Using Digital Media to Decrease Peritoneal Dialysis Related Infections
- 1. Department of Medicine, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, U.S.A
Abstract
Background: Peritonitis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality for peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients. One of the most important ways to decrease the risk of peritonitis and exit site infections (ESI) is with proper hand washing technique. We propose the use of a video to teach patients appropriate hand washing techniques to decrease the risk for peritonitis and ESI.
Methods: Nine patients were randomized into two groups. Group A watched the hand washing video monthly and group B was the control. All patients were tested on technique at the start of the study, and at month 3.
Results: At baseline, Group A had an average score of 83.25 and Group B had an average score of 82.20. After 3 months, Group A score was 90.25 and Group B score was 94.80. There were no cases of peritonitis in Group A and one ESI in Group A. There was one case of peritonitis in Group B and no cases of ESI in Group B.
Conclusions: Digital media can be used to reinforce hand washing technique. This can allow patients to review the technique remotely and on their own time. It is as effective as the standard of care.
Keywords
• Video • Hand washing • Exit site infections • Peritonitis
CITATION
Fertel S, Naljayan MV (2017) Using Digital Media to Decrease Peritoneal Dialysis Related Infections. J Clin Nephrol Res 4(5): 1076.
ABBREVIATIONS
PD: Peritoneal Dialysis; ESI: Exit Site Infections
INTRODUCTION
Peritonitis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality for peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients. Various studies have shown that peritonitis leads to increase in mortality as well as increase in ultra filtration failure, which eventually leads to PD failure [1]. One of the most important ways to prevent peritonitis and exit site infections is with excellent hand washing technique. The World Health Organization has guidelines for appropriate hand washing technique [2]. Staphylococcus species remains a major organism for peritonitis, and these organisms are typically found on surfaces of the hands [3].
At this time, there is no formal and standardized education in hand washing in PD units nationwide [4]. Most units, like our own, teach patient hand washing technique during the 2 week training period at the initiation of PD and then annually review technique with the patients. In one study of PD patients, there was a 51% decline in correct hand washing technique 6 months after initial training [5].
We have developed a 14 step hand washing sheet (Figure 1)
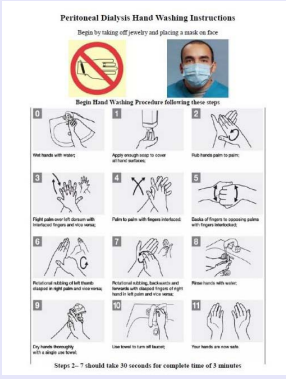
Figure 1 Hand washing Teaching sheet using WHO guidelines.
which includes written and picture based cues to describe each step. This sheet is based on the World Health Organization hand washing guidelines. We have also developed a checklist (Figure 2)
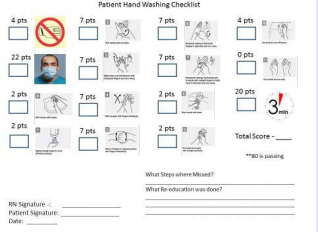
Figure 2 Hand washing checklist using WHO guidelines.
using this same sheet to be used by a reviewer to observe and score each patient performing a hand washing routine. These checklists are scored, and the score is stored for data collection purposes. Lastly, we have developed a 4 minute hand washing video (Figure 3)

Figure 3 Hand washing video posted to YouTube (https://youtu.be/ CzJKfbE9Dko).
that outlines each step with audio prompts that the patients watch in the PD unit.
We hypothesized that with repeated education and watching of the training video, we will improve hand washing technique and decrease rates of exit site infections and peritonitis compared to a control group. The use of digital media to decrease peritonitis and exit site infections in PD patients is a novel approach in teaching proper hand hygiene.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was conducted on patients from June 2015 to August 2015. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center-New Orleans. All patients were recruited from the Louisiana State University (LSU) Peritoneal Dialysis practice at Davita Crescent City Dialysis Center, 3909 Bienville St. New Orleans, Louisiana. All patients were on peritoneal dialysis before the study was conducted. Patients with active peritonitis or exit site infection at the time of consent were excluded from the study. Informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients. After informed consent was obtained, the physician and a PD nurse reviewed the hand washing sheet (Figure 1) with all patients in our PD practice to ensure that every patient received the appropriate initial review of appropriate hand washing technique. Two weeks later, all patients were observed and scored on their hand washing routine using a checklist (Figure 2). The same nurse scored all patients to account for any subjective discrepancies in amount of points given. Patients were randomized into two groups: Group A was the intervention group, and Group B was the control group. Group A watched the video (Figure 3) after they performed the test and were given feedback on any steps they performed incorrectly. Group B only received feedback on any steps they performed incorrectly. During their monthly lab visits with the PD nurse, Group A watched the video again. Group B had no further education.
