; Res: Retinyl Esters; ROL: Retinol.
Retinyl esters (REs) are animalderived forms of vitamin A. They are hydrolyzed to retinol in the lumen of the small intestine and then absorbed. β- carotene is a vegetable-derived form of vitamin A. It enters absorptive epithelial cells, after which it is converted to retinal [1]. Both retinol and retinal bind to cellular retinol-binding protein II (CRBP II, gene symbol Rbp2) in the absorptive epithelial cells, forming a retinol/retinal-CRBP II complex. CRBP II-bound retinal is reduced to retinol. The CRBP II-bound retinol thus produced is esterified to REs by a vitamin A-esterifying enzyme, lecithin: retinol acyltransferase (LRAT). REs are then discharged basolaterally into lymphatics as a component of chylomicrons (CMs) and delivered to the liver via general circulation [2]. CMs are lipoprotein particles with the lowest density and the largest size. Apo lipoprotein (apo) A-I, II, IV and apo B-48 reside on the surface of the CMs. CRBP II comprises approximately 1% of the total soluble protein in the intestinal mucosa. CRBP II plays an important role in vitamin A homeostasis [3].
SHORT BOWEL SYNDROME AND VITAMIN A
Short bowel (SB) syndrome is caused by resection of a large part of the small intestine due to various diseases [4]. SB patients suffer from insufficient absorption of every kind of nutrient, including proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins. Specifically, vitamin A deficiency was reported in patients with a history of intestinal surgery such as intestinal bypass and bowel resection [5]. After surgical resection of the small intestine, the intestinal cells proliferate to increase crypt depth and also the length and width of the villi. This phenomenon is called “intestinal adaptation”, and it increases absorptive capacity [6]. Vitamin A is trophic to the intestine, enhancing the intestinal adaptation [7]. Deficiency of vitamin A may have negative consequences for adaptation.
In this short review, we introduce studies reported thus far analyzing changes in expression levels of factors which are involved in vitamin A absorption using SB model animals.
RODENT SB MODEL
Rubin et al. reported that 48 h after resecting 70% of the small intestine in rats, mRNAs levels for apo A-IV (Apoa4) and fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 2 (Fabp2) were increased in the adaptive remnant ileum compared with shams. They also reported that increased Apoa4 mRNA levels were maintained for one week after resection compared with controls [8]. Moreover, Dodson et al. reported that ileal lipid binding protein (ILBP) mRNA levels were also increased in the adaptive remnant ileum [9]. ILBP, now called FABP6 (Fabp6), strongly binds to conjugated bile acids and is thought to be involved in enterohepatic circulation of bile acids [10]. They also reported that intestinal adaptation was facilitated by retinoic acid, an active form of vitamin A. Intravenous administration of retinoic acid has trophic effects in SB rats by stimulating crypt cell proliferation [7]. Based on these previous reports, we confirmed the elevated expression levels of Rbp2 and Apoa4 mRNAs in SB rats compared to shams [11]. We observed a reduction of vitamin A content in the intestine of SB rats, in spite of the up regulation of Rbp2 mRNA.
In addition to Rbp2 mRNA, the expression levels of Apoa4 mRNA in SB rat intestine were significantly higher than in sham animals. Thus, the up regulation of Apoa4 mRNA might lead to enhanced transport of vitamin A from the absorptive epithelial cells to the lymphatics, resulting in a reduction of vitamin A content in the intestine of SB rats. In spite of the 75% resection of the intestine, our quantitative analysis showed no significant differences in the contents of retinol or REs in SB and sham rat livers, the major storage organ for vitamin A. These data may be explained by the functional adaptation of the SB rat intestine mediated by the up regulation of Rbp2 and Apoa4 mRNAs. Our results suggested that both esterification and transport of vitamin A in absorptive epithelial cells in the small intestine were accelerated in order to compensate for the reduction of the absorptive area by massive bowel resection.
RODENT JEJUNAL BYPASS MODEL
Takase and her colleagues previously reported that jejunal bypass surgery led to a marked increase in the amounts of CRBP II in the residual jejunal segment of rats [12].They also mentioned an increase of apo B proteins in the ileum, suggesting that absorption of fat-soluble compounds is upregulated in the absorptive epithelial cells in accord with upregulation of vitamin A absorption.
PIGLET SB MODEL
Using a piglet SB model, Stephens et al. reported that protein levels of apo A-IV, FABP1, FABP2 and FABP6 were upregulated in SB piglet intestine compared to shams [13]. FABPs are involved in intracellular transport of lipophilic substances such as fatty acids and retinoids. Therefore, upregulation of FABP protein levels may contribute to vitamin A absorption in the intestine. Pereira-Fantini et al. reported that composition of bile acids was altered in the SB piglet model [14]. Bile acids facilitate absorption of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins. Compositional changes in bile acids may affect vitamin A absorption in the intestine.
SUMMARY
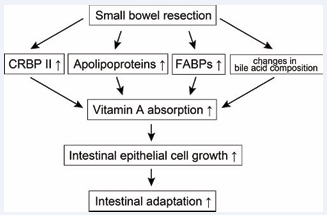
In summary, histological and physiological changes caused by small bowel resection are now understood at the molecular level (Figure 2).
Figure 2: A proposed schema suggesting a potential impact of bowel resection on vitamin A absorption and subsequent intestinal adaptation. See text for details.
More detailed understanding of the effects of major bowel resection on nutrient absorption, especially for vitamin A, will contribute to improved management of SB syndrome in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 23592623, 25504001, 23590228.