PDA Closure in the Presence of a Dilated Main Pulmonary Artery and Ductal Spasm: Importance of Proper Technique and Hardware Selection
- 1. Head of Department, Department of cardiology, GGMC and Sir JJ Hospital, India
- 2. Senior resident, Department of cardiology, GGMC and Sir JJ Hospital, India
- 3. Assistant Professor, Department of cardiology, GGMC and Sir JJ Hospital, India
- 4. Associate Professor, Department of cardiology, GGMC and Sir JJ Hospital, India
- 5. Post DM SR, Department of cardiology, GGMC and Sir JJ Hospital, India
Abstract
Transcatheter patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) closure is a device-based technique for correcting PDA. In general, an isolated PDA is easier to close, but conditions such as a smaller PDA, PDA spasm, or a dilated main pulmonary trunk make device closure a significant challenge. More over re-crossing the PDA becomes difficult in situations if there is device size mismatch. This article highlights the management of PDA device closure in a patient with a smaller PDA and a dilated main pulmonary artery due to severe pulmonary stenosis, complicated by ductal spasm. It also emphasizes the importance of selecting the proper hardware to address this situation effectively.
KEYWORDS
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Device closure of PDA
- Dilated MPA
- Severe PS
- Ductal Spasm
CITATION
Munde K, Jain P, Kantak D, Kothari G, Munde A, et al. (2025) PDA Closure in the Presence of a Dilated Main Pulmonary Artery and Ductal Spasm: Importance of Proper Technique and Hardware Selection. J Cardiol Clin Res. 13(2): 1212.
INTRODUCTION
The ductus arteriosus is a central vascular shunt connecting the proximal descending aorta to the pulmonary artery near the origin of the left branch of the pulmonary artery [1]. It allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the uninflated fetal lungs and enter the systemic circulation. Rapid closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth is essential for the vascular transition to a mature, divided pattern of arteriovenous circulation [1,2]. As the clinical signs and symptoms of PDA can vary, all patients at risk of developing or having PDA should undergo echocardiography [3]. Closure is recommended for patients regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms. Transcatheter device closure is the treatment of choice for all patients whenever it is technically feasible [1-5]. Ductal spasm is common in smaller PDAs, and utmost care should be taken to avoid undersizing the device. Ductal spasm during the procedure can lead to procedural failure [6,7].
CASE REPORT
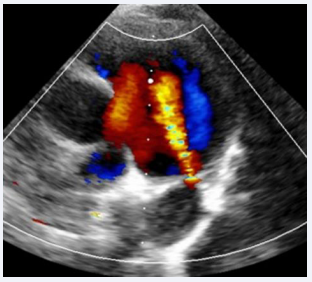
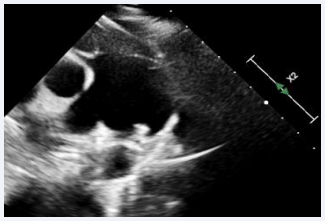
A 7-year-old male child, born to a diabetic mother from a non-consanguineous marriage, presented with a history of respiratory distress immediately after birth, for which he received NICU care during the neonatal period. The patient never underwent a screening echocardiogram during infancy. During a consultation for exertional breathlessness while playing, he was evaluated and underwent screening echocardiography. The echocardiogram (Figure 1),
Figure 1: Transthoracic echocardiogram showing PDA with left-to- right shunt.
suggested a small 2 mm PDA with a left-to-right shunt, moderate pulmonary valve stenosis with a peak gradient of 48 mmHg, and a dilated main pulmonary artery measuring 34 mm.