After three months, all patients were observed performing a hand washing routine again and scored using the checklist (Figure 2). The scores were recorded again and stored. The hand washing technique taught was within the standard of care, as it was developed using the World Health Organization guidelines on hand washing. There were no risks associated with this study.
The primary endpoint of the study was change in total score on the hand washing checklist. Secondary endpoints included episodes of peritonitis and episodes of exit site infections. All scores in each group were averaged, and those averages were compared between the start of the study and the 3-month test.
The video was a 4 minute presentation of step-by step hand washing technique, which featured a nurse performing the steps in the order of proper technique (Figure 3). It was uploaded to YouTube (https://youtu.be/CzJKfbE9Dko) and shown to patients in Group A during monthly lab appointments.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
At baseline, Group A had an average score of 83.25 and Group B had an average score of 82.20. After 3 months, Group A had an average score of 90.25 and Group B had an average score of 94.80. There were no cases of peritonitis in Group A and one exit site infection in Group A. There was one case of peritonitis in Group B and no cases of exit site infections in Group B. The grades of each patient for the initial and third months can be seen in the tables attached see Table 1.
Table 1: Initial and 3 month scores for Group A (video) and Group B (control).
| Group A | Initial Score | 3 Month Score |
| Patient 1 | 73 | 94 |
| Patient 2 | 86 | 67 |
| Patient 3 | 74 | 100 |
| Patient 4 | 100 | 100 |
| Group B | Initial Score | 3 Month Score |
| Patient 5 | 59 | 88 |
| Patient 6 | 93 | 100 |
| Patient 7 | 59 | 86 |
| Patient 8 | 100 | 100 |
| Patient 9 | 100 | 100 |
At this time, ongoing clinic education is not performed and digital media is not routinely used as an educational tool for hand washing technique in dialysis patients even though there is a 14 step technique outlined by the World Health Organization. Hand washing technique is especially important for peritoneal dialysis patients who dialyze from home because they are essentially their own caregivers. It is imperative that these patients practice proper hand hygiene in order to avoid exit site infection and peritonitis. Most patients have never received direction in proper hand washing technique, which could seriously mitigate these dreaded infections.
This study aimed to teach patients currently using peritoneal dialysis proper hand washing technique per World Health Organization’s 14-step guide. In this day and age, media has become the means of communication and learning. Therefore, this study not only incorporated a visual checklist to guide the patients while performing the steps, it also gave patients a chance to watch a video created by the clinic’s physician and nurse.
Although the results did not show a marked difference between those who watched the video and received verbal directive in hand washing technique compared to the control group who only received verbal directive in hand washing technique, it was still just as effective. Peritoneal dialysis patients come to clinic once a month to discuss dialysis management and get their monthly blood work and urinalysis. All of their dialysis is done at home. Therefore, the ability to watch a video remotely from home is a great tool to allow patients to continue practicing proper hand washing hygiene and review their skills. Clinic teaching is a great way to ensure patients are informed, but with a video, patients are also able to view the video as needed and in the comfort of their own homes.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed that using digital media to promote efficient hand washing was just as effective as the control and could be used as a tool for patients who do peritoneal dialysis at home. For the patient who does not have to come into the clinic daily, digital media is a novel tool that allows one to review proper hand washing remotely.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to acknowledge the NIDDK T35DK093428 for the funding support of this study.








































































































































