Intravenous Thrombolysis in Two Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated with Chronic Hemodialysis
- 1. Department of Neurology and Stroke Unit of Holy Spirit Specialist Hospital in Sandomierz, Poland
Abstract
Patients with renal failure have a higher risk for cerebrovascular events and silent brain damage and a higher cardiovascular mortality rate when compared with the general population. We present two cases where alteplase was used for hemodialysis patients (HP) with acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
A 70-year-old Caucasian female with a 2-year history of hemodialysis was admitted with right hemiparesis and aphasia (National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, NIHSS: 15 pts.), which occurred during a hemodialysis session (HS). On the third day of hospitalization, after initial neurological improvement (NIHSS after 24 hours: 9 pts.), the patient died because of massive intestinal bleeding.
A 54-year-old Caucasian female with a 4-year history of hemodialysis was admitted after two incidents of ipsilateral transient ischemic attacks (TIA), which occurred between HSs. 30 min after admission, right hemiparesis and aphasia occurred (NIHSS: 16 pts. ). 3 months after stroke onset, the patient was functionally independent (NIHSS:2).
Keywords
Ischemic stroke; Thrombolysis; Brain damage; Hemodialysis; Renal insufficiency
Citation
Sobolewski P, ?ledzi?ska-D?wiga? M, Szczuchniak W, Sobota A, Hatalska-?erebiec R (2013) Intravenous Thrombolysis in Two Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated with Chronic Hemodialysis. J Neurol Disord Stroke 1(3): 1024.
INTRODUCTION
Renal insufficiency (RI) is highly prevalent in the general population [1,2]. Patients with RI, especially patients with renal failure, show abnormalities in coagulation and platelet function that favor thrombosis, but also augment bleeding risks [3]. Patients with even mild renal impairment suffer from complex hemostatic disorders including platelet hyperactivity, reduced tissue plasminogen activator dysfunction and von Willebrand factor abnormalities [4]. Thus, those patients have a higher risk for cerebrovascular events and silent brain damage and a higher cardiovascular mortality rate when compared with the general population [5,6].
Intravenous thrombolysis (IV-thrombolysis) with rt-PA is an effective therapy for acute ischemic stroke (AIS), but is associated with a number of hemorrhagic complications and is contraindicated in patients with severe hemostatic disorders [7]. We present two cases in which alteplase were used for hemodialysis patients (HP) with AIS.
CASES REPORT
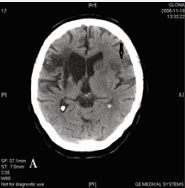
A 70-year-old Caucasian female with a history of ischemic heart disease (IHD) and hypertension was on a maintenance dose of 75mg of aspirin per day. She had a 2-year history of hemodialysis. Routine hemodialysis sessions were carried out 3 times weekly. The patient was admitted with right hemiparesis and aphasia of 195-min duration (National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, NIHSS: 15 pts. ), which occurred during a hemodialysis session (HS). During dialysis heparin was used. On admission, her blood pressure (BP) was 163/87 mmHg, and blood glucose, creatinine and hemoglobin levels were 6.49 mmol/L, 518.2 µmol/L and 13.7 g/L, respectively. The coagulation profile were as follows: International Normalized Ratio (INR) – 1.1, aPTT 30.6 sec. , Fibrinogen 3.05 g/L. In the baseline CT we found old ischemic changes (ICs). At 270 min after symptom onset, she received IV 40 mg rt-PA (weight estimated at 45 kg) without complications. After 24 hours, neurological improvement was observed (NIHSS: 9 pts. ). In the controlled CT, performed 24-h after thrombolysis, a small IC was located in the left temporal lobe (Figure 1a).
Figure 1(a): Brain CT scans of the 1st patient performed 24-h after stroke onset
During the next few days, standard dialysis was performed. On the 3rd day of hospitalization, the patient’s deterioration was noted; massive hemorrhage from the gastrointestinal tract was noted and the patient died.
A 54-year-old Caucasian female with a history of IHD, two incidences of myocardial infarction, hypertension, permanent atrial fibrillation and a prior ischemic stroke was on a maintenance dose of 150 mg of aspirin per day. She had a 4-year history of hemodialysis. Routine hemodialysis sessions were carried out 3 times weekly. The last dialysis took place 1 day before hospitalization. During dialysis heparin was used. The patient was admitted after two incidents of ipsilateral transient ischemic attacks (TIA), which occurred between HSs. 30 min after admission, right hemiparesis and aphasia occurred (NIHSS: 16 pts.). On admission, her BP was 170/90 mmHg, and blood glucose, creatinine and hemoglobin levels were 6.43 mmol/L, 553.8 µmol/L and 12.9 g/L, respectively. The coagulation profile was as follows: INR – 1.08, aPTT 26.4 sec., Fibrinogen 2.92 g/L. In the baseline CT we found an old IC, which was inconsistent with the current symptoms.