PROCEDURE
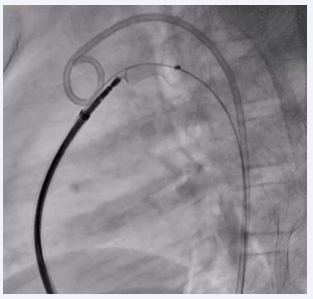
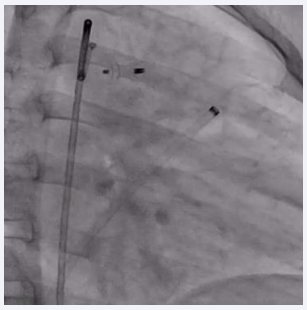
Procedure was done under general anesthesia. Right femoral artery and vein, along with left femoral venous access, were established and 6F sheaths were inserted. A 6F pigtail catheter was advanced through the right femoral artery along the descending aorta up to the PDA defect. An aortic shoot was performed via the pigtail catheter to visualize and confirm the size of the defect. Pressures across the main pulmonary artery (MPA), were recorded using a 6F MPA catheter. A 0.025 mm J-tip Terumo wire was passed through the right femoral vein into the right atrium, followed by the right ventricle, and then into the main pulmonary artery. The MPA catheter was replaced with a 6F Judkins right catheter. Due to the dilated MPA and PDA spasm from repeated attempts to cross the defect, there was difficulty in advancing the terumo wire through the defect. After multiple attempts, the 0.025 mm Terumo wire was successfully passed through the defect and subsequently exchanged for an Amplatzer Super Stiff wire. The ductal spasm led to a possible underestimation of the required device size. A Lifetech CERA 8/6 mm device was loaded onto the device delivery sheath. To facilitate the challenging recrossing, a Mullins long sheath, one size larger than recommended for the Lifetech CERA device, was inserted and advanced up to the defect over the Amplatzer Super Stiff wire. The Super Stiff wire was then exchanged for the Terumo wire, which was snared through the left femoral artery to secure access during the trial of device placement (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Fluoroscopic image showing PDA device inflated across the PDA with the Terumo wire maintained across the defect.
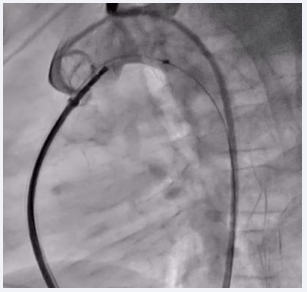
The device was then passed through the defect, and both the aortic and MPA ends of the device were sequentially inflated. A check aortic angiogram showed no residual shunt across the device (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Fluoroscopic image showing the inflated PDA device in situ with no residual shunt across the defect.
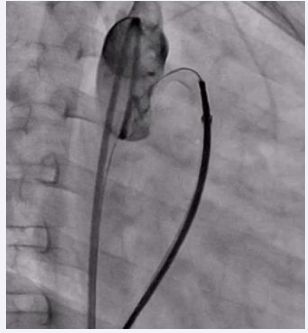
The Terumo wire was then gently removed, and the device was released in place (Figure 4,5).
Figure 4: Fluoroscopic image showing the inflated PDA device in situ with no residual shunt across the defect.
Figure 5: Final fluoroscopic image showing PDA device in place after release.
Post Procedure
Postoperative transthoracic echocardiography confirmed the correct device position with no residual shunt across the device (Figure 6).
Figure 6: Post-procedure 2D echocardiography showing the PDA device in place.
Patient recovery after procedure was uneventful. Patient was planned for BPV after one year of follow up and was discharged thereafter.
