Natural Molecules as IKK a or b Inhibitors useful in the Treatment of Inflammation
- 1. Institute of Biomedicine and Molecular Immunology “Alberto Monroy”, National Research Council, Italy
Abstract
Recently, there is a renewed interest in natural molecules used as protein kinase inhibitors with therapeutic potential. The possibility of obtaining these inhibitors from plants or vegetables, more safe compared to the synthetic one, represents a good target for the health demand. Natural compounds have been discovered to be effective in many disease treatments. Among these compounds are polyphenols and other natural molecules. They have been found to be able to interfere with many disease-related biochemical processes in vitro. They are capable of suppressing inflammation, tumor growth, bacterial infection, and virus infection. Thus, they have drawn great attention on the potential effects on disease prevention and treatment of carcinogenic, obesity, diabetic, and Alzheimer’s diseases. In this review, the potential of natural molecules is elucidated in detail with an overview of recent researches and these studies would suggest that IKK inhibitors could be excellent new therapeutics.
Keywords
Inhibitory kappa B kinase, Nuclear factor kappa B, Kinase inhibitors, Phytochemical, inflammation
CITATION
Lampiasi N, Montana G (2016) Natural Molecules as IKK α/b Inhibitors useful in the Treatment of Inflammation. JSM Cell Dev Biol 4(1): 1018.
ABBREVIATIONS
IKK: IκB Kinase; LPS: Lip Poly Saccharide; NEMO: NF-κB Essential Modifier; IL6: Inter Leukin 6; TNFα: Tumor Necrosis Factor
INTRODUCTION
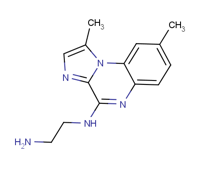
The IKK kinase β complex is one of the most studied of all protein kinases and it consists of the protein kinases IKKα and IKKβ (also called IKK-1 and IKK-2) with a regulatory component called NEMO (NF-κB essential modifier) [1,2]. It has featured in over 10.000 papers since its discovery in 1998 due to its essential role in activating NF-κB, which is considered the ‘master’ transcription factor of inflammation. Indeed, the transcription factor NF-κB is known for its central role in inflammatory diseases and aberrant regulation of NF-κB has also been observed in autoimmune disorders and various types of cancer [1-4]. In fact, transcriptions of several proteins, which play important roles in the chronic inflammatory process, are mediated by NF-κB [5,6]. These proteins include cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-8; adhesion molecules such as E-select in, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), the enzymes nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) [7]. Therefore, targeting the activation of NF-κB-dependent transcription by pharmacologic agents may prove to be quite useful in the treatment of inflammatory disorders. NF-kB frequently exists as a p65-p50 hetero dimer in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complex with inhibitor of kappa B protein (IkB). Binding of IkB protein to the NF-kB prevents its translocation to the nucleus and modulates its transcriptional function. All IkB proteins contains six ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) that is responsible for interaction surface around the NF-kB dimer and a signal responsive domain (SRD) that contains phosphorylation and ubiquitination sites for signal responsive degradation. Degradation of IkB regulates specific phosphorylation by activating IkB kinase (IIK) proteins results in activation or translocation of NF-kB to nucleus. The mammalian transcriptional factor (NF-kB) family consist of five major members such as RelA (p65), RelB, c-Rel, p50 (NF-kB1) and p52 (NF-kB2). All five members have a distinctive feature: the conserved Rel Homology Domain (RHD). The dimer binds to the kB sites in DNA of their target genes and forms homo or hetero dimeric DNA-binding complexes. The Rel Homology Domain is a distinctive feature of eukaryotic transcription factors, such as, NFkB, Dorsal, and Relish. RHD can be subdivided into two domains: N-terminal DNA binding motif that functions as a dimerization domain; the C-terminal dimerization domain, contains the site for interaction with NIK or NF-kappa-B-inducing kinase. There are two pathways of interest related to NF-kB activation: canonical and alternate, both involve ubiquitination of repressors; phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitory IkB proteins (IkBα) by NEMO/IKK-α/IKK-β complex or with semi proteolysis of p100 (for non canonical pathway). NIK phosphorylates IKK-α which phosphorylates and attaches ubiquitin marker on the C-terminal end of p-100.The partial proteolysis of p100 frees p52/ RelB to be transported to nucleous [8]. In 1996, the biochemical identification and purification of the serine/threonine kinase IkB kinase, i.e. IKK complex [9,10], IKK was defined through its ability to catalyze the phosphorylation of the serines in the N-terminal regulatory region on IkBα and IkBβ, as well as its rapid activation in response to cell stimulated by TNF-α, IL-1 or LPS. These studies resulted in the identification of three IKK