A Structured Multidisciplinary Protocol for Swallow Assessment: Integrating a Comprehensive FEES Checklist
- 1. Lebanese American University Gilbert and Rose-Marie Chagoury School of Medicine, Lebanon
- 2. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Lebanese American University Medical Center, Lebanon
- 3. Speech Language Pathology, Lebanese American University Medical Center, Lebanon
Abstract
Background: Dysphagia is a prevalent and high-risk condition in hospitalized patients, with inconsistent assessment practices contributing to adverse outcomes like aspiration pneumonia. While Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) is a gold-standard diagnostic tool, its effectiveness relies on systematic execution and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Objective: To develop and implement a standardized, three-phase protocol for dysphagia assessment, centered around a comprehensive FEES checklist, to improve diagnostic consistency and patient management.
Methods: We hereby present the structured protocol and Swallow assessment pathway we have constructed and have been following for the past 2 years at the Lebanese American University Medical Center consisting of: 1) an initial bedside screening and ENT triage phase, and 2) a collaborative multidisciplinary FEES examination performed jointly by an ENT physician and a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP), guided by a detailed checklist. This tool, adapted and further elaborated from the Langmore swallow procedure, standardizes the entire process from patient history and pre-swallow baseline assessment to systematic feeding trials and final recommendations. 3) A collaborative management plan between the SLP, ENT physician, Nutritionist, Radiologist and Intensive Care Unit (ICU) / Ward Physicians and Nursing teams.
Results: The Dysphagia Management Protocol checklist ensures a comprehensive evaluation by structuring the documentation of key physiological events, stratifying severity via a 7-point Swallowing Performance Scale, and generating evidence-based recommendations for diet and therapy. The protocol emphasizes the critical need for multidisciplinary collaboration, closing the communication loop with intensivists, neurologists, nutritionists, and radiologists to contextualize findings and guide management.
Conclusion: This protocol provides a practical, scalable framework that minimizes clinical variability and enhances patient safety. It serves as an effective foundation for quality improvement initiatives, ensuring a consistent, high-standard approach to dysphagia care through structured collaboration and systematic assessment.
Keywords
• Dysphagia
• Swallow Assessment
• Aspiration
• Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES)
• Speech Swallow Therapy
• Safety Checklist
• Multidisciplinary Care
• Risk Stratification
• Quality Improvement
Citation
Saade R, Atwi G, Swaidan D, Keyrouz E, Harb M, et al. (2025) A Structured Multidisciplinary Protocol for Swallow Assessment: Integrating a Comprehensive FEES Checklist. Ann Otolaryngol Rhinol 12(3): 1362.
INTRODUCTION
Dysphagia in hospitalized patients presents a significant challenge, with its mismanagement leading to severe complications like aspiration pneumonia. While instrumental evaluations such as Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) are the gold standard, their efficacy hinges on systematic execution. To address the variability in practice, we developed a structured, three-phase protocol centered around a detailed, standardized checklist-the Dysphagia Management Protocol. This tool ensures a consistent, reproducible, and comprehensive approach from initial patient intake to final therapeutic recommendations. Our protocol is built upon the robust foundation of the Langmore FEES examination protocol, a well-established standard in the field [1,2]. We have adapted and expanded this framework to create a more granular, checklist-driven tool tailored to the needs of a high-volume, academic hospital setting, with a focus on standardizing training and interdisciplinary collaboration between ENT and SLP services.
The Protocol Workflow: From Screening to Specialized Assessment
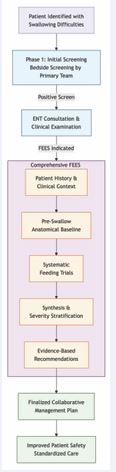
The protocol is built on a sequential, three-phase model that streamlines the patient journey from initial identification to a definitive, instrumental assessment (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Protocol Workflow.
Phase 1: Initial Screening and ENT Triage
The process begins at the bedside, where the primary clinical team identifies at-risk patients based on their medical history (e.g., stroke, head and neck surgery) and current symptoms (e.g., coughing with meals, wet voice). A positive screen triggers an Otolaryngology consultation. The ENT physician then performs a focused clinical examination to confirm the need for an instrumental evaluation, based on predefined criteria such as persistent dysphagia or a history of aspiration.
Phase 2: The Comprehensive FEES Checklist
The core of the protocol is the collaborative FEES, performed by an ENT physician and a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) using the structured Dysphagia Management Protocol form. This checklist is not merely a documentation tool but a procedural guide that structures the entire examination into logical, sequential sections.
Deconstructing the Comprehensive FEES Checklist
The checklist’s design ensures no critical element of the assessment is overlooked. Its sections guide the clinician through a thorough evaluation.