DISCUSSION
PDA is a common congenital heart disease (CHD) having a broad spectrum of clinical manifestation, varying from asymptomatic cardiac murmur to heart failure. PDA comprises 5 – 10 % of all CHDs. PDA is most commonly seen in females than males [1,2]. In advance cases PDA if not treated can cause heart failure and Eisenmenger syndrome [1]. Many studies have shown transcatheter device closure of PDA is superior to surgical closure as it is safe with high success rate and little morbidity when compared with surgical closure [1-4,7]. More over surgical closure of PDA is associated with complications like pneumothorax, bleeding and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury [4]. Surgical closure in adult can be challenging secondary to calcified ductus, left ventricular dysfunction, pulmonary artery hypertension [4]. Now a day’s surgical closure of PDA is restricted to cases with larger PDA, unsuitable anatomy like aneurysmal PDA [4]. Ductal Spasm occurs during repeated manipulation of wire is a well-known complication and can sometimes lead to procedural failure. Absence of murmur can confirm the diagnosis of ductal spasm [2]. PDA is considered to be small when it is < 1.5 mm, moderate when it ranges from 1.5 and 3 mm and large if its dimension is more than 3 mm [6]. If pulmonary vascular resistance is elevated, a large PDA may not exhibit significant left-to-right shunting. Instead, the presence of a right-to-left shunt suggests considerable pulmonary hypertension. In such cases, closing the ductus abruptly is not recommended, as it may lead to worsening right heart failure [3]. For larger defects ADO I device is preferred over ADO II which is preferred for small to medium sized defects. Transcatheter device closure is considered superior to coils [4,5]. When closing a PDA via catheter-based intervention, two primary approaches are used: antegrade and retrograde. Antegrade approach is through venous route and catheter is advanced from right atrium to right ventricle to pulmonary artery and crossing PDA and getting into descending aorta. In this approach device is delivered from pulmonary side. Retrograde approach is where catheter is advanced from arterial system inside descending aorta followed by crossing PDA and getting to pulmonary side. In this approach device is delivered from aortic side [4,7]. Snaring of guidewire is typically done in antegrade approach as the sheath is inserted through pulmonary side and it may be difficult to position delivery sheath correctly. Snaring can also help to facilitate smooth device, better stability, and better control during crossing of device through PDA [4,7]. Snaring of guidewire is useful in cases with smaller PDA, dilated MPA and in cases requiring more controlled and stable delivery system manipulation [2,4].
Challenges faced during closure of PDA in our case were:
- Dilated MPA: The dilated MPA did not provide sufficient support to our catheter for advancing the Terumo wire through the lesion, leading to repeated attempts to cross the defect.
- Ductal Spasm: The need of repeated manipulation to cross PDA resulted in ductal spasm.
- Underestimation of Device Size: The ductal spasm presented a risk of underestimating the device size required for closure.
- Larger Mullins Long Sheath: A larger-sized Mullins long sheath was selected to ensure incorporation of both device and double length terumo wire simultaneously.
- Wire and Device Positioning: The Terumo wire was reinstated prior to device positioning and snared across the defect to ensure access, even in the event of device size mismatch or failure to plug the device.
Hence, in this case we preferred antegrade approach to deal with situation, a larger size delivery system was used to incorporate both terumo wire and device into it, snaring of guidewire before positioning device over the defect to prevent recrossing of wire in this challenging condition and removing guidewire before final placement of device across PDA.
CONCLUSION
Closing a PDA through catheter-based methods can be more challenging when dealing with a small PDA, a dilated main pulmonary artery and complications like ductal spasm. In such complex cases, careful planning is essential. This includes a detailed assessment of the PDA size and shape, as well as choosing the right devices and techniques tailored to the patient’s specific anatomy. Being aware of potential issues, such as ductal spasm, and being prepared to adjust strategies as needed are crucial for a safe and effective PDA closure.
REFERENCES
- Khan A, Ullah Z, Ilyas S, Wazir HD, Reman Y, Hussain I, et al. The Outcome of Trans-catheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Single-Center Experience. Cureus. 2022; 14: e21577.
- Batlivala SP, Glatz AC, Gillespie MJ, Dori Y, Rome JJ. Ductal spasm during performance of transcatheter ductal occlusion. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014; 83: 762-767.
- Arlettaz R. Echocardiographic Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants. Front Pediatr. 2017; 5: 147.
- Gillam-Krakauer M, Reese J. Diagnosis and Management of Patent Ductus Arteriosus. Neoreviews. 2018; 19: e394-e402.
- Alkashkari W, Albugami S, Alrahimi J, Althobaiti M, Kinsara A, Abousa A, et al. Percutaneous Device Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Adult Patients with 10-Year Follow-up. Heart Views. 2019; 20: 139- 145.
- Y?ld?z K Sr, Kir M, Prencuva P, Genc HZ, Celiktepe V, Bozyer HE, et al. Transcatheter Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Children With Different Devices and Long-Term Results. Cureus. 2023; 15: e46504.
- Garg N, Raja DC, Khanna R, Kumar S. A Challenging Case of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Device Closure in an Adult with Unconventional Views and Catheters. Heart Views. 2018; 19: 20-22.