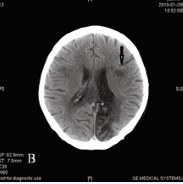
At 125 min after symptom onset, she received IV 40 mg rt-PA (weight estimated at 47 kg) without any complications. After 24 hours, neurological improvement was observed (NIHSS: 10 pts. ). A controlled CT, performed 24-h after thrombolysis, did not show any new IC or HT. Upon CT on the 7th day, a small IC was located in the left temporal lobe (Figure 1b).
Figure 1(b): Brain CT scans of the 2nd patient performed at 7th day
During next days, standard dialysis was performed. 3 months after stroke onset, the patient was functionally independent (NIHSS: 2).
DISCUSSION
It is believed that iv-thrombolysis is not a safe method of treatment of AIS in patients undergoing hemodialysis. The management of chronic HP, in whom AIS has occurred, is a great challenge. The previous clinical trials testing intravenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) for acute ischemic stroke did not specifically exclude hemodialysis patients, and major guidelines are silent on this issue [8-11]. There is no consensus regarding the impact of RI and especially renal failure on the effectiveness and safety of cerebral thrombolysis [12 14]. Patients with renal failure suffer from complex hemostatic disorders that are mainly due to abnormalities of primary hemostasis; in particular, platelet dysfunction and impaired platelet-vessel wall interaction [15]. HP has multiple risk factors and therefore they require many drugs. Additionally heparin is routinely used for dialysis circuit anticoagulation. However, the effect of unfractionated heparin can be monitored using the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Elevated aPTT after dialysis may lead to an increase in intra-cerebral hemorrhage (ICH) rate after IV rt-PA administration. It is recommended that the aPTT must be in the normal range if heparin has been given in the previous 48 hours [16-17]. Up to 34% of the ischemic stroke in patients on maintenance dialysis occur during or less than 30 minutes after the dialysis procedure [18]. Alignment of aPTT within a time window to 4.5 hours opens the way for use of alteplase in HP. Even between dialysis treatments, patients are predisposed to bleeding, suspected to be due to uremic platelet dysfunction [19].
Beyond the conventional stroke risk factors in HP, other non conventional factors are mentioned, such as: volume overload, anemia, oxidative stress, sympathetic over-drive, malnutrition, chronic inflammation (high c-reactive protein, low serum albumin), calcium, phosphate, parathyroid hormone levels disturbance and sleep disorders. Dialysis related factors are also specified, such as: hemodynamic, vascular access, dialysis amyloidosis, vascular calcification, dialysate (acetate) and dialysis vintage [20].
Only three case reports have mentioned the successful use of IV-thrombolysis in HP with AIS [21-23]. A recently published paper, by Tariq et al. showed no difference in the incidence of intra-cerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and the 2-fold higher odds of in-hospital mortality associated with administration of IV thrombolytics in dialysis-dependent patients who present with AIS. In this study, patients undergoing hemodialysis population numbered more than 1.000. The authors observed also that the percentage of patients with moderate-to-severe disability at the time of discharge was lower in the dialysis-dependent group, but this phenomenon was because of the increased inpatient mortality. The authors warranted a careful assessment of risk benefit ratio in this population [24].
Despite the concerns about bleeding risk and the absence of prospective controlled study, most surveyed stroke experts in thrombolytic therapy of acute ischemic stroke, favored using rt-PA in these patients. However, seventy-eight percent of the experts indicated the possibility of treating hemodialysis patients with intra-arterial approach and would have preferred mechanical clot retrieval to thrombolysis [25].
In our study, two female patients were treated with hemodialysis; one patient died on the third day of hospitalization because of massive intestinal bleeding, while the second had a good outcome. However, the adverse event occurred in the first patient during the subsequent hemodialysis session, in which heparin was used routinely. In addition, the patient continued to receive an aspirin. Older age and longer onset to treatment time were also important predictors of poor outcome in this case [26 28]. We believe that presented cases can bring certain values as assessment of safety of iv-thrombolysis in HP.
REFERENCES
- Nissenson AR, Pereira BJ, Collins AJ, Steinberg EP. Prevalence and characteristics of individuals with chronic kidney disease in a large health maintenance organization. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 37: 1177-1183.
- Garg AX, Kiberd BA, Clark WF, Haynes RB, Clase CM. Albuminuria and renal insufficiency prevalence guides population screening: results from the NHANES III. Kidney Int. 2002; 61: 2165-2175.
