The Electron Leak Pathways of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain and its Potential Application in Medical Research
- 1. Institute of Biophysics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Citation
Jian-Xing X (2015) The Electron Leak Pathways of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain and its Potential Application in Medical Research. JSM Cell Dev Biol 3(1): 1014.
Perspective
This is a review on our 10 selected publications listed in the reference. The purpose of the review is further understanding the biomedical meanings of the electron leakage of mitochondrial respiratory chain and call for attention to “Chi” (see Douglas C. Wallace: Mitochondria as “chi”. http://www.genetics.org/ content/179/2/727.short). “Chi” is a Chinese character used by Chinese doctor to describe the healthy state of patients. The first part of the review summarized the experiments shown the pathological significance of the electron leakage. The second part analyzed the physiological meanings theoretically. The third part presented an idea on health and longevity in thermodynamic principle. Thinking of health and longevity thermodynamically is helpful for scientists to understand the scientific connotation of Chinese medicine.
The four electron leak pathways of mitochondrial respiratory chain and their potential application in medicine
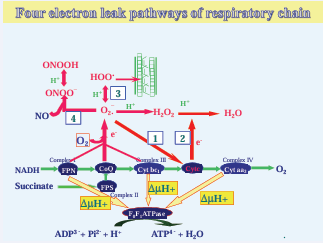
Studies in our lab have shown that the production of ATP in mitochondria by the way of electron transfer of the respiratory chain is always combined with the generation of O2 -. and H2 O2 through the electron leak pathways. There are four electron leak pathways in the respiratory chain, as shown in the red part of the Figure (1) [1-4].
Figure 1: The dark cycles are the enzymes involved in ATP synthesis of mitochondria. Green color arrows show the way of electron transfer in the respiratory chain. Yellow color shows the theory of Mitchell on the coupling mechanism of respiratory chain and ATPase. The red colored part shows the four electron leak pathways established in our lab. They are 4 metabolic routs of O2-.. A reactive path of O2 →O2-. →H2 O2 →H2 O is involved in the 4 electron leak pathways. Oxygen consumed in the electron leakage is not used in ATP production but spent in the generation of toxic oxygen species O2- and H2 O2 .
Two of the cytochrome c mediated pathways play a role in down regulating the level of O2 -. and H2 O2 in mitochondria. The third pathway of O2 -. + H+ →HOO? is related to the process of maintaining body temperature because the reaction of HOO?with the double allyl hydrogen atom of the unsaturated fatty acid is heat releasing. Whether or not this pathway is related to obesity is not known. The fourth pathway is O2 -. + NO→ONOO?. The ONOO? is able to pass through the cellular membrane when it combines with H+ , but we do not know if the long distance penetrates membrane transfer occurs in human body. Animal models show that the level of electron leakage in the mitochondrial respiratory chain is always higher in pathological conditions. The H2 O2 , as the product of electron leakage, has higher pathological significance as it has longer life-span and can be spread across membranes.
The finding of electron leak pathways of the respiratory chain reveals that the mitochondrial oxygen consumption is divided into two parts: the oxygen consumed in ATP production is KCNinhibitory and obey the Mitchell’s theory; while the oxygen consumed in ROS generation is KCN-insensible and linked in electron leakage.
The pathological significance of electron leakage of mitochondrial respiratory chain
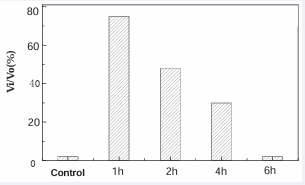
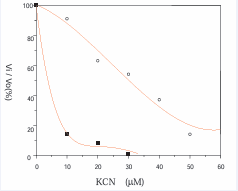
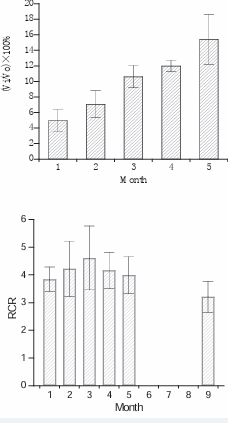
It is obvious that the ATP production in mitochondria by the way of electron transfer of respiratory chain is KCN inhibitory, whereas the generation of O2 -. and H2 O2 through the electron leak pathways is KCN insensible. Then the KCN sensitivity can be a signature to report the level of electron leakage of respiratory chain. With this in mind some animal models were examined and found that the level of electron leakage of mitochondrial respiratory chain is always higher when animal in pathological conditions as shown in the Figure (2-5).
Figure 2: A group of female mouse injected with oxytocin. The cyanide resistant respiration of liver mitochondria was measured at 1, 2, 4 and 6 hours after the injection (each measurement take 5 mouse liver). Result shows that the KCN-insensitive respiration is remarkable higher than control at 1hour after injection, and it is decreased hour by hour, after 6 hours it turn back to normal.
Figure 3: The KCN sensitivity is lower in the tumor growing mouse. 5 mouses intraperitoneal injected with H2 O2 and mouse liver mitochondria prepared after 8 days growing of ascites tumor. ?–?: injected group; ?–? control group.
Figure 4: The cyanide insensitive respiration of mouse liver mitochondria is increasing monthly from 1-5 months growing. Older than 5 months mouse the cyanide insensitive respiration keep in high level and the RCR ratio decrease can be observed after 9 months growing. (P<0.05).
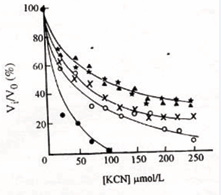
Figure 5: Injection T3 with 0.5mg/g per day to five groups of mouse, each group have 5 mouses and killed after injection. Mix 5 livers and prepare mitochondria to test the state 4 respiration in different concentration of KCN. Result shows that the KCN sensitivity is decreased with increasing T3 injected. ?–?: one day injection; x–x: two days injection ?–? three days injection?????five days injection ?–? control (no injection).
The damaging effect of ROS on human body is well established in publications. If think of the ROS generation refer to the electron leak of respiratory chain, the methods controlling ROS generation by means of effecting on the respiratory chain would give some biomedical understanding as shown in the following examples. A synthesized weak inhibitor (3-nitro-Nmethyl amine has less than 50% inhibition) of complex I and II shows protective effect in ischemia reperfusion [5]. This result indicates that the explosive generation of ROS by the fast electron leak of the respiratory chain plays a key role in reperfusion damage. A strong ROS scavenger (Salvianic acid A extracted from Chinese herb) shows the protective effect on the MPTP-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells [6-8]. This further indicates that the ROS generated in the electron leak of the respiratory chain play a key role in the neurodegenerative diseases [9,10].
The mitochondrial ROS play an important role in health and longevity
The ROS generated in the electron leak pathways of the respiratory chain can be a dangerous factor causing oxidative damage and aging. However, more importantly, the function of ROS as the signals to stimulate anti-oxidative function and strengthen the ability of damage repair has the theoretical means in health and longevity. The physiological role of the four electron leak pathways of mitochondrial respiratory chain is a new investigative field.
It is well known that NO can be bound to the oxygen reactive center of complex IV to reduce ATP production in mitochondria, whereas the binding of O2 -. With NO (the pathway 4) can release the restricted ATP production. Therefore, the ratio of O2 -. and NO could be a factor in controlling the rate of ATP production in mitochondria. The physiological role of this effect is worth for searching.
Cytochrome c exhibits different roles in different locations of the mitochondria. It is involved in ATP production when it functions as an electron carrier in the respiratory chain. It is a scavenger to dispose of O2 -. and H2 O2 in the inner membrane space of mitochondria. It also functions to stimulate cell apoptosis in the cytosol outside of the mitochondria. A functional migration of cytochrome c in the life span of cell is performed during aging. The O2 -. and H2 O2 generated in the electron leakage of the respiratory chain plays a role in driving the cytochrome c functional migrating.
Coenzyme Q has been used clinical to improve energy metabolism in heart diseases and also used as a health care product in the public market. A side effect of oral coenzyme Q is causing stomach discomfort. According to the ROS generation in the electron leakage of mitochondrial respiratory chain, the side effect can be avoided by combined eating of coenzyme Q, vitamin E, and selenium.
The respiratory chain functions as molecular lifeengine
The finding of electron leak pathways of respiratory chain inspires us to investigate human health with a new insight of bioenergetics. In view of biophysics, the function of the respiratory chain is similar as engine. The negative effect of ROS generated in the electron leakage of respiratory chain can be considered as the “idol work” which causing aging of the engine. A significant difference between the life-engine and the non-life-engine is that the O2 -. and H2 O2 generated in life-engine also play roles as signals to stimulate the power of antioxidative function and strengthen the ability of damage repair. This is the theoretical base of health and longevity.
The human body can be considered as an aggregate of a huge amount of life-engines. The normal operation of life-engines makes the human body healthy. The damage on life-engines causes the human body aging or diseases. The thermodynamic theory can be used to study the health and longevity if treating the human body as a thermodynamic dissipative structure. Dissipative structure is highly ordered and maintained in a way of continued exchange of energy and material with the environment. The life-engine plays a key role in maintaining the orderliness of human body as a dissipative structure. Once the life-engines are damaged or aged, the highly ordered human body would be disordered, which causes diseases or aging. Then we can define health and longevity in terms of thermodynamics.
Health is the maintenance of the inherent orderliness of infant and the longevity is the duration of the inherent orderliness that can be maintained
Thinking of health and longevity thermodynamically is helpful for understanding the scientific connotation of Chinese medicine.
The Chinese medicine stresses the integrity of human body and emphasizes its unity with the environment. This is in agreement with the property of the thermodynamic dissipative structure continued exchange energy and material with the environment. JING_LUO (??) is a concept to describe the integrity of human body. It is the embodiment of the dissipative structure of the human body, reflecting a family tree of different cell line of the body. It is an interconnection network making all cells of the body in functional unity. Chi_XUE (??) is the concept to describe the unity of human body with environment. It is a web of the metabolisms of human body continuously exchange energy and material with the environment. The Chinese medicine describes the functions of the human body with the term of ZHEN_ Chi (??) and believes that ZHEN_ Chi (??) is consisted of YU_ Chi (??) GU_ Chi (??) and QING_ Chi (??) . The meaning of YU_ Chi (??) is the inherent orderliness of the infant as the dissipative structure. GU_ Chi (??) means nutritious substances from digested food. QING_ Chi (??) is the oxygen obtained from lung respiration. Both GU_ Chi (??) and QING_ Chi (? ?) are the substrates of respiratory chain. The ATP produced in mitochondria is the force that keeps the inherent orderliness of the human body in good condition. The basic principles of Chinese medicine are YANG_YUAN_Chi (???),FU_ZHENG_QU_ XIE (????) ZHI_WEI_BING” (???) . The meaning of YANG_ YUAN_Chi (???) is take care of the inherent orderliness. FU_ZHENG_QU_XIE (????) means strengthening the power of bodily immune ability against harmful invader. ZHI_WEI_BING (???) means maintaining human body in good condition so as to avoid illness. YIN_YANG (??) is the concept to describe the deviation of human body from the normal physiological functions. WU_XING_XIANG_SHENG_XIANG_KE (????? ?) is the theory of Chinese medicine to describe the functional unity of all the internal organs. Chinese medicine believes that the harmonious adaptation of all the internal organs is the base of health. The art of Chinese medicine is to regulate the functions of different organs by means of prescription or acupuncture.
CONCLUSION
The development of Western medicine is keeping in step of the experimental life science. In the face of the complexity of the human body the experimental research method always has limitations. Chinese medicine jump over the complexity, treating the human body as a dark box and investigating diseases in a way of direct observation on the curative effect of herbs prescription. During 5 thousands year accumulation of the cure efficiency on huge patients, Chinese medicine developed a systematic theory and therapeutic method. The thermodynamic principle of health and longevity could help scientists understand the scientific connotation of the Chinese medicine and develop a new medicine by combining the advantages of the western medicine and the Chinese medicine.