subunits, two catalytic subunits such as IKKα (or IKK-1) and IKKβ (or IKK2) and a regulatory subunit IKKγ, also called NEMO or IKKAP1 [11]. IKKα is an 85-kD protein, which was initially identified as a serine threonine kinase of unknown function, named CHUK, conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase, in a search for cDNAs related to cMyc. The second catalytic subunit, IKKβ is an 87-kD protein related to IKKα [12,13]. Both subunits, which are 52% identical, contain an N-terminal kinase domain, a leucine zipper (LZ) and a helix-loop-helix (HLH). IKKγ is present as a 50-52-kD doublet, containing several N-terminal helical regions coiled-coil repeat motifs, a LZ and a Zn-finger at its C-terminus. The IKK complex is both a signaling hub for NF-kB activation and an interface for crosstalk between NF-kB activating pathways and other physiological processes. The IKKs generally serve to transduce pro-inflammatory- and growth-stimulating signals that contribute to major cellular processes, but also play a key role in the pathogenesis of a number of human diseases. There is ample evidence that IKK activity is not restricted to NF-kBdependent pathways but can also mediate cross talk with other signaling cascades, such as mTOR and MAPK pathways [14]. The importance of protein kinase inhibitors as potential drug targets is become most important over the past two decades. Therefore, the catalytic IKKs represent attractive targets for intervention with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Many studies are looking to synthesize a new series of IKK-1 and IKK2 inhibitors. The 4(2-aminoethyl) amino-1, 8-dimethylimidazo (1,2-a) quinoxaline (BMS-345541) is a standard of comparison between IKK inhibitors and showed highly selective IKK-2 inhibition (Figure 1).
Figure 1: BMS-345541 is a potent, selective, and allosteric site-binding inhibitor of IKK ß (IKK-2) and shows 10 times greater selectivity over IKK a (IKK-1).
In fact, it was identified as a selective inhibitor of the catalytic subunits of IKK with different affinity (IKK-2 IC50 = 0.3 μM, IKK-1 IC50 = 4 μM). However, the compound has a remarkable specificity since it failed to inhibit a panel of 15 other kinases. Indeed, it selectively inhibited the induction of IkBα phosphorylation in cells (IC50 = 4μM), while failing to affect c-Jun and STAT3 phosphorylation, as well as mitogenactivated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 activation in cells [15]. It has been proposed a binding model in which BMS-345541 binds to similar allosteric sites on IKK-1and IKK2, which then affects the active sites of the subunits differently. Docking studies in the IKK-2 binding site was performed in order to determine the residues implicated in the binding for a better IKK-2 inhibition activity [15]. Most of the FDA-approved protein kinase inhibitors are competitive with respect to the ATP. Many protein kinase inhibitors bind to their target enzyme by forming 1-3 hydrogen bonds with the hinge residues, while interacting with the residues that make up the adenine bindingsite and hydrophobic pockets I or II. This review focuses on the therapeutic potential of natural molecules as protein kinase inhibitors and highlights the mechanisms of these compounds against inflammation because natural product extracts such as plants, have low toxicity, minor side-effects, and they are more cost-effective than chemical drugs. It is of paramount importance identify new natural, effective, and affordable anti-IKK agents suitable for beneficial in human health.
Mechanisms of IKK activation
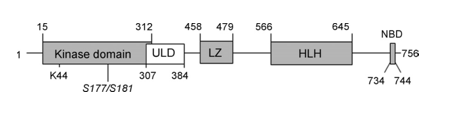
IkB kinases are activated by a plethora of agents and conditions, including extracellular ligand that bind membrane receptors, such as TNFR, TLR, or IL-1R, intracellular stress, such as DNA damage and reactive oxygen species, as well as the recognition of intracellular pathogens mediated by the NOD. Protein phosphorylation, non degradative ubiquitination, adapter protein interactions and most likely higher order oligomerization events all contribute to IKK activation .IKK activation in mammalian cells requires the presence of the IKK, NEMO, IKK AP1 regulatory subunits. Mouse cells deficient in this protein fail to phosphorylates and degrade IKΒs and consequently to activate NF-κB in response to diverse stimuli including TNFα, IL-1 and LPS. In mammalian cells, as well as insect cells, activation of IKK depends on the phosphorylation of its catalytic subunits. Treatment of IKK complexes, purified from TNF-stimulated cells with protein phosphates 2A (PP2A), abolishes their catalytic activity [16]. In addition, treatment of cells with okadaic acid, a specific PP2A inhibitor, results in the accumulation of active IKK and in turn in activation of NF-κB. These results were the first to indicate that IKKβ, but not IKKα, is the target for pro-inflammatory signals. However, since the activation loops of IKKα and IKKβ are identical (Figure 2) and their kinase domains are highly similar, it is plausible that IKKα could serve as a target for a different class of signals.
Figure 2: Scheme of the IKKb domain structure.
ULD: Ubiquitin-Like Domain; LZ: Leucine Zipper; HLH: Helix–Loop–Helix domain; NBD, NEMO-Binding Domain. Numbering of domain borders differ slightly between different references. The catalytic active site lysine residue (K44) is indicated and the two serine-residues (S177/S181) of the activation loop, which are phosphorylated upon activation, are shown in italics.
The activities of IKKα and IKKβ are also modulated by their C-terminal HLH motifs. Mutations disrupting the α-helical structures within these motifs in either sub units dramatically decrease kinase activity, without interfering with dimerization or complex assembly [17,18]. Initially, it was proposed that the HLH motif was a binding site for regulatory subunits such as IKKγ, but it soon became clear that this is not the way it functions. Most importantly, the HLH mutations were found to have devastating effects on activities of recombinant IKKα or IKKβ not associated with any other subunit [18]. Recently, the HLH motif of IKKβ was found to directly interact with the kinase domain and stimulate its activity involved in the control of epidermal differentiation. Deletion mutant containing amino acids 559, but lacking the C-terminal region, is completely inactive when expressed in either mammalian or insect cells. The HLH motif is an intrinsic activator of the IKKβ when extensively phosphorylates at its C-terminal region. The C-terminal phospho-acceptor sites are located between amino acids 670 and 705 and their phosphorylation down regulates kinase activity. The accumulation of negative charges in the C-terminal region of IKKβ are weak the interaction between the HLH motif and the kinase domain.
The development of small natural molecule inhibitors of the IKKs
For centuries, the only effective way to relieve pain and cure diseases has been the use (either by oral or topical administrations) of natural products, mainly of vegetal origin. The first record of using plants is to treat illnesses come from Mesopotamia and date from about 2600 BC. Later, older western civilizations such as the Egyptians with the Ebers Papyrus dating from 1500 BC, the Greeks with the History of Plants from Theophrastus dating from 300 BC and also the Romans with the De materia medica from Pedanius Dioscorides written between 65 and 75 AD, documented naturally drugs. Oriental civilizations such as those in China and in India have also extensively documented the medicinal use of endemic plants since ancient times. For example, Wu Shi Er Bing Fang reported 52 prescriptions around 1100 BC, and the Indian Ayurvedic system dates from about 1000 BC. These reports are the basis of traditional medicines that are extensively used today. One of the most notable effects of certain medicinal plants is their anti-inflammatory activity. In recent years the use of specific database allowed the search for IKK-2 inhibitors of natural origin that compete with ATP [19]. Analysis of these natural products revealed that some of them are polyphenols, which are secondary metabolic products in plants, whose roles as antioxidants and in the prevention of degenerative diseases such as the biflavonoid ayanin, which is found in seven extracts and has been claimed to be of use in treating allergic asthma [20].
Based on early studies that identified IKKβ as the key driver of classical NF-κB signalling, large pharmaceutical companies have developed diverse, large-scale, high-throughput screening (HTS) programmes encompassing hit-to-lead development and characterization of structure–activity relationships (SAR), all in the absence of resolved crystal structures for IKKα and IKKβ. This has led to a number of chemical entities of relatively low molecular weight with drug-like features that commonly function as IKKβ selective inhibitors. Majority of these compounds perform as adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-competitive molecules or alternatively possess allosteric action to limit IKK activities.
Furthermore, a number of these molecules have been pursued in vivo in animal models of disease (Table 1).
|
Table 1: List of The most significant phenolic compounds found in anti-inflammatory extracts. |
|
|
Malvidin
|
|
|
Iristectorigenina
|
|
|
Baicalein
|
|
|
Epicatechin
|
|
|
Aristolactam
|
|
|
Harmol
|
|
|
Ferulic acid
|
|
The most significant phenolic compounds found in these 36 anti-inflammatory extracts are as follows:
The isoflavone iristectorigenin A and the anthocyanin malvidin, which show strong inhibitory activity against NO production [21,22] are found in Iris germanica extracts and in Lavandula angustifolia and in Vaccinium myrtillus extracts, respectively. The flavone baicalein [21], which is found in Oroxylum indicum, Scutellaria baicalensis and Terminalia arjuna extracts. The epicatechin derivate 4b-(2-aminoethylthiol) epicatechin [23], which is found in Vitis vinifera extracts. In addition to polyphenols, other molecules were found to be present in known anti-inflammatory extracts, such as the Aristolactam FI (CAS: 112501-42-5), which is found in Piper longum extracts and has been shown to inhibit NO generation in RAW 264.7 macrophages LPS-stimulated [20]. The Harmol (CAS: 487-03-6), which is found in Passiflora edulis [24] extracts and belongs to the b-carbolines (a group of methylated natural product derivatives identified as hIKK-2 inhibitors several times) [25]. The 2-tertbutyl-hydroquinone (CAS: 1948-33-0), which is found in Paeonia suffruticosa extracts and is a component of experimental diets which, in synergy with other compounds, reduces atherosclerotic plaque in the aortic [26,27]. The Ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3- methoxy cinnamic acid CAS: 1135-24-6) which is an abundant phenolic phytochemical it is found in plant cell wall components such as arabinoxylans covalent side chains. Ferulic acid (FA) is a major phenolic acid extracted from Ligusticum chuanxiong, which is a traditional Chinese herb medicine [28]. It has been recently reported that FA exerts its anti-inflammatory role via the suppression of IKK-mediated NF-κB activation [29]. Indeed, FA may interfere with IKK/IκB/NF-κB signalling, both reducing NF-κB nuclear translocation and the phosphorylation of IKKα/β and IkB/α in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The attenuation of IKK phosphorylation may be an effect that is mediated by FA, which could regulate the NF-κB activity and consequently inhibit cytokines production. It is known that the molecular mechanism underlying the inhibition of kinase proteins consists of the formation of a ligand-receptor complex. Pharmacophore models have suggested that a common feature shared by all classes of kinase inhibitors is the presence of a central aromatic ring and a lateral side chain that is able to achieve binding by hydrophobic forces and hydrogen bonding [30]. It is also known that FA acts by its phenolic nucleus and an extended side chain conjugation: it forms a resonance stabilized phenoxy radical. These data showed that FA works not only chemically, thanks to its structure, but may also influence NF-κB pathway. The first crystal structures of an IKKβ, reported for the phospho-mimetic mutant of Xenopus laevis IKKβ, (S177E/S181E), have greatly advanced our understanding of IKK [31]. Nevertheless, despite the vast number of publications that have focused on this protein kinase, its mechanism of activation is still controversial. Understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the specific interactions in IKK-ligand recognition is of fundamental importance for the biological implication and for the rational design of new selective IKK inhibitors. It is well-known that kinase inhibitors tend to form hydrogen-bonds to the hinge region, which is a highly conserved segment among protein kinases [32,33]. Therefore, the IKK-β inhibitors are also supposed to interact with the hinge motif, which in case of IKK-β is composed of Glu97 and Cys99, to stabilize inhibitor binding and contribute to the reduction of catalytic enzyme activity. Furthermore, the molecules contain an aromatic ring and hydrophobic moiety in most cases has the topological features that contribute to disrupt the catalytic activity of the enzyme [21].
DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION
Conclusions
IKK-β plays a crucial role in the control of NF-κB activity. The efforts to investigate naturals compounds involved in the IKK-β inhibitions is allowed by the crystallographic structure and by using a computational approach involving Homology Modelling, Molecular Docking and Pharmacophore/3D-QSAR analysis. Data suggest that molecular mechanism involved in the IKK-β inhibition is similar to that observed in the case of other kinase proteins, the formation of a ligand-receptor complex able to mimic ATP or the natural substrate kinase proteins. Computational approaches have revealed the presence of three broad hydrophobic pockets able to accept a steric hindrance and a loop constituted by residues Glu97, Tyr98, Cys99, Glu100, Gly101, and Gly102 that is involved in the formation of several hydrogen bonds with each ligand. The Molecular Docking approach share that the presence of a central aromatic ring and a side chain group are commons features of all classes of inhibitors.