Patient Identification and Clinical Context: This section captures essential data, including patient demographics, medical history, and the specific reason for the test. It systematically inventories the patient’s swallowing symptoms—such as nasal regurgitation, painful swallowing, and weight loss—establishing a clinical baseline.
Pre-Swallow Anatomical and Functional Baseline: Before introducing any food or liquid, the clinician performs a critical baseline assessment. This includes evaluating the patient’s:
- Global Readiness: Level of alertness, cooperation, and posture.
- Secretions Management: The presence and management of pharyngeal secretions, a key indicator of aspiration risk.
- Sensorimotor Integrity: A structured examination of oral-motor and laryngeal function, including facial symmetry, velopharyngeal closure, base of tongue retraction, vocal fold mobility, and laryngeal elevation.
Systematic Feeding Trials and Impairment Inventory
This is the dynamic core of the FEES. The checklist provides a matrix for administering boluses of various consistencies, aligned with the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) framework (e.g., Thin Liquid, Nectar-thick, Pureed, Minced & Moist) [3].
For each consistency, the clinician records: ·
- Trial Parameters: Number of trials, quantity given, and utensils used.
- Key Physiological Events: The presence or absence of penetration, aspiration, residue (vallecular/ pyriform pooling), and the adequacy of laryngeal closure and elevation.
- Patient Response: The patient’s reaction to residue or aspiration, such as coughing, throat clearing, or, worryingly, no response. A parallel Swallowing Impairment Checklist prompts the clinician to grade qualitative aspects of the swallow, such as bolus transit time and epiglottic movement.
Synthesis and Severity Stratification
Following the feeding trials, the collected data is synthesized. The clinician documents the patient’s current feeding method and diet. Crucially, findings are consolidated into a Swallowing Performance Scale—a 7-point ordinal scale ranging from “Normal” to “Severe Impairment.” This scale provides a standardized, overarching severity score that directly informs the acuity of the intervention required.
Phase 3: Collaborative Management Plan The Comprehensive FEES Checklist Evidence Based Recommendations and Disposition:
The final section translates the assessment into a clear, actionable care plan. It includes:
- Recommendations: Specific actions such as diet modification (using NDD/IDDSI levels)3, declaring the patient NPO (nil by mouth), initiating swallowing therapy, initiating enteral feeding support (e.g., PEG tube), or ordering further tests (e.g., MBS, CT scan).
- Swallowing Precautions: A list of compensatory strategies (e.g., chin tuck, supraglottic swallow, alternating consistencies) to be employed during oral intake.
- Accountability: Signature lines for both the ENT and SLP clinicians, formalizing the collaborative interpretation and plan.
Linking Physiology and Common Pathologic findings: A deep understanding of normal swallow physiology is paramount to interpreting FEES findings. Swallowing is a complex sensorimotor act classically divided into three phases [4,5], and our protocol is designed to assess impairments at each level.
A. Oral Preparatory & Oral Phase: This voluntary phase involves mastication, bolus formation, and posterior propulsion by the tongue. Our checklist assesses for Oral Preparation Impairment, such as Drooling, Poor bolus control, and Oral stasis, commonly seen in stroke, neurodegenerative diseases, and cranial nerve injuries [4]. This directly informs the need for specific oral-motor therapies.
B. Pharyngeal Phase: This reflexive phase is critical for airway protection. It involves velopharyngeal closure, laryngeal elevation and anterior tilt, base of tongue retraction, and sequential pharyngeal contraction [5]. Our checklist’s “Swallowing Impairment Checklist” is vital here, identifying pathologies such as:
- Reduced Velar Elevation: Leading to nasal regurgitation.
- Impaired Base of Tongue Retraction & Reduced Pharyngeal Squeeze: Causing Vallecular pooling.
- Delayed/Absent Laryngeal Elevation & Closure: Resulting in Penetration and Aspiration, often observed in brainstem strokes or after head and neck radiotherapy.
- Reduced Epiglottic Retroflexion: Compromising the deflection of the bolus away from the larynx.
C. Esophageal Phase: While FEES does not visualize the esophagus, it can infer esophageal pathology. Significant Pyriform sinus pooling that is not cleared by multiple swallows may suggest a downstream obstruction or motility disorder (e.g., cricopharyngeal bar, stricture, or achalasia), guiding referrals for further workup.
Closing the Loop: The Multidisciplinary Imperative: The value of this protocol is fully realized only through active multidisciplinary collaboration. Closing the communication loop with all stakeholders is essential:
- Intensivists/Internists/Neurologists: Provide the clinical history (e.g., recent stroke, state of consciousness, neurodegenerative disease) that frames the FEES findings. They must be informed of the results to integrate swallowing status into the overall medical management.