- Fox KA, Antman EM, Montalescot G, Agewall S, SomaRaju B, Verheugt FW, et al. The impact of renal dysfunction on outcomes in the ExTRACT-TIMI 25 trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49: 2249-2255.
- Jalal DI, Chonchol M, Targher G. Disorders of hemostasis associated with chronic kidney disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2010; 36: 34-40.
- Kuo CC, Lee CT, Ho SC, Kuo HW, Wu TN, Yang CY. Haemodialysis and the risk of stroke: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan, a country of high incidence of end-stage renal disease. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012; 17: 243-248.
- Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, et al. Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: a pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15: 1307-1315.
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359: 1317-1329.
- [No authors listed]. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333: 1581-1587.
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Ledaffre E, von Kummer R, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The ECASS Study Group. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA. 1995; 274: 1017-1025.
- Bluhmki E, Chamorro A, Davalos A, Machnig T, Sauce C, Wahlgren N, et al. Stroke treatment with alteplase given 3.0-4.5 h after onset of acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS III): additional outcomes and subgroup analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8: 1095-1102.
- IST-3 collaborative group Sandercock P, Wardlaw JM, Lindley RI, Dennis M, Cohen G, et al. The benefits and harms of intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 6 h of acute ischaemic stroke (the third international stroke trial [IST-3]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012; 379:2352-63.
- Naganuma M, Koga M, Shiokawa Y, Nakagawara J, Furui E, Kimura K, et al. Reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate is associated with stroke outcome after intravenous rt-PA: the Stroke Acute Management with Urgent Risk-Factor Assessment and Improvement (SAMURAI) rt-PA registry. Cerebrovasc Dis 2011; 31: 123-129.
- Agrawal V, Rai B, Fellows J, McCullough PA. In-hospital outcomes with thrombolytic therapy in patients with renal dysfunction presenting with acute ischaemic stroke. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25: 1150-1157.
- Sobolewski P, Kozera G, Kaźmierski R, Michalak S, Szczuchniak W, Sledzińska-Dźwigał M, et al. Intravenous rt-PA in patients with ischaemic stroke and renal dysfunction. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115: 1770-1774.
- Boccardo P, Remuzzi G, Galbusera M. Platelet dysfunction in renal failure. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2004; 30: 579-589.
- Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, Grubb RL: Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke. A guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups. Stroke. 2007; 38: 1655-1711.
- European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: Actilyse.
- Toyoda K, Fujii K, Fujimi S, Kumai Y, Tsuchimochi H, Ibayashi S, et al. Stroke in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a 22-year single-center study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45: 1058-1066.
- Sohal AS, Gangji AS, Crowther MA, Treleaven D. Uremic bleeding: pathophysiology and clinical risk factors. Thromb Res. 2006; 118: 417-422.
- seki K. Stroke feature and management in dialysis patients. Contrib Nephrol. 2013; 179: 100-109.
- Power A, Moser S, Duncan N. Successful thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke on haemodialysis. NDT Plus. 2010; 3: 576-578.
- McCloskey M, Masengu A, Shields J, Wiggam MI. Acute stroke in a patient with advanced uraemia: should thrombolysis be given? BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013.
- Naganuma M, Mori M, Nezu T, Makihara N, Koga M, Okada Y, et al.; on behalf of the Stroke Acute Management with Urgent Risk-Factor Assessment and Improvement (SAMURAI) Study Investigators. Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator therapy for stroke patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: the Stroke Acute Management with Urgent Risk-Factor Assessment and Improvement (SAMURAI) rt-PA registry. Eur Neurol. 2011; 66: 37-41.
- Tariq N, Adil MM, Saeed F, Chaudhry SA, Qureshi AI. Outcomes of Thrombolytic Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Dialysis-Dependent Patients in the United States. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; .
- Palacio S, Gonzales NR, Sangha NS, Birnbaum LA, Hart RG. Thrombolysis for acute stroke in hemodialysis: international survey of expert opinion. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 6: 1089-1093.
- Engelter ST, Reichhart M, Sekoranja L, Georgiadis D, Baumann A, Weder B, et al. Thrombolysis in stroke patients aged 80 years and older: Swiss survey of IV thrombolysis. Neurology. 2005; 65: 1795-1798.
- Mouradian MS, Senthilselvan A, Jickling G, McCombe JA, Emery DJ, Dean N, et al. Intravenous rt-PA for acute stroke: comparing its effectiveness in younger and older patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005; 76: 1234-1237.
- Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, del Zoppo G, Sandercock P, Lindley RL, et al. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischaemic stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012; 379: 2364-2372.