- Nutritionists/Dietitians: Are crucial for translating the IDDSI/NDD diet recommendations into practical, nutritionally adequate tray preparations, ensuring patient safety and preventing malnutrition.
- Radiologists: A FEES exam often works in conjunction with a Modified Barium Swallow (MBS) study. While FEES excels at visualizing anatomy, secretions, and subtle pharyngeal motility, MBS provides a dynamic view of the entire swallow from the oral cavity to the stomach. The two are complementary, and findings from one often guide the need for the other.
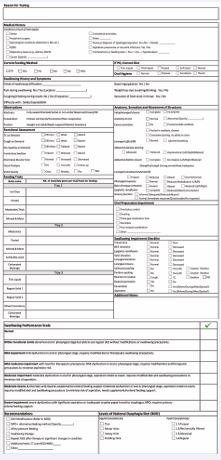
Special Considerations in Head and Neck Cancer: Patients with head and neck malignancies represent a unique subgroup where dysphagia significantly impacts quality of life. Both the disease process and its treatments including surgery, radiation, and chemoradiation—can profoundly alter swallowing physiology and airway protection. Establishing a detailed functional baseline before any intervention provides a critical snapshot of the patient’s physiological reserve. This baseline is profoundly prognostic, as pretreatment swallowing function remains the strongest independent predictor of long-term functional outcomes in Head and Neck cancer patients undergoing conservative chemoradiotherapy [6], beyond tumor stage or treatment modality. Swallowing function at baseline hence can be an independent factor impacting choice of best treatment modality. This protocol enables structured longitudinal follow up. Using the same standardized checklist during treatment and post-treatment allows for objective comparison against the baseline, facilitating early detection of complications like aspiration or radiation induced dysphagia. This ensures timely interventions such as swallow therapy intensification [7], dietary modifications or PEG consideration Ultimately, integrating this dysphagia protocol into the multidisciplinary tumor board workflow safeguards that functional outcomes remain central to the comprehensive cancer patient care from diagnosis through survivorship (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Dysphagia Management Protocol Checklist.
Practical Pointers for Implementation:
A Primer for a Quality Improvement Initiative: For centers and hospitals aiming to improve dysphagia management, this protocol serves as an ideal starting point for a Quality Improvement (QI) initiative. The goal is to systematically capture high-risk patients and stratify their risk through a standardized, multidisciplinary approach. Successful implementation begins by starting small with a pilot unit such as the Neurology ward or ICU, and forming a dedicated core team comprising a motivated ENT physician, a speech language pathologist, a nurse champion, and a dietitian. The process involves adopting and adapting the provided checklist into the local electronic health record and workflow, while establishing clear clinical pathways for screening, referral, and the collaborative FEES procedure. To ensure efficacy and demonstrate impact, it is critical to track key performance indicators like time from referral to FEES, rates of aspiration pneumonia, and diet upgrade success. Finally, the initiative must be supported by comprehensive education through in-service trainings and a steadfast commitment to “closed-loop” communication, guaranteeing that findings and recommendations are seamlessly relayed back to the referring physician and the entire care team.
CONCLUSION
The Dysphagia Management Protocol checklist is more than a form; it is the backbone of a standardized, collaborative approach to swallow assessment. By providing a structured framework for the FEES examination, it minimizes inter-clinician variability, ensures comprehensive data collection, and directly links diagnostic findings to a stratified management plan. This protocol, when embedded within a multidisciplinary QI culture, guarantees that every patient receives a consistent, high-quality evaluation, ultimately enhancing patient safety and improving clinical outcomes in dysphagia management.
REFERENCES
- Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examinationof swallowing safety: A new procedure. Dysphagia. 1988; 2: 216-219.
- Langmore S. Endoscopic evaluation and treatment of swallowingdisorders. Thieme. 2011.
- Cichero JA, Lam P, Steele CM, Hanson B, Chen J, Dantas RO, et al Development of international terminology and definitions for texture-modified foods and thickened fluids used in dysphagia management: The IDDSI framework. Dysphagia. 2017; 32: 293-314.
- Logemann JA. Dysphagia: Evaluation and treatment. Folia PhoniatrLogop. 1995; 47: 140-64.
- Lang IM. Coordination of pharyngeal and esophageal phases ofswallowing. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024; 30: 397-406.
- Rosenthal DI, Lewin JS, Eisbruch A. Prevention and treatment of dysphagia and aspiration after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24: 2636-2643.
- Hutcheson KA, Bhayani MK, Beadle BM, Gold KA, Shinn EH, Lai SY, et al. Eat and exercise during radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for pharyngeal cancers: Use it or lose it. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 139: 1127